presentation
... Adverse selection: arranger already knows the borrower through previous deals, so needs to show to participant that (s)he will not abuse it → arranger needs to retain more of loans to repeat borrowers ...
... Adverse selection: arranger already knows the borrower through previous deals, so needs to show to participant that (s)he will not abuse it → arranger needs to retain more of loans to repeat borrowers ...
Shapiro CHAPTER 5 solutionsOrig
... Comment on the following statements: a. “Because our new expansion project has the same systematic risk as the firm as a whole, we need do no further risk analysis on the project.” Answer: Investors holding the firm’s stock in their portfolios will consider the systematic risk calculation most impor ...
... Comment on the following statements: a. “Because our new expansion project has the same systematic risk as the firm as a whole, we need do no further risk analysis on the project.” Answer: Investors holding the firm’s stock in their portfolios will consider the systematic risk calculation most impor ...
Investment Analysis (FIN 670)
... 26. What is the most correct relationship between a company's ROE and ROA when the company does ...
... 26. What is the most correct relationship between a company's ROE and ROA when the company does ...
Systematic risk
... 4. In the boom market, which stock do you choose 5. In the recession market, which stock do you choose 6. How do investors know whether the return they get in the market is high enough to reward for the level of risk taken ...
... 4. In the boom market, which stock do you choose 5. In the recession market, which stock do you choose 6. How do investors know whether the return they get in the market is high enough to reward for the level of risk taken ...
Lending Booms, Reserves and the Sustainability of Short
... The Loans: Numbers, Spreads, and Issuers East Asian borrowers have dominated the international loan market. Of the 5,115 loans issued between 1991 and 1997, 3,373 were to East Asia, followed by Latin America and the Caribbean with 543, and Eastern Europe, Middle East and North Africa, and South Asia ...
... The Loans: Numbers, Spreads, and Issuers East Asian borrowers have dominated the international loan market. Of the 5,115 loans issued between 1991 and 1997, 3,373 were to East Asia, followed by Latin America and the Caribbean with 543, and Eastern Europe, Middle East and North Africa, and South Asia ...
AMP Capital Understanding Infrastructure – a reference guide
... Most infrastructure funds around the world use fixed term, closed ended fund structures, although the increasing interest in infrastructure as a source of long–term inflation linked cash flows has meant that open ended, evergreen and/or hybrid structures have become more common over the last few yea ...
... Most infrastructure funds around the world use fixed term, closed ended fund structures, although the increasing interest in infrastructure as a source of long–term inflation linked cash flows has meant that open ended, evergreen and/or hybrid structures have become more common over the last few yea ...
Chapter 7 12
... portfolio’s expected annual rate of return is 9 percent, and the annual standard deviation is 10 percent. Amanda Reckonwith, Percival’s financial adviser, recommends that Percival consider investing in an index fund which closely tracks the Standard and Poor’s 500 index. The index has an expected re ...
... portfolio’s expected annual rate of return is 9 percent, and the annual standard deviation is 10 percent. Amanda Reckonwith, Percival’s financial adviser, recommends that Percival consider investing in an index fund which closely tracks the Standard and Poor’s 500 index. The index has an expected re ...
Balance Sheet Capacity and Endogenous Risk
... may trade at different prices. He and Krishnamurthy (2007) have studied a dynamic asset pricing model with intermediaries, where the intermediaries’ capital constraints enter into the asset pricing problem as a determinant of portfolio capacity. Brunnermeier and Sannikov (2009) shares with our paper ...
... may trade at different prices. He and Krishnamurthy (2007) have studied a dynamic asset pricing model with intermediaries, where the intermediaries’ capital constraints enter into the asset pricing problem as a determinant of portfolio capacity. Brunnermeier and Sannikov (2009) shares with our paper ...
FM10 Ch 5 - Bryon Gaskin
... PEH tells us that three-year securities will yield 6.7%, two years from now (x%). Copyright © 2002 by Harcourt, Inc. ...
... PEH tells us that three-year securities will yield 6.7%, two years from now (x%). Copyright © 2002 by Harcourt, Inc. ...
Finance Notes 2008 Size: 351.5kb Last modified
... Option Pricing (ROV): DCF applicable for traditional firms with cash cow characteristics (i.e. relatively predictable cash flows). Firms with high risk characteristics from either financial difficulty (telecom) or growth firms (Internet) have unpredictable cash flows that are difficult to evaluate u ...
... Option Pricing (ROV): DCF applicable for traditional firms with cash cow characteristics (i.e. relatively predictable cash flows). Firms with high risk characteristics from either financial difficulty (telecom) or growth firms (Internet) have unpredictable cash flows that are difficult to evaluate u ...
AIFMD – Assets other than financial instruments held in custody
... an asset as well as cases where the AIF holds legal title to an asset. Since depositaries may not have possession of the AIF's "other assets", it will be necessary for depositaries to obtain the relevant information either directly from the AIF or its manager (AIFM) or from other sources. ...
... an asset as well as cases where the AIF holds legal title to an asset. Since depositaries may not have possession of the AIF's "other assets", it will be necessary for depositaries to obtain the relevant information either directly from the AIF or its manager (AIFM) or from other sources. ...
Value at Risk - dedeklegacy.cz
... credit risk refers to potential losses that are experienced when i) counterparties are unwilling or unable to fulfil their contractual obligations (i.e. repayment of a bond or coupons of the bond, repayment of loan or charged interest); ii) debtors are downgraded by credit agencies iii) credit sprea ...
... credit risk refers to potential losses that are experienced when i) counterparties are unwilling or unable to fulfil their contractual obligations (i.e. repayment of a bond or coupons of the bond, repayment of loan or charged interest); ii) debtors are downgraded by credit agencies iii) credit sprea ...
Investment Options and Risk
... and total return characteristics similar to the broader Australian share market (as represented by the S&P/ ASX 200 Index). The portfolio holds securities included in the Australian Sustainable Asset Management (SAM) Sustainability Index (the AuSSI). SAM selects approximately 70 stocks for inclusion ...
... and total return characteristics similar to the broader Australian share market (as represented by the S&P/ ASX 200 Index). The portfolio holds securities included in the Australian Sustainable Asset Management (SAM) Sustainability Index (the AuSSI). SAM selects approximately 70 stocks for inclusion ...
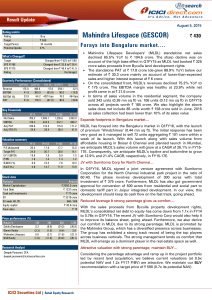
SA BlackRock VCP Global Multi Asset Portfolio Summary
... The Portfolio incorporates a volatility control process that seeks to reduce risk when the portfolio’s volatility is expected to exceed an annual level of 10%. Volatility is a statistical measure of the magnitude of changes in the Portfolio’s returns over time without regard to the direction of thos ...
... The Portfolio incorporates a volatility control process that seeks to reduce risk when the portfolio’s volatility is expected to exceed an annual level of 10%. Volatility is a statistical measure of the magnitude of changes in the Portfolio’s returns over time without regard to the direction of thos ...
chapter 31 - Pearsoncmg.com
... then calculate the NPV of these cash flows. 31.2.2. When do these two methods give the same NPV of the foreign project? The two methods give the same NPV of a foreign project when markets are internationally integrated and uncertainty in spot exchange rates are uncorrelated with the foreign currency ...
... then calculate the NPV of these cash flows. 31.2.2. When do these two methods give the same NPV of the foreign project? The two methods give the same NPV of a foreign project when markets are internationally integrated and uncertainty in spot exchange rates are uncorrelated with the foreign currency ...
general bearing corporation
... The Private Securities Litigation Reform Act of 1995 provides a "safe harbor" for forward-looking statements, which are statements other than those of historical fact, including, without limitation, ones identified by the use of the words: "anticipates," "estimates," "believes," "expects," "intends, ...
... The Private Securities Litigation Reform Act of 1995 provides a "safe harbor" for forward-looking statements, which are statements other than those of historical fact, including, without limitation, ones identified by the use of the words: "anticipates," "estimates," "believes," "expects," "intends, ...