The Nervous System
... Fasciculus gracilis (axon of first-order sensory neuron) Lumbar spinal cord ...
... Fasciculus gracilis (axon of first-order sensory neuron) Lumbar spinal cord ...
Drug-Evoked Synaptic Plasticity Causing Addictive Behavior
... levels, which mediate their reinforcing effect (Wise, 1987; Di Chiara and Imperato, 1988). While this statement is supported by many experiments, particularly early behavioral pharmacology studies, it has been challenged, most prominently by genetic manipulations. For example, even though cocaine in ...
... levels, which mediate their reinforcing effect (Wise, 1987; Di Chiara and Imperato, 1988). While this statement is supported by many experiments, particularly early behavioral pharmacology studies, it has been challenged, most prominently by genetic manipulations. For example, even though cocaine in ...
CHAPTER 10: NERVOUS SYSTEM I
... Summation = many subthreshold stimuli received one after another may allow threshold potential to be reached, trigger an AP and begin a NI on a neuron. a. +15 mV = threshold = AP = NI b. +5, +5, +5, = +15 mV = threshold = AP = NI. ...
... Summation = many subthreshold stimuli received one after another may allow threshold potential to be reached, trigger an AP and begin a NI on a neuron. a. +15 mV = threshold = AP = NI b. +5, +5, +5, = +15 mV = threshold = AP = NI. ...
Gobbi 2005 - Iowa Medical Marijuana
... emotional behavior and the pathogenesis of depression (5). The idea that the mood-elevating properties of cannabis might be harnessed to treat depression was proposed first in the mid-19th century, but soon was disputed on account of the multiple side effects and inconsistent efficacy of the drug (6 ...
... emotional behavior and the pathogenesis of depression (5). The idea that the mood-elevating properties of cannabis might be harnessed to treat depression was proposed first in the mid-19th century, but soon was disputed on account of the multiple side effects and inconsistent efficacy of the drug (6 ...
Visual7
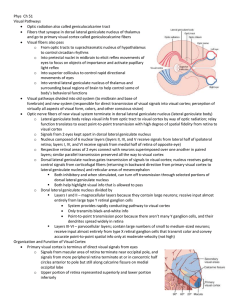
... Optic nerves from both eyes converge at optic chiasm: partial cross-over. Images in the nasal hemiretina from both sides cross over (temporal stay ipsilateral). This allows for complete cross-over of each visual field (see Fig. 7-3C). ...
... Optic nerves from both eyes converge at optic chiasm: partial cross-over. Images in the nasal hemiretina from both sides cross over (temporal stay ipsilateral). This allows for complete cross-over of each visual field (see Fig. 7-3C). ...
Sliding
... pre then post->LTP: easy, the AP “boosts” the activation of the NMDAR by reducing the Mg block post then pre-> LTD: several hypothesis 1) Ca entry during the AP. Ca is not fully removed by the time synapses are activated and help to bring [Ca]i to the LTD threshold 2) Ca entry during the AP desensit ...
... pre then post->LTP: easy, the AP “boosts” the activation of the NMDAR by reducing the Mg block post then pre-> LTD: several hypothesis 1) Ca entry during the AP. Ca is not fully removed by the time synapses are activated and help to bring [Ca]i to the LTD threshold 2) Ca entry during the AP desensit ...
CHAPTER 10: NERVOUS SYSTEM I
... Summation = many subthreshold stimuli received one after another may allow threshold potential to be reached, trigger an AP and begin a NI on a neuron. a. +15 mV = threshold = AP = NI b. +5, +5, +5, = +15 mV = threshold = AP = NI. ...
... Summation = many subthreshold stimuli received one after another may allow threshold potential to be reached, trigger an AP and begin a NI on a neuron. a. +15 mV = threshold = AP = NI b. +5, +5, +5, = +15 mV = threshold = AP = NI. ...
PhD Thesis - Laboratory of Cerebral Cortex Development
... signaling molecules that specify different neuronal cell types at precise positions along the anterior–posterior (A/P) and dorsal–ventral (D/V) axes of the neural tube during development. Among signaling molecules, a special role is played by morphogens. A morphogen is a secreted factor form a local ...
... signaling molecules that specify different neuronal cell types at precise positions along the anterior–posterior (A/P) and dorsal–ventral (D/V) axes of the neural tube during development. Among signaling molecules, a special role is played by morphogens. A morphogen is a secreted factor form a local ...
SPINAL CORD II
... mostly crossed. Pathway has two neurons. 1st osrder in dorsal root ganglion 2nd in spinal cord. Axons of 2nd order neurons runs over superior cerebellar peduncle to enter the cerebellum. Concerned with coordinated movement and posture of lower limb. ...
... mostly crossed. Pathway has two neurons. 1st osrder in dorsal root ganglion 2nd in spinal cord. Axons of 2nd order neurons runs over superior cerebellar peduncle to enter the cerebellum. Concerned with coordinated movement and posture of lower limb. ...
Broca`s Area in Language, Action, and Music
... degree of speech comprehension deficits. These deficits became more evident when they were tested with verbal material requiring syntactic understanding.3,4 Thus, the functional segregation between Broca’s and Wernicke’s areas could be differentiated by their encoding of syntax. In fact, it has been ...
... degree of speech comprehension deficits. These deficits became more evident when they were tested with verbal material requiring syntactic understanding.3,4 Thus, the functional segregation between Broca’s and Wernicke’s areas could be differentiated by their encoding of syntax. In fact, it has been ...
Motivation - Blackwell Publishing
... Reward and satiety are different processes. Reward is produced by factors such as the taste and smell of food. Satiety is produced by gastric, intestinal and other signals after the food is absorbed from the intestine. Hunger and satiety signals modulate the reward value of food (i.e. the taste and ...
... Reward and satiety are different processes. Reward is produced by factors such as the taste and smell of food. Satiety is produced by gastric, intestinal and other signals after the food is absorbed from the intestine. Hunger and satiety signals modulate the reward value of food (i.e. the taste and ...
Neurodegenerative Changes in the Motor Cortex and Cerebellum in Wistar... Following Acute Pneumococcal Meningitis
... The rats were perfused transcardially with 100 ml of saline, followed by 200 mls of 10% formalin. Brain was removed and post fixed for 48 hrs in the same fixative. The tissue was processed for paraffin sectioning. Motor cortex and cerebellar tissue were selected for study. Tissue pieces were dehydra ...
... The rats were perfused transcardially with 100 ml of saline, followed by 200 mls of 10% formalin. Brain was removed and post fixed for 48 hrs in the same fixative. The tissue was processed for paraffin sectioning. Motor cortex and cerebellar tissue were selected for study. Tissue pieces were dehydra ...
Efficient Neural Codes under Metabolic Constraints
... framework for optimal neural codes with monotonic tuning curves in the brain, and makes predictions that can be directly tested with physiological experiments. ...
... framework for optimal neural codes with monotonic tuning curves in the brain, and makes predictions that can be directly tested with physiological experiments. ...
Basic Science Award Recipients 2003
... “Dissection of a Newly Discovered DNA Damage Response Pathway in Early Zebrafish Embryogenesis” Cells with extensive DNA damage are typically eliminated via apoptosis, but pre¬- and early-gastrulation embryos of most organisms cannot induce apoptosis. What happens to damaged cells in early embryogen ...
... “Dissection of a Newly Discovered DNA Damage Response Pathway in Early Zebrafish Embryogenesis” Cells with extensive DNA damage are typically eliminated via apoptosis, but pre¬- and early-gastrulation embryos of most organisms cannot induce apoptosis. What happens to damaged cells in early embryogen ...
Different Types of Cerebellar GABAergic Interneurons Originate from
... Leverkusen, Germany) supplemented by xylazine (5 mg/kg; Rompun; Bayer) or diazepam (2.5 mg/kg; Roche, Mannheim, Germany). The experimental plan was designed according to the European Communities Council Directive of 1986 (86/609/EEC), National Institutes of Health guidelines, and the Italian law for ...
... Leverkusen, Germany) supplemented by xylazine (5 mg/kg; Rompun; Bayer) or diazepam (2.5 mg/kg; Roche, Mannheim, Germany). The experimental plan was designed according to the European Communities Council Directive of 1986 (86/609/EEC), National Institutes of Health guidelines, and the Italian law for ...
Spinal motor neurons are regenerated after
... In adult zebrafish, relatively quiescent progenitor cells show lesioninduced generation of motor neurons. Developmental motor neuron generation from the spinal motor neuron progenitor domain (pMN) sharply declines already at 48 hours post-fertilisation (hpf). After that, mostly oligodendrocytes are ...
... In adult zebrafish, relatively quiescent progenitor cells show lesioninduced generation of motor neurons. Developmental motor neuron generation from the spinal motor neuron progenitor domain (pMN) sharply declines already at 48 hours post-fertilisation (hpf). After that, mostly oligodendrocytes are ...
phys chapter 51 [3-20
... Areas of max excitation occur along sharp borders of visual pattern; visual signal in primary visual cortex concerned mainly with contrasts in visual scene rather than with noncontrasting areas o Equally stimulated adjacent retinal receptors mutually inhibit one another o At any border in visual s ...
... Areas of max excitation occur along sharp borders of visual pattern; visual signal in primary visual cortex concerned mainly with contrasts in visual scene rather than with noncontrasting areas o Equally stimulated adjacent retinal receptors mutually inhibit one another o At any border in visual s ...
Complete morphologies of basal forebrain cholinergic neurons in
... acetylcholine. This network has a key role in cognition, and its neurons are among the first to degenerate in Alzheimer's disease. However, relatively little is known about the structure of these ‘cholinergic’ neurons because their large size makes them difficult to study using standard techniques. ...
... acetylcholine. This network has a key role in cognition, and its neurons are among the first to degenerate in Alzheimer's disease. However, relatively little is known about the structure of these ‘cholinergic’ neurons because their large size makes them difficult to study using standard techniques. ...
Integrating Top-Down and Bottom
... A hierarchical network of reciprocally connected areas consisting of different parallel pathways is shown in Fig. 1A. Each pair of functionally adjacent areas is connected by reciprocal bottom-up and top-down projections. We picked out two neighboring areas at different hierarchical levels (area A a ...
... A hierarchical network of reciprocally connected areas consisting of different parallel pathways is shown in Fig. 1A. Each pair of functionally adjacent areas is connected by reciprocal bottom-up and top-down projections. We picked out two neighboring areas at different hierarchical levels (area A a ...
Auditory–vocal mirroring in songbirds
... HVCX cells in song motor control cannot be excluded, mediated perhaps by their long-range projections to area X or by the excitatory synapses that their local collaterals make on HVCRA cells and HVC interneurons [66]. In the former scenario, the singing-related activity of HVCX cells could influence ...
... HVCX cells in song motor control cannot be excluded, mediated perhaps by their long-range projections to area X or by the excitatory synapses that their local collaterals make on HVCRA cells and HVC interneurons [66]. In the former scenario, the singing-related activity of HVCX cells could influence ...
Title : Physiology of respiratory system
... A. Automatic Control of Breathing - Control Centers in the Brain Stem 1. Control Centers in Medulla Oblongata a. Breathing relies on repetitive stimulation from the brain stem. b. Two types of respiratory neurons are present in the medulla oblongata: inspiratory (I) neurons, which discharge during i ...
... A. Automatic Control of Breathing - Control Centers in the Brain Stem 1. Control Centers in Medulla Oblongata a. Breathing relies on repetitive stimulation from the brain stem. b. Two types of respiratory neurons are present in the medulla oblongata: inspiratory (I) neurons, which discharge during i ...
Biological Rhythms
... • The sun rises and sets every 24 hours. • In humans the light level is detected in the eyes and passed on to retinal ganglion cells, which also contain a light sensitive pigment. These cells release (NT) acetylcholine and have several effects. They activate the neurones that cause dreaming and some ...
... • The sun rises and sets every 24 hours. • In humans the light level is detected in the eyes and passed on to retinal ganglion cells, which also contain a light sensitive pigment. These cells release (NT) acetylcholine and have several effects. They activate the neurones that cause dreaming and some ...
Weight Regulation Activity
... stimulus (the high temperatures in the house). Most homeostatic control mechanisms in the body work by negative feedback. For example, the body’s temperature is maintained around 37°C. If you get too warm, sensors in the hypothalamus of the brain will signal control centers that will produce sweatin ...
... stimulus (the high temperatures in the house). Most homeostatic control mechanisms in the body work by negative feedback. For example, the body’s temperature is maintained around 37°C. If you get too warm, sensors in the hypothalamus of the brain will signal control centers that will produce sweatin ...
Computational approaches to sensorimotor transformations
... spatial location of the visual stimulus (kinematics). The second problem is specifying and controlling the application of force to determine the movement trajectory (dynamics)1, 2. This review focuses almost exclusively on kinematics (see Wolpert and Ghahramani, this issue, for models of movement d ...
... spatial location of the visual stimulus (kinematics). The second problem is specifying and controlling the application of force to determine the movement trajectory (dynamics)1, 2. This review focuses almost exclusively on kinematics (see Wolpert and Ghahramani, this issue, for models of movement d ...
Rapid Critical Period Induction by Tonic Inhibition in Visual Cortex
... release with stimulation and do not respond to brief MD (Hensch et al., 1998). Importantly, functional enhancement of GABAergic transmission fully restores OD plasticity to GAD65 KO mice. Rescue is achieved by diazepam, one of the best-characterized benzodiazepine agonists, which selectively bind su ...
... release with stimulation and do not respond to brief MD (Hensch et al., 1998). Importantly, functional enhancement of GABAergic transmission fully restores OD plasticity to GAD65 KO mice. Rescue is achieved by diazepam, one of the best-characterized benzodiazepine agonists, which selectively bind su ...
Optogenetics

Optogenetics (from Greek optikós, meaning ""seen, visible"") is a biological technique which involves the use of light to control cells in living tissue, typically neurons, that have been genetically modified to express light-sensitive ion channels. It is a neuromodulation method employed in neuroscience that uses a combination of techniques from optics and genetics to control and monitor the activities of individual neurons in living tissue—even within freely-moving animals—and to precisely measure the effects of those manipulations in real-time. The key reagents used in optogenetics are light-sensitive proteins. Spatially-precise neuronal control is achieved using optogenetic actuators like channelrhodopsin, halorhodopsin, and archaerhodopsin, while temporally-precise recordings can be made with the help of optogenetic sensors for calcium (Aequorin, Cameleon, GCaMP), chloride (Clomeleon) or membrane voltage (Mermaid).The earliest approaches were developed and applied by Boris Zemelman and Gero Miesenböck, at the Sloan-Kettering Cancer Center in New York City, and Dirk Trauner, Richard Kramer and Ehud Isacoff at the University of California, Berkeley; these methods conferred light sensitivity but were never reported to be useful by other laboratories due to the multiple components these approaches required. A distinct single-component approach involving microbial opsin genes introduced in 2005 turned out to be widely applied, as described below. Optogenetics is known for the high spatial and temporal resolution that it provides in altering the activity of specific types of neurons to control a subject's behaviour.In 2010, optogenetics was chosen as the ""Method of the Year"" across all fields of science and engineering by the interdisciplinary research journal Nature Methods. At the same time, optogenetics was highlighted in the article on “Breakthroughs of the Decade” in the academic research journal Science. These journals also referenced recent public-access general-interest video Method of the year video and textual SciAm summaries of optogenetics.