Lecture 17
... In baseband transmission, the required bandwidth is proportional to the bit rate; if we need to send bits faster, we need more bandwidth (the frequency will need to increase) ...
... In baseband transmission, the required bandwidth is proportional to the bit rate; if we need to send bits faster, we need more bandwidth (the frequency will need to increase) ...
Harmonic Analysis of 230 V AC Power Supply
... kB of embedded high speed Flash memory [11]. A 128-bit wide memory interface and a unique accelerator architecture enable 32-bit code execution at maximum clock rate. For critical code size applications, the alternative 16-bit Thumb® Mode reduces code by more than 30 % with minimal performance penal ...
... kB of embedded high speed Flash memory [11]. A 128-bit wide memory interface and a unique accelerator architecture enable 32-bit code execution at maximum clock rate. For critical code size applications, the alternative 16-bit Thumb® Mode reduces code by more than 30 % with minimal performance penal ...
Broadly tunable, low timing jitter, high repetition rate optoelectronic
... in a process known as time-to-frequency mapping [11]. Three phase modulators are used to increase the modulation index, each contributing roughly 20 lines. Besides the benefit of a flat top profile, which is ideal for applications requiring pulse shaping or channel equalization, the line spacing of thi ...
... in a process known as time-to-frequency mapping [11]. Three phase modulators are used to increase the modulation index, each contributing roughly 20 lines. Besides the benefit of a flat top profile, which is ideal for applications requiring pulse shaping or channel equalization, the line spacing of thi ...
download
... Signals & Waves The following general observations may be made in conjunction with the frequency spectrum of a given function: 1. A discrete frequency spectrum belongs to a signal that is periodic and can be represented by a Fourier series (either finite or infinite) 2. A continuous frequency spe ...
... Signals & Waves The following general observations may be made in conjunction with the frequency spectrum of a given function: 1. A discrete frequency spectrum belongs to a signal that is periodic and can be represented by a Fourier series (either finite or infinite) 2. A continuous frequency spe ...
download
... Signals & Waves The following general observations may be made in conjunction with the frequency spectrum of a given function: 1. A discrete frequency spectrum belongs to a signal that is periodic and can be represented by a Fourier series (either finite or infinite) 2. A continuous frequency spe ...
... Signals & Waves The following general observations may be made in conjunction with the frequency spectrum of a given function: 1. A discrete frequency spectrum belongs to a signal that is periodic and can be represented by a Fourier series (either finite or infinite) 2. A continuous frequency spe ...
Minimal modifications of the primordial power spectrum from an
... Inflation, in addition to explaining the homogeneity and flatness of the universe, provides a platform for computing the properties of the small inhomogeneities which give rise to the large scale structures [1, 2]. When initially in the vacuum, the quantized fluctuations of the coupled system of met ...
... Inflation, in addition to explaining the homogeneity and flatness of the universe, provides a platform for computing the properties of the small inhomogeneities which give rise to the large scale structures [1, 2]. When initially in the vacuum, the quantized fluctuations of the coupled system of met ...
Electrical circuits wyklad 8
... An overtone is a harmonic produced by a particular device. The “first” overtone is the first frequency greater than the fundamental, while the “second” overtone is the next greater frequency produced. Successive overtones may or may not correspond to incremental harmonics, depending on the device pr ...
... An overtone is a harmonic produced by a particular device. The “first” overtone is the first frequency greater than the fundamental, while the “second” overtone is the next greater frequency produced. Successive overtones may or may not correspond to incremental harmonics, depending on the device pr ...
radio communications: am and fm
... signal, and thus corrupt the zero-crossings. It is the corruption of the zero-crossings that will affect the demodulated signal in FM. Any FM detector, irrespective of the implementation, must in some manner measure the instantaneous frequency. This will mean measurement of the intervals between zer ...
... signal, and thus corrupt the zero-crossings. It is the corruption of the zero-crossings that will affect the demodulated signal in FM. Any FM detector, irrespective of the implementation, must in some manner measure the instantaneous frequency. This will mean measurement of the intervals between zer ...
Fourier Spectra for Non-Homogeneous Patterns
... fourier transforms will prevent the generation of meaningless spectra. The analysis must be limited to the domain of k-space where the results are physically meaningful. Actually, because only limited resolution is possible, smearing of the spectrum will occur over a band t:.k (I (l1'f) wide in k-sp ...
... fourier transforms will prevent the generation of meaningless spectra. The analysis must be limited to the domain of k-space where the results are physically meaningful. Actually, because only limited resolution is possible, smearing of the spectrum will occur over a band t:.k (I (l1'f) wide in k-sp ...
Atomic_spectra
... Calculating the Balmer & Lyman Series As noted earlier, the four bands of light calculated by Balmer could be simply calculated using the Rydberg equation: ...
... Calculating the Balmer & Lyman Series As noted earlier, the four bands of light calculated by Balmer could be simply calculated using the Rydberg equation: ...
Low Phase Noise Rubidium Atomic Oscillator Module
... IQD’s latest high performance rubidium oscillator, the IQRB-2, delivers low phase noise of -112dBc/Hz at 1Hz and -158dBc/Hz at 10kHz. It is housed in a 95.5 x 62.5 x 44.3mm module so can be used in a 1U rack. The electrical connections include an SMA connector for RF output, RS232 connectors RX & TX ...
... IQD’s latest high performance rubidium oscillator, the IQRB-2, delivers low phase noise of -112dBc/Hz at 1Hz and -158dBc/Hz at 10kHz. It is housed in a 95.5 x 62.5 x 44.3mm module so can be used in a 1U rack. The electrical connections include an SMA connector for RF output, RS232 connectors RX & TX ...
Capacitor Self-Resonance
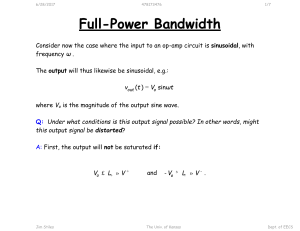
... R1 and RF), connect a generator producing a sinusoidal input voltage (and it MUST be sinusoidal, since any other waveform has harmonics, and to measure bandwidth you must put in a single frequency). Be sure to keep the frequency low at first (low means well below the expected upper breakpoint freque ...
... R1 and RF), connect a generator producing a sinusoidal input voltage (and it MUST be sinusoidal, since any other waveform has harmonics, and to measure bandwidth you must put in a single frequency). Be sure to keep the frequency low at first (low means well below the expected upper breakpoint freque ...
Lecture 1 - Digilent Learn site
... absolutely remove all components outside the passband. • Also point out that these cannot be implemented in the real world (turns out that they would need to respond to the input before the input is applied – they need to see into the future) ...
... absolutely remove all components outside the passband. • Also point out that these cannot be implemented in the real world (turns out that they would need to respond to the input before the input is applied – they need to see into the future) ...
localization of small fast moving objects using doppler radar
... spectrums, labelled as spectrogram, can be clearly depicted as a two dimensional chart, where the first coordinate corresponds to the frequency, whereas the second one represents the time. The amplitude of the corresponding spectrum coefficients is distinguished by a color. Disadvantage of discrete ...
... spectrums, labelled as spectrogram, can be clearly depicted as a two dimensional chart, where the first coordinate corresponds to the frequency, whereas the second one represents the time. The amplitude of the corresponding spectrum coefficients is distinguished by a color. Disadvantage of discrete ...
Spectrum analyzer

A spectrum analyzer measures the magnitude of an input signal versus frequency within the full frequency range of the instrument. The primary use is to measure the power of the spectrum of known and unknown signals. The input signal that a spectrum analyzer measures is electrical, however, spectral compositions of other signals, such as acoustic pressure waves and optical light waves, can be considered through the use of an appropriate transducer. Optical spectrum analyzers also exist, which use direct optical techniques such as a monochromator to make measurements.By analyzing the spectra of electrical signals, dominant frequency, power, distortion, harmonics, bandwidth, and other spectral components of a signal can be observed that are not easily detectable in time domain waveforms. These parameters are useful in the characterization of electronic devices, such as wireless transmitters.The display of a spectrum analyzer has frequency on the horizontal axis and the amplitude displayed on the vertical axis. To the casual observer, a spectrum analyzer looks like an oscilloscope and, in fact, some lab instruments can function either as an oscilloscope or a spectrum analyzer.