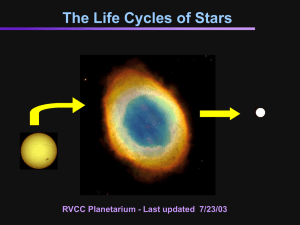
Life Cycle of a Star
... The star’s mass is lost until it collapses into a _____________ dwarf, which will lose energy and become a ______________ dwarf. ...
... The star’s mass is lost until it collapses into a _____________ dwarf, which will lose energy and become a ______________ dwarf. ...
L5 Protoplanetary disks Part I
... Note that not all high Z material condenses at temperatures in the nebula. The dust to gas ratio is a function temperature, and thus of the distance from the star. Ice line In hot regions close to the star, only refractory “rocky” elements (iron, silicates) remain solid. In colder regions further aw ...
... Note that not all high Z material condenses at temperatures in the nebula. The dust to gas ratio is a function temperature, and thus of the distance from the star. Ice line In hot regions close to the star, only refractory “rocky” elements (iron, silicates) remain solid. In colder regions further aw ...
WORD - hrsbstaff.ednet.ns.ca
... Moon, and all the other planets orbiting Earth. ____________________________ model of the solar system holds that Earth, like all the other planets, orbits the Sun and was made popular by ____________________________. This model naturally explains ____________________________ motion, which is the ba ...
... Moon, and all the other planets orbiting Earth. ____________________________ model of the solar system holds that Earth, like all the other planets, orbits the Sun and was made popular by ____________________________. This model naturally explains ____________________________ motion, which is the ba ...
A-36_SF
... – Protostars shine by gravity as they contract – Disks form through conservation of angular momentum • Their properties tell us about planet formation process • Inner holes and clumps provide evidence of young solar systems • Debris disks get their dust from grinding of planetesimals ...
... – Protostars shine by gravity as they contract – Disks form through conservation of angular momentum • Their properties tell us about planet formation process • Inner holes and clumps provide evidence of young solar systems • Debris disks get their dust from grinding of planetesimals ...
Day-6
... This is the path of the temperature and luminosity with time. Protostars get less luminous and hotter. The star first appears as a T Tauri star. The star moves on the Hayashi track and arrives on the main sequence. Since L = (area) (T4), the star contracts. ...
... This is the path of the temperature and luminosity with time. Protostars get less luminous and hotter. The star first appears as a T Tauri star. The star moves on the Hayashi track and arrives on the main sequence. Since L = (area) (T4), the star contracts. ...
Describing the Solar System File
... that of mars and Jupiter are thousands of asteroids. Asteroids could be the remains of a smashed up planet or moon. Asteroids are lumps of rock ranging from a tennis ball in size up to 700km across. It is thought that Jupiter’s gravity keeps the asteroids smeared out around this belt and stops ...
... that of mars and Jupiter are thousands of asteroids. Asteroids could be the remains of a smashed up planet or moon. Asteroids are lumps of rock ranging from a tennis ball in size up to 700km across. It is thought that Jupiter’s gravity keeps the asteroids smeared out around this belt and stops ...
report - Hungarian American Coalition
... mass, and half of them harbor a planet about the mass of Neptune, which is 17 times the mass of Earth. About one-fifth of them are home to a gas giant like Jupiter or a still more massive planet. "One can point at almost any random star and say there are planetsorbiting that star," said astronomer U ...
... mass, and half of them harbor a planet about the mass of Neptune, which is 17 times the mass of Earth. About one-fifth of them are home to a gas giant like Jupiter or a still more massive planet. "One can point at almost any random star and say there are planetsorbiting that star," said astronomer U ...
Exploration of the Universe
... Exploration of the Universe 1. What astronomical observations allow us to know the time of day, the date, direction and the timing of ocean tides? 2. What is the difference between an asterism and a constellation? 3. How would observations of stars differ from the observations of planets? 4. What is ...
... Exploration of the Universe 1. What astronomical observations allow us to know the time of day, the date, direction and the timing of ocean tides? 2. What is the difference between an asterism and a constellation? 3. How would observations of stars differ from the observations of planets? 4. What is ...
Powerpoint Presentation (large file)
... are glowing, ionized clouds of gas • Emission nebulae are powered by ultraviolet light that they absorb from nearby hot stars • Reflection nebulae are produced when starlight is reflected from dust grains in the interstellar medium, producing a characteristic bluish ...
... are glowing, ionized clouds of gas • Emission nebulae are powered by ultraviolet light that they absorb from nearby hot stars • Reflection nebulae are produced when starlight is reflected from dust grains in the interstellar medium, producing a characteristic bluish ...
Formation of Stars
... Gravity works to compress a cloud. As an interstellar cloud collapses, it heats up. The rise in internal temperature and pressure works to counter gravity and stop the compression. ...
... Gravity works to compress a cloud. As an interstellar cloud collapses, it heats up. The rise in internal temperature and pressure works to counter gravity and stop the compression. ...
SHELL H II REGIONS IN NGC 6334
... • Orbital motions in protostars will provide important constraints on the early phases of stellar evolution • We are getting reasonable results, but must follow “strange” cases such as IRAS 162932422 ...
... • Orbital motions in protostars will provide important constraints on the early phases of stellar evolution • We are getting reasonable results, but must follow “strange” cases such as IRAS 162932422 ...
Lecture 1 Review Sheet
... How many years after the Big Bang began did the Universe become visible? How many millions of years after the Big Bang before the first stars ignited? Review Questions: Explain the significance of the cosmic microwave background radiation. What wavelength did it start out as? What does it record? Ex ...
... How many years after the Big Bang began did the Universe become visible? How many millions of years after the Big Bang before the first stars ignited? Review Questions: Explain the significance of the cosmic microwave background radiation. What wavelength did it start out as? What does it record? Ex ...
The Milky Way
... “an object in the Solar System that orbits the Sun and is not a satellite of a planet or other celestial body. It must be spherical (or nearly so) in shape.” ...
... “an object in the Solar System that orbits the Sun and is not a satellite of a planet or other celestial body. It must be spherical (or nearly so) in shape.” ...
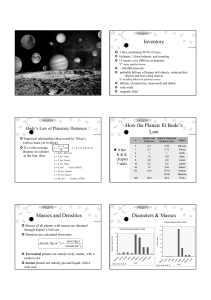
Planetary Overview Inventory How the Planets fit Bode`s Law
... temperatures of over 1000ºC facing the star Detecting Earth-like planets will not be easy 47 UMa has at least 2 giant planets in circular orbit at a distance of several AU a new era in astronomy has dawned new instruments, including giant mirrors and custom designed ...
... temperatures of over 1000ºC facing the star Detecting Earth-like planets will not be easy 47 UMa has at least 2 giant planets in circular orbit at a distance of several AU a new era in astronomy has dawned new instruments, including giant mirrors and custom designed ...
PLANETS
... (just dust & rocks), outflow has stopped, the star is visible. Theory: Gas disperses, “planetesimals” form (up to 100 km diameter rocks), collide & stick together due to gravity forming protoplanets). Protoplanets interact with dust disks: tidal torques cause planets to migrate inward toward their h ...
... (just dust & rocks), outflow has stopped, the star is visible. Theory: Gas disperses, “planetesimals” form (up to 100 km diameter rocks), collide & stick together due to gravity forming protoplanets). Protoplanets interact with dust disks: tidal torques cause planets to migrate inward toward their h ...
Are we Alone? The Search for Life Beyond the
... • They pointed out that the background noise (atmosphere, Galaxy, CMB etc.) was a minimum between ~1 to 10 GHz. • This band included the (radio) Hydrogen Line at 1.4 GHz and the OH Lines at ~ 1.6 GHz. • The band from 1.4 to 1.6 GHz is called the Water Hole ...
... • They pointed out that the background noise (atmosphere, Galaxy, CMB etc.) was a minimum between ~1 to 10 GHz. • This band included the (radio) Hydrogen Line at 1.4 GHz and the OH Lines at ~ 1.6 GHz. • The band from 1.4 to 1.6 GHz is called the Water Hole ...
Star Formation
... Cloud fragmentation • The molecular cloud does not collapse into a single star. • It fragments into many clumps. • These clumps can further collapse to form stars. • 10 - 1000 stars can be formed from the cloud. ...
... Cloud fragmentation • The molecular cloud does not collapse into a single star. • It fragments into many clumps. • These clumps can further collapse to form stars. • 10 - 1000 stars can be formed from the cloud. ...
Is Pluto a Planet? AST 248
... Below 0.076 M, H cannot undergo stable nuclear fusion But, Deuterium (2H) fuses at lower temperatures Brown dwarfs are objects that • fuse all the D in their cores • have masses between 0.013 and 0.076 M • burn their D quickly, then slowly cool. • form like stars. ...
... Below 0.076 M, H cannot undergo stable nuclear fusion But, Deuterium (2H) fuses at lower temperatures Brown dwarfs are objects that • fuse all the D in their cores • have masses between 0.013 and 0.076 M • burn their D quickly, then slowly cool. • form like stars. ...