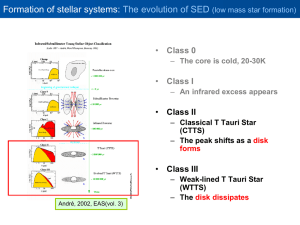
Astronomy Objectives
... Evolution of low mass (red dwarf) stars, medium mass main sequence stars, massive stars, all from nebulae to their final phases ...
... Evolution of low mass (red dwarf) stars, medium mass main sequence stars, massive stars, all from nebulae to their final phases ...
25drake3s
... fp -- Finding Planets Studies of star forming regions reveal that circumstellar disks are common around young stars ...
... fp -- Finding Planets Studies of star forming regions reveal that circumstellar disks are common around young stars ...
solar system formation and gal
... anything that can support it • The many craters on the moon and other planets indicate many collisions occurred in the formation of the universe. ...
... anything that can support it • The many craters on the moon and other planets indicate many collisions occurred in the formation of the universe. ...
11.2-11.3 PPT
... Our solar system is full of planets, moon, asteroids, and comets, all in motion around the Sun. Most of these components are separated by great distances. Each planet has its own distinct characteristics. Comets, icy debris, and dwarf planets travel at the outermost reaches of our solar system. ...
... Our solar system is full of planets, moon, asteroids, and comets, all in motion around the Sun. Most of these components are separated by great distances. Each planet has its own distinct characteristics. Comets, icy debris, and dwarf planets travel at the outermost reaches of our solar system. ...
Origin of the Solar System
... proceeds, the gravitational energy released will be partitioned equally between radiation and heating. If this continues long enough, the radiative flux from the protostar will become important in shaping its surroundings, e.g., by heating the surrounding dust. The second is that the continued decre ...
... proceeds, the gravitational energy released will be partitioned equally between radiation and heating. If this continues long enough, the radiative flux from the protostar will become important in shaping its surroundings, e.g., by heating the surrounding dust. The second is that the continued decre ...
Planet Kepler-78b is just like Earth, but 2000 degrees hotter
... respectively – also similar to Earth's 5.5 grams and implying a composition of rock and iron. This made Kepler-78, which orbits its star every 8.5 hours, the exoplanet most similar to Earth for which the mass, radius and density has been determined. "Its existence bodes well for the discovery and ch ...
... respectively – also similar to Earth's 5.5 grams and implying a composition of rock and iron. This made Kepler-78, which orbits its star every 8.5 hours, the exoplanet most similar to Earth for which the mass, radius and density has been determined. "Its existence bodes well for the discovery and ch ...
coSmoS in youR PockET
... If you can’t see it, try again another night until you see it and then draw a picture of the Moon. ...
... If you can’t see it, try again another night until you see it and then draw a picture of the Moon. ...
Why are so many extra-solar planets eccentric?
... Binary stars A weak tidal force can excited large ecc. Force needs to be stronger than other effect Problems Expected: multi-planet system have low ecc. Expected: high ecc. in binary system. Unseen companions? ...
... Binary stars A weak tidal force can excited large ecc. Force needs to be stronger than other effect Problems Expected: multi-planet system have low ecc. Expected: high ecc. in binary system. Unseen companions? ...
WORD - hrsbstaff.ednet.ns.ca
... 1. Fill in the Blanks ____________________________ models of the universe, such as the Ptolemaic model, have the Sun, the Moon, and all the other planets orbiting Earth. ____________________________ model of the solar system holds that Earth, like all the other planets, orbits the Sun and was made p ...
... 1. Fill in the Blanks ____________________________ models of the universe, such as the Ptolemaic model, have the Sun, the Moon, and all the other planets orbiting Earth. ____________________________ model of the solar system holds that Earth, like all the other planets, orbits the Sun and was made p ...
Condensation of the Solar Nebula
... during the early stage of the solar system formation process, when there were still many planetesimals floating around. Evidences of Impact ...
... during the early stage of the solar system formation process, when there were still many planetesimals floating around. Evidences of Impact ...
Gravity`s Influence on the Development of the Solar System
... the planets orbit the sun and discounted the age-old theory of an earthcentered system [Kaufman & Freedman, Universe, Fifth Edition]. Even though the universal laws of gravity assist in explaining the interactions within the solar nebula, they don’t encompass the variables involved in the evolution ...
... the planets orbit the sun and discounted the age-old theory of an earthcentered system [Kaufman & Freedman, Universe, Fifth Edition]. Even though the universal laws of gravity assist in explaining the interactions within the solar nebula, they don’t encompass the variables involved in the evolution ...
The Solar System and the Universe
... 8. Energy is released in the core of the Sun through a process called _____________________. When this process is accompanied by high temperature within the sun it is referred to as ___________________________. 9. During thermonuclear fusion, four ________________ nuclei fuse together to form one __ ...
... 8. Energy is released in the core of the Sun through a process called _____________________. When this process is accompanied by high temperature within the sun it is referred to as ___________________________. 9. During thermonuclear fusion, four ________________ nuclei fuse together to form one __ ...
Extrasolar Planets = 403
... grains very quickly • If moon formed at same distance: should have the same density but it does not ...
... grains very quickly • If moon formed at same distance: should have the same density but it does not ...
Section 17.1 - CPO Science
... 17.1 What is the solar system? • Today, we define the solar system as the sun and all objects that are gravitationally bound to the sun. • The solar system is roughly divided into the inner planets (Mercury, Venus, Earth, and Mars) and the outer planets (Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus, and Neptune) • The ...
... 17.1 What is the solar system? • Today, we define the solar system as the sun and all objects that are gravitationally bound to the sun. • The solar system is roughly divided into the inner planets (Mercury, Venus, Earth, and Mars) and the outer planets (Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus, and Neptune) • The ...
Study Guide - James E. Neff
... What were the 5 main elements comprising the pre-solar nebula, and what were the relative amounts (e.g. mostly hydrogen and helium; what percentage of the others)? Why does a rotating, collapsing cloud form a disk? Why do all the planets orbit the Sun in more or less the same direction the same plan ...
... What were the 5 main elements comprising the pre-solar nebula, and what were the relative amounts (e.g. mostly hydrogen and helium; what percentage of the others)? Why does a rotating, collapsing cloud form a disk? Why do all the planets orbit the Sun in more or less the same direction the same plan ...