Habitability of the Goldilocks planet Gliese 581g: results from
... span strongly depends on the relative continental area r and increases with decreasing r. Therefore, “water worlds” are favored in the facilitation of habitability as previously obtained in models of fictitious Earth-mass planets for 47 UMa and 55 Cnc (Cuntz et al. 2003; Franck et al. 2003; von Bloh ...
... span strongly depends on the relative continental area r and increases with decreasing r. Therefore, “water worlds” are favored in the facilitation of habitability as previously obtained in models of fictitious Earth-mass planets for 47 UMa and 55 Cnc (Cuntz et al. 2003; Franck et al. 2003; von Bloh ...
Exploring the Solar System - Rourke Publishing eBook Delivery
... discoveries. Many spacecraft have been launched into the solar system to photograph and gather information. People have even walked on the Moon. ...
... discoveries. Many spacecraft have been launched into the solar system to photograph and gather information. People have even walked on the Moon. ...
Chapter 1: Introduction to Earth Science Indiana State Standards 1
... planets have been identified orbiting stars other than the sun. SCI.ES.2.3 2010 Recognize that the sun is the main source of external energy for the Earth. Describe the cycles of solar energy and some of their impacts on the Earth. SCI.ES.2.4 2010 Describe the motions of the various kinds of objects ...
... planets have been identified orbiting stars other than the sun. SCI.ES.2.3 2010 Recognize that the sun is the main source of external energy for the Earth. Describe the cycles of solar energy and some of their impacts on the Earth. SCI.ES.2.4 2010 Describe the motions of the various kinds of objects ...
The universe and our planet
... galaxy clusters. A galaxy is a large group of stars: between 100 000 and 500 million. Towards the centre of the galaxy, the stars are close together, but in the outer areas of the galaxy they are farther apart. Stars are made up mainly of hydrogen and helium, the two most abundant gases in the unive ...
... galaxy clusters. A galaxy is a large group of stars: between 100 000 and 500 million. Towards the centre of the galaxy, the stars are close together, but in the outer areas of the galaxy they are farther apart. Stars are made up mainly of hydrogen and helium, the two most abundant gases in the unive ...
Introduction to Astronomy (high school)
... daily or diurnal motion of the celestial sphere, and is in reality a consequence of the daily rotation of the earth on its axis. The diurnal motion affects all objects in the sky and does not change their relative positions: the diurnal motion causes the sky to rotate as a whole once every 24 hours. ...
... daily or diurnal motion of the celestial sphere, and is in reality a consequence of the daily rotation of the earth on its axis. The diurnal motion affects all objects in the sky and does not change their relative positions: the diurnal motion causes the sky to rotate as a whole once every 24 hours. ...
RP 4E1 Earth in the Universe - NC Science Wiki
... with the tilt of the planet’s spin axis (or axis of rotation), have altered the intensity and distribution of sunlight falling on Earth. These phenomena cause cycles of climate change, including the relatively recent cycles of ice ages. Gravity holds Earth in orbit around the sun, and it holds the m ...
... with the tilt of the planet’s spin axis (or axis of rotation), have altered the intensity and distribution of sunlight falling on Earth. These phenomena cause cycles of climate change, including the relatively recent cycles of ice ages. Gravity holds Earth in orbit around the sun, and it holds the m ...
Document
... 1. Why is Astronomy different that any other science in the way in which the scientific method is applied (especially when dealing with stars and galaxies)? ...
... 1. Why is Astronomy different that any other science in the way in which the scientific method is applied (especially when dealing with stars and galaxies)? ...
VENUS A VEILED PLANET Transit of Venus 6
... Its backward (retrograde) and forward (prograde) motion is most noticeable and… ...
... Its backward (retrograde) and forward (prograde) motion is most noticeable and… ...
kepler`s laws and newton`s discovery of universal
... appeared in the sky, one so bright that it was visible even in daytime. The Danish astronomer Tycho Brahe found (using parallax measurements) that the light (now called Tycho’s Supernova) originated from far beyond the planets. Contrary to Aristotelian doctrine, which held that the stellar sphere wa ...
... appeared in the sky, one so bright that it was visible even in daytime. The Danish astronomer Tycho Brahe found (using parallax measurements) that the light (now called Tycho’s Supernova) originated from far beyond the planets. Contrary to Aristotelian doctrine, which held that the stellar sphere wa ...
History of Astronomy
... Kepler's three laws. (A) A planet moves in an elliptical orbit with the Sun at one focus. (B) A planet moves so that a line from it to the Sun sweeps out equal areas in equal times. Thus the planet moves fastest when nearest the Sun. (C) The square of a planet's orbital period (in years) equals the ...
... Kepler's three laws. (A) A planet moves in an elliptical orbit with the Sun at one focus. (B) A planet moves so that a line from it to the Sun sweeps out equal areas in equal times. Thus the planet moves fastest when nearest the Sun. (C) The square of a planet's orbital period (in years) equals the ...
October - Sonoma County Astronomical Society
... with one possible exception, astronomers still are not able to “see” planets orbiting around other stars. So how then have astronomer been able to identify more than 200 Extra-Solar Planets? The most successful technique has not been to attempt to detect the planet itself, but rather to detect the p ...
... with one possible exception, astronomers still are not able to “see” planets orbiting around other stars. So how then have astronomer been able to identify more than 200 Extra-Solar Planets? The most successful technique has not been to attempt to detect the planet itself, but rather to detect the p ...
The Naked Eye Stars as Data Supporting Galileo`s
... Galileo's ideas -- to say that the stars are not suns scattered through space -- requires explaining why it happens to be that N* increases with magnitude in a way so consistent with Galileo's ideas. ...
... Galileo's ideas -- to say that the stars are not suns scattered through space -- requires explaining why it happens to be that N* increases with magnitude in a way so consistent with Galileo's ideas. ...
Answer to question 1 - Northwestern University
... to the sun and astrometry to give us accurate positions to the (2) A satellite dedicated to the [boring, tedious] task of accurately measuring star positions to yield accurate (to the few percent level) the distances to “Cepheid Variables.” And Cepheid Variables are our closest standard candles and ...
... to the sun and astrometry to give us accurate positions to the (2) A satellite dedicated to the [boring, tedious] task of accurately measuring star positions to yield accurate (to the few percent level) the distances to “Cepheid Variables.” And Cepheid Variables are our closest standard candles and ...
A Brief History of the Solar System
... These two sources were the brightest among all the other light sources in the sky. But they also noticed that five other bright lights, although did not have any impact on life, behaved similar to the Sun and to the Moon in their motion and in their appearance. It is the famous Greek scholar and phi ...
... These two sources were the brightest among all the other light sources in the sky. But they also noticed that five other bright lights, although did not have any impact on life, behaved similar to the Sun and to the Moon in their motion and in their appearance. It is the famous Greek scholar and phi ...
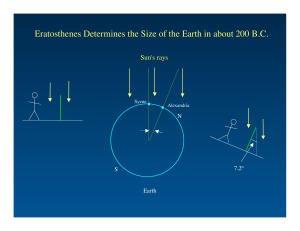
Eratosthenes Determines the Size of the Earth in about 200 B.C.
... To locate an object, two numbers (in degrees), like longitude and latitude are sufficient. Question: why is this “view” totally imaginary? ...
... To locate an object, two numbers (in degrees), like longitude and latitude are sufficient. Question: why is this “view” totally imaginary? ...
early greek astrophysics: the foundations of modern science and
... international literature. The Orphic Hymns prove that the roots of Science goe back in time for millennia, as first discovered and proved by the late Chasapis and his student Papathanasiou (1978), which continued his work and whose studies are used in this chapter. In the Orphic hymns we can read th ...
... international literature. The Orphic Hymns prove that the roots of Science goe back in time for millennia, as first discovered and proved by the late Chasapis and his student Papathanasiou (1978), which continued his work and whose studies are used in this chapter. In the Orphic hymns we can read th ...
6th Grade Winter - Partnership for Effective Science Teaching and
... 3. Why does Jupiter have so many moons? 4. Why don’t things fly off in space? 5. What would the solar system look like if it didn’t have gravity? Constructed Response 1. Describe which has more gravity Jupiter or the Earth. Why? 2. Twirl a ball on a string, if my hand is the sun and the ball is the ...
... 3. Why does Jupiter have so many moons? 4. Why don’t things fly off in space? 5. What would the solar system look like if it didn’t have gravity? Constructed Response 1. Describe which has more gravity Jupiter or the Earth. Why? 2. Twirl a ball on a string, if my hand is the sun and the ball is the ...
Bringing E.T. into Your Classroom The Search for
... 4. Small diameter planets or large diameter planets. 5. Small mass planets or large mass planets. 6. Planets close to star or planets far from star. ...
... 4. Small diameter planets or large diameter planets. 5. Small mass planets or large mass planets. 6. Planets close to star or planets far from star. ...
Resources - gmu ttac - George Mason University
... undertake the exercise themselves. Place a small representation of Polaris somewhere high up in the room, and point it out to the students. Tell them that the globe represents Earth, the floor represents the plane of Earth’s flat orbit around the sun, and the lamp elevated in the center of the room ...
... undertake the exercise themselves. Place a small representation of Polaris somewhere high up in the room, and point it out to the students. Tell them that the globe represents Earth, the floor represents the plane of Earth’s flat orbit around the sun, and the lamp elevated in the center of the room ...
An Introduction to Islamic Astronomy (al-Falak al-Shar`i)
... Perfect timing if the Sunnah is followed (Salat al-Maghrib should be fairly short) Look at the western horizon, near where the sun set ...
... Perfect timing if the Sunnah is followed (Salat al-Maghrib should be fairly short) Look at the western horizon, near where the sun set ...
Basic Astronomical Estimates
... 4.1 Distance from the Earth to the Sun Hipparchus (190-120 BC) estimated the distance from the Earth to the Sun to be approximately 500 Earth radii. Claudius Ptolemy (AD 90-168), a Roman mathematician living in Egypt, used the method developed by Hipparchus to deduce that the Sun is about 1200 earth ...
... 4.1 Distance from the Earth to the Sun Hipparchus (190-120 BC) estimated the distance from the Earth to the Sun to be approximately 500 Earth radii. Claudius Ptolemy (AD 90-168), a Roman mathematician living in Egypt, used the method developed by Hipparchus to deduce that the Sun is about 1200 earth ...
Night/Day and Earth Years
... Mini Lab: What does Earth’s rotation cause? • In pairs of 2, one student is the Sun and will hold a flashlight and shine it at the stomach of the other student who is Earth… • The sun (flashlight holder) stands still, while the Earth ROTATES (spins) in a circle—mimicking the motion of the Earth on ...
... Mini Lab: What does Earth’s rotation cause? • In pairs of 2, one student is the Sun and will hold a flashlight and shine it at the stomach of the other student who is Earth… • The sun (flashlight holder) stands still, while the Earth ROTATES (spins) in a circle—mimicking the motion of the Earth on ...
The Kepler spacecraft has found thousands of likely extrasolar
... “missing.” Scientists know what colors correspond to different gases from laboratory experiments on Earth. Ozone (O3), for example, absorbs light at 9.6 micrometers; carbon dioxide (CO2) absorbs radiation at 15 micrometers. To search for life, astronomers look for gases that “don’t belong” according ...
... “missing.” Scientists know what colors correspond to different gases from laboratory experiments on Earth. Ozone (O3), for example, absorbs light at 9.6 micrometers; carbon dioxide (CO2) absorbs radiation at 15 micrometers. To search for life, astronomers look for gases that “don’t belong” according ...
5th Grade “I Can Statements”
... Solar System (Motion): I can describe each planet's unique orbital period (year) and rotational period (day). I can explain that planets stay in an orbit around the sun due to the gravity between the sun and the planets. I can explain that a moon is a natural satellite that orbits a larger body (lik ...
... Solar System (Motion): I can describe each planet's unique orbital period (year) and rotational period (day). I can explain that planets stay in an orbit around the sun due to the gravity between the sun and the planets. I can explain that a moon is a natural satellite that orbits a larger body (lik ...
Copernican heliocentrism

Copernican heliocentrism is the name given to the astronomical model developed by Nicolaus Copernicus and published in 1543. It positioned the Sun near the center of the Universe, motionless, with Earth and the other planets rotating around it in circular paths modified by epicycles and at uniform speeds. The Copernican model departed from the Ptolemaic system that prevailed in Western culture for centuries, placing Earth at the center of the Universe, and is often regarded as the launching point to modern astronomy and the Scientific Revolution.Copernicus was aware that the ancient Greek Aristarchus had already proposed a heliocentric theory, and cited him as a proponent of it in a reference that was deleted before publication, but there is no evidence that Copernicus had knowledge of, or access to, the specific details of Aristarchus' theory. Although he had circulated an outline of his own heliocentric theory to colleagues sometime before 1514, he did not decide to publish it until he was urged to do so late in his life by his pupil Rheticus. Copernicus's challenge was to present a practical alternative to the Ptolemaic model by more elegantly and accurately determining the length of a solar year while preserving the metaphysical implications of a mathematically ordered cosmos. Thus his heliocentric model retained several of the Ptolemaic elements causing the inaccuracies, such as the planets' circular orbits, epicycles, and uniform speeds, while at the same time re-introducing such innovations as,Earth is one of several planets revolving around a stationary Sun in a determined orderEarth has three motions: daily rotation, annual revolution, and annual tilting of its axisRetrograde motion of the planets is explained by Earth's motionDistance from Earth to the Sun is small compared to the distance to the stars.↑ 1.0 1.1 ↑