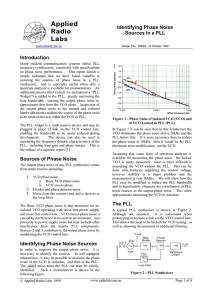
2.2 The Telstra Wholesale Spectrum Sharing Service is a
... RSU means a remote subscriber unit which performs an equivalent function to an RSS. Splitter means the equipment that separates the voice and non-voice ADSL spectrum and complies with the Telstra Splitter Specification. Telstra Customer Access Module (TCAM) is a device owned by Telstra that provides ...
... RSU means a remote subscriber unit which performs an equivalent function to an RSS. Splitter means the equipment that separates the voice and non-voice ADSL spectrum and complies with the Telstra Splitter Specification. Telstra Customer Access Module (TCAM) is a device owned by Telstra that provides ...
Adaptive Systems in Digital Communication Designs
... channel is a cable then this dispersion will have a continuous impulse response which may spread over many intervals, thus causing inter-symbol interference (ISI).1 In the case of a radio channel the dispersion is more likely to be discrete in nature and caused by multipath effects. If the multipath ...
... channel is a cable then this dispersion will have a continuous impulse response which may spread over many intervals, thus causing inter-symbol interference (ISI).1 In the case of a radio channel the dispersion is more likely to be discrete in nature and caused by multipath effects. If the multipath ...
A Direct Digital Frequency Synthesizer With Fourth
... with ultra fine resolution. Modern communication systems are placing increasing demands on frequency resolution, channel switching speed and bandwidth requirements of frequency synthesis. For instance, spread-spectrum applications require frequency synthesizers that are capable of tuning to differen ...
... with ultra fine resolution. Modern communication systems are placing increasing demands on frequency resolution, channel switching speed and bandwidth requirements of frequency synthesis. For instance, spread-spectrum applications require frequency synthesizers that are capable of tuning to differen ...
Get PDF - OSA Publishing
... High stability and spectral purity microwave and millimeter-wave sources have become increasingly crucial in several areas of applications, including communication systems, signal processing, radars, radio astronomy, satellites, GPS navigation, spectroscopy, time-frequency metrology, etc. Although h ...
... High stability and spectral purity microwave and millimeter-wave sources have become increasingly crucial in several areas of applications, including communication systems, signal processing, radars, radio astronomy, satellites, GPS navigation, spectroscopy, time-frequency metrology, etc. Although h ...
Chapter 1 : Introduction to Electronic Communications
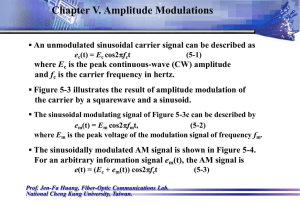
... Vam(t ) Ec mEc sin( 2fmt )sin 2fct ...
... Vam(t ) Ec mEc sin( 2fmt )sin 2fct ...
Subluminal wave bullets: Exact localized subluminal
... in any homogeneous linear media, are herein obtained for arbitrarily chosen frequencies and bandwidths, avoiding in particular any recourse to the noncausal 共backward moving兲 components that so frequently plague the previously known localized waves. Such solutions are suitable superpositions of—zero ...
... in any homogeneous linear media, are herein obtained for arbitrarily chosen frequencies and bandwidths, avoiding in particular any recourse to the noncausal 共backward moving兲 components that so frequently plague the previously known localized waves. Such solutions are suitable superpositions of—zero ...
ELEC 7770: Advanced VLSI Design Spring 2010 Radio Frequency (RF) Testing
... frequency band 2.4 – 2.5GHz. It is required to have a gain of 20dB and a gain flatness of 1dB. Test: Under properly matched conditions, S21 is measured at several frequencies in the range of operation: S21 = 15.31 at 2.400GHz S21 = 14.57 at 2.499GHz From the measurements: At 2.400GHz, Gain = 2 ...
... frequency band 2.4 – 2.5GHz. It is required to have a gain of 20dB and a gain flatness of 1dB. Test: Under properly matched conditions, S21 is measured at several frequencies in the range of operation: S21 = 15.31 at 2.400GHz S21 = 14.57 at 2.499GHz From the measurements: At 2.400GHz, Gain = 2 ...
Digital oscilloscopes
... markings, whether located directly on the screen or on a removable plastic filter, usually consist of a 1 cm grid with closer tick marks (often at 2 mm) on the centre vertical and horizontal axis. One expects to see ten major divisions across the screen; the number of vertical major divisions varies ...
... markings, whether located directly on the screen or on a removable plastic filter, usually consist of a 1 cm grid with closer tick marks (often at 2 mm) on the centre vertical and horizontal axis. One expects to see ten major divisions across the screen; the number of vertical major divisions varies ...
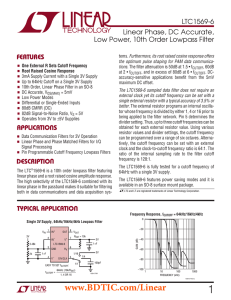
LTC1569-6 - Linear Phase, DC Accurate, Low Power, 10th Order
... frequency at which the filter AC response exhibits >1dB of gain peaking. Note 5: The minimum clock frequency is arbitrarily defined as the frequecy at which the filter DC offset changes by more than 5mV. Note 6: For more details refer to the Input and Output Voltage Range paragraph in the Applicatio ...
... frequency at which the filter AC response exhibits >1dB of gain peaking. Note 5: The minimum clock frequency is arbitrarily defined as the frequecy at which the filter DC offset changes by more than 5mV. Note 6: For more details refer to the Input and Output Voltage Range paragraph in the Applicatio ...
CVM-144 - CIRCUTOR
... The manual you hold in your hands contains information and warnings that the user should respect in order to guarantee a proper operation of all the instrument functions and keep its safety conditions. The instrument must not be powered and used until its definitive assembly on the cabinet’s door. I ...
... The manual you hold in your hands contains information and warnings that the user should respect in order to guarantee a proper operation of all the instrument functions and keep its safety conditions. The instrument must not be powered and used until its definitive assembly on the cabinet’s door. I ...
Making Sense of Effective Bits in Oscilloscope Measurements
... directly, without having to set up a histogram manually. It is important not to include the DC offset in this measurement, so histograms or AC RMS measurements must be used. The Figure 5 screen capture shows a baseline noise measurement. Figure 6 shows a comparison of baseline noise for the Tektroni ...
... directly, without having to set up a histogram manually. It is important not to include the DC offset in this measurement, so histograms or AC RMS measurements must be used. The Figure 5 screen capture shows a baseline noise measurement. Figure 6 shows a comparison of baseline noise for the Tektroni ...
Spectrum analyzer

A spectrum analyzer measures the magnitude of an input signal versus frequency within the full frequency range of the instrument. The primary use is to measure the power of the spectrum of known and unknown signals. The input signal that a spectrum analyzer measures is electrical, however, spectral compositions of other signals, such as acoustic pressure waves and optical light waves, can be considered through the use of an appropriate transducer. Optical spectrum analyzers also exist, which use direct optical techniques such as a monochromator to make measurements.By analyzing the spectra of electrical signals, dominant frequency, power, distortion, harmonics, bandwidth, and other spectral components of a signal can be observed that are not easily detectable in time domain waveforms. These parameters are useful in the characterization of electronic devices, such as wireless transmitters.The display of a spectrum analyzer has frequency on the horizontal axis and the amplitude displayed on the vertical axis. To the casual observer, a spectrum analyzer looks like an oscilloscope and, in fact, some lab instruments can function either as an oscilloscope or a spectrum analyzer.


![High frequency characterization of the Gsanger LM0202P eletro-optic [i.e. electro-optic] modulator](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/008539595_1-15b150bba37609ff7a759829ad2a5a86-300x300.png)