COMPUTER CONTROLLED SYSTEM FOR COMPLEX
... equipped with a fixed APC−7 connector. The HP4192A can also be used to measure the complex impedance of coaxial cells loaded with magnetic cores (in the frequency range from about 100 kHz to 13 MHz). Since this instrument terminates with four BNC connectors, it requires to use the terminal adapter 1 ...
... equipped with a fixed APC−7 connector. The HP4192A can also be used to measure the complex impedance of coaxial cells loaded with magnetic cores (in the frequency range from about 100 kHz to 13 MHz). Since this instrument terminates with four BNC connectors, it requires to use the terminal adapter 1 ...
Amplifiers
... Let’s look at this first problem first. The ideal amplifier impulse response g (t ) Av (t ) means that the signal at the output occurs instantaneously with the signal at the input. This of course cannot happen, as it takes some small, but non-zero ...
... Let’s look at this first problem first. The ideal amplifier impulse response g (t ) Av (t ) means that the signal at the output occurs instantaneously with the signal at the input. This of course cannot happen, as it takes some small, but non-zero ...
2. Representation of Signals
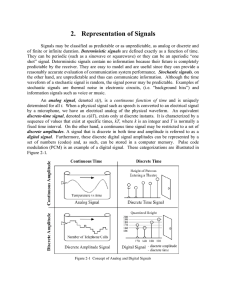
... An analog signal, denoted x(t), is a continuous function of time and is uniquely determined for all t. When a physical signal such as speech is converted to an electrical signal by a microphone, we have an electrical analog of the physical waveform. An equivalent discrete-time signal, denoted as x(k ...
... An analog signal, denoted x(t), is a continuous function of time and is uniquely determined for all t. When a physical signal such as speech is converted to an electrical signal by a microphone, we have an electrical analog of the physical waveform. An equivalent discrete-time signal, denoted as x(k ...
Troubleshooting Guide for Amptek Digital Pulse Procesors
... product, while an electronic copy is on the installation CD. Follow the instructions for your product. 2) Incorrect installation of the application software or USB drivers is the most common source of problems with Amptek's DPPs. Software installation is simple but must be done correctly. It is desc ...
... product, while an electronic copy is on the installation CD. Follow the instructions for your product. 2) Incorrect installation of the application software or USB drivers is the most common source of problems with Amptek's DPPs. Software installation is simple but must be done correctly. It is desc ...
1 INTRODUCTION
... 4.1.2 Power Density Spectrum of Periodic Signals. 4.1.3 The Fourier Transform for Continuous-Time Aperiodic Signals. 4.1.4 Energy Density Spectrum of Aperiodic Signals. 4.2 Frequency Analysis of Discrete-Time Signals 4.2.1 The Fourier Series for Discrete-Time Periodic Signals. 4.2.2 Power Density S ...
... 4.1.2 Power Density Spectrum of Periodic Signals. 4.1.3 The Fourier Transform for Continuous-Time Aperiodic Signals. 4.1.4 Energy Density Spectrum of Aperiodic Signals. 4.2 Frequency Analysis of Discrete-Time Signals 4.2.1 The Fourier Series for Discrete-Time Periodic Signals. 4.2.2 Power Density S ...
10.3.2.1.1 Spectral apparatus An optical arrangement or an
... spectral instrument. If the entrance aperture, which may be a slit, is sharply imaged in both dimensions, i.e., length and width in the same focal plane, it is called a stigmatic arrangement or when the focal planes are different in the two dimensions, astigmatic. When the radiation passes through t ...
... spectral instrument. If the entrance aperture, which may be a slit, is sharply imaged in both dimensions, i.e., length and width in the same focal plane, it is called a stigmatic arrangement or when the focal planes are different in the two dimensions, astigmatic. When the radiation passes through t ...
Single-pulse coherent anti-Stokes Raman scattering microscopy
... excitation of various Raman modes with energies within the pulse bandwidth. As a result the spectral resolution is limited by the pulse bandwidth. Thus, it is necessary to suppress both the nonresonant signals and the resonant signals from nontarget Raman modes or to extract only the target signal o ...
... excitation of various Raman modes with energies within the pulse bandwidth. As a result the spectral resolution is limited by the pulse bandwidth. Thus, it is necessary to suppress both the nonresonant signals and the resonant signals from nontarget Raman modes or to extract only the target signal o ...
2188 Input Bias Current Commutation
... The noise level of a filtered chopper amplifier is on-par with non-chopper topologies TI Information – Selective Disclosure ...
... The noise level of a filtered chopper amplifier is on-par with non-chopper topologies TI Information – Selective Disclosure ...
pasive filters - Portal UniMAP
... • BPF is essential for applications where a particular band or frequencies need to be filtered from a wider range of mixed signals. • There are 3 important parameters that characterize a BPF, only two of them can be specified independently: – Center frequency (and two cutoff frequencies) – Bandwidth ...
... • BPF is essential for applications where a particular band or frequencies need to be filtered from a wider range of mixed signals. • There are 3 important parameters that characterize a BPF, only two of them can be specified independently: – Center frequency (and two cutoff frequencies) – Bandwidth ...
Low-noise computer-controlled current source for quantum
... serial data signals are distributed in a daisy-chain configuration of the three potentiometers. The potentiometers are set with the nonstandard logic levels of 0 and 2.5 V, which we generate with voltage dividers on the board. We designed the current source without a feedback loop. Such a loop might ...
... serial data signals are distributed in a daisy-chain configuration of the three potentiometers. The potentiometers are set with the nonstandard logic levels of 0 and 2.5 V, which we generate with voltage dividers on the board. We designed the current source without a feedback loop. Such a loop might ...
Spectrum analyzer

A spectrum analyzer measures the magnitude of an input signal versus frequency within the full frequency range of the instrument. The primary use is to measure the power of the spectrum of known and unknown signals. The input signal that a spectrum analyzer measures is electrical, however, spectral compositions of other signals, such as acoustic pressure waves and optical light waves, can be considered through the use of an appropriate transducer. Optical spectrum analyzers also exist, which use direct optical techniques such as a monochromator to make measurements.By analyzing the spectra of electrical signals, dominant frequency, power, distortion, harmonics, bandwidth, and other spectral components of a signal can be observed that are not easily detectable in time domain waveforms. These parameters are useful in the characterization of electronic devices, such as wireless transmitters.The display of a spectrum analyzer has frequency on the horizontal axis and the amplitude displayed on the vertical axis. To the casual observer, a spectrum analyzer looks like an oscilloscope and, in fact, some lab instruments can function either as an oscilloscope or a spectrum analyzer.