Some Photographs of the Tracks of Penetrating Radiation Author(s
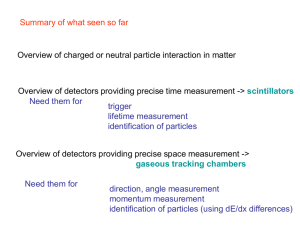
... on the effective time of expansion. The latter is not likely to be more than 1/20 second. From measurements with counters it is known that about 1*5 fast particles fall, from all directions, on 1 sq. cm. per second. Roughly consistent with these figures are the results found with cloud chambers. Sko ...
... on the effective time of expansion. The latter is not likely to be more than 1/20 second. From measurements with counters it is known that about 1*5 fast particles fall, from all directions, on 1 sq. cm. per second. Roughly consistent with these figures are the results found with cloud chambers. Sko ...
charged particles are prevented from going faster than the speed of
... where dtproper and dtimproper are the proper duration and improper duration of time, respectively. According to the space-time interpretation of the Special Theory of Relativity, the force-acceleration relation is nonlinear because a moving particle experiences a constant force for a shorter duratio ...
... where dtproper and dtimproper are the proper duration and improper duration of time, respectively. According to the space-time interpretation of the Special Theory of Relativity, the force-acceleration relation is nonlinear because a moving particle experiences a constant force for a shorter duratio ...
Charged Particles are Prevented from Going
... where dtproper and dtimproper are the proper duration and improper duration of time, respectively. According to the space-time interpretation of the Special Theory of Relativity, the force-acceleration relation is nonlinear because a moving particle experiences a constant force for a shorter duratio ...
... where dtproper and dtimproper are the proper duration and improper duration of time, respectively. According to the space-time interpretation of the Special Theory of Relativity, the force-acceleration relation is nonlinear because a moving particle experiences a constant force for a shorter duratio ...
GSI_OP-Training_Accelerator_Physics
... offsets are small – put QF in place where vertical offsets are small – then effect of QD on x respectively QF on y should be small ...
... offsets are small – put QF in place where vertical offsets are small – then effect of QD on x respectively QF on y should be small ...
Electric Charge in an Electric Field
... 18.7. THOMSON’S ‘PLUM PUDDING’ MODEL OF THE ATOM All of the measurements made thus far led scientists established the following: 1) Since atoms are electrically neutral, there must be equal amounts of positive and negative charge in each atom. 2) The negative charge is from the same particles that a ...
... 18.7. THOMSON’S ‘PLUM PUDDING’ MODEL OF THE ATOM All of the measurements made thus far led scientists established the following: 1) Since atoms are electrically neutral, there must be equal amounts of positive and negative charge in each atom. 2) The negative charge is from the same particles that a ...
linacs_CAS_al_2 - Indico
... RF structure perturbs the accelerating field configuration and leaves a wake field behind. A following (test) particle will experience a transverse field proportional to the displacement and to the charge of the source particle: L=period of the structure W= wake function, depends on the delay betwee ...
... RF structure perturbs the accelerating field configuration and leaves a wake field behind. A following (test) particle will experience a transverse field proportional to the displacement and to the charge of the source particle: L=period of the structure W= wake function, depends on the delay betwee ...
Direct photon production in heavy-ion collisions
... At low pT the predicted D/B (electron) suppression is smaller than the one for light particles At pT > 40 GeV they become comparable. (Residual matching model dependence) LHC is critical to cover the pT range needed for b-quark, Bmeson dynamics ...
... At low pT the predicted D/B (electron) suppression is smaller than the one for light particles At pT > 40 GeV they become comparable. (Residual matching model dependence) LHC is critical to cover the pT range needed for b-quark, Bmeson dynamics ...
New Approach to Supernova Simulations - GSI
... Neutrinos have finite mass, helicity Parity violation on the largest scale Net excess of neutrinos emitted along “North ...
... Neutrinos have finite mass, helicity Parity violation on the largest scale Net excess of neutrinos emitted along “North ...
Classical field theory
... The quantities pi are called generalized momenta. Imposing the boundary condition (1.3) so that δqi (t1 ) = δqi (t2 ) = 0, the last term in (1.12) vanishes. Thus the requirement that the action be stationary with respect to variations of the coordinate functions yields the Euler-Lagrange equations ( ...
... The quantities pi are called generalized momenta. Imposing the boundary condition (1.3) so that δqi (t1 ) = δqi (t2 ) = 0, the last term in (1.12) vanishes. Thus the requirement that the action be stationary with respect to variations of the coordinate functions yields the Euler-Lagrange equations ( ...
15. GRAND UNIFIED THEORIES 15. Grand Unified Theories 15.1. Grand Unification 1
... SU(3)C × SU(2)L × U(1)Y , and why 3 families of quarks and leptons? Moreover, why does one family consist of the states [Q, uc , dc ; L, ec ] transforming as [(3, 2, 1/3), (3̄, 1, −4/3), (3̄, 1, 2/3); (1, 2, −1), (1, 1, 2)], where Q = (u, d), and L = (ν, e) are SU(2)L doublets, and uc , dc , ec are ...
... SU(3)C × SU(2)L × U(1)Y , and why 3 families of quarks and leptons? Moreover, why does one family consist of the states [Q, uc , dc ; L, ec ] transforming as [(3, 2, 1/3), (3̄, 1, −4/3), (3̄, 1, 2/3); (1, 2, −1), (1, 1, 2)], where Q = (u, d), and L = (ν, e) are SU(2)L doublets, and uc , dc , ec are ...
9 Dynamics of Single Aerosol Particles
... THE MEAN FREE PATH As we begin our study of the dynamics of aerosols in a fluid (e.g., air), we would like to determine, from the perspective of transport processes, how the fluid "views" the particle or equivalently how the particle "views" the fluid that surrounds it. On the microscopic scale flui ...
... THE MEAN FREE PATH As we begin our study of the dynamics of aerosols in a fluid (e.g., air), we would like to determine, from the perspective of transport processes, how the fluid "views" the particle or equivalently how the particle "views" the fluid that surrounds it. On the microscopic scale flui ...
Exploring the fundamental properties of matter with
... est that this picture is far too simple. Countless other gluons and a “sea” of i-quarks pop in and out of existence within each hadron. ...
... est that this picture is far too simple. Countless other gluons and a “sea” of i-quarks pop in and out of existence within each hadron. ...
Whites and Wu - Keith W. Whites - South Dakota School of Mines
... The dielectric reduction afforded by interacting particle edges and corners reported in the last section is an intriguing phenomenon and one that, to our knowledge, has not been previously recorded in the literature. To provide additional evidence for this phenomenon, we have constructed the measure ...
... The dielectric reduction afforded by interacting particle edges and corners reported in the last section is an intriguing phenomenon and one that, to our knowledge, has not been previously recorded in the literature. To provide additional evidence for this phenomenon, we have constructed the measure ...
An Integration of General Relativity and Relativistic Quantum
... operator L in linear vector space of fundamental operators, L = aiLi , i = 1, 2, … with closure L|a> = |b> Assume that the Li form a non-commutative algebra of fundamental actions [Li , Lj] = cijk Lk. and which is (normally) a Lie algebra. Thus |a> must be a representation space of this algebra wher ...
... operator L in linear vector space of fundamental operators, L = aiLi , i = 1, 2, … with closure L|a> = |b> Assume that the Li form a non-commutative algebra of fundamental actions [Li , Lj] = cijk Lk. and which is (normally) a Lie algebra. Thus |a> must be a representation space of this algebra wher ...
Permission to make digital or hard copies of all or part of this work
... quantum theory of fields1 that realizes the merging of quantum physics and restricted relativity. The study of the universe as a whole is the objective of cosmology, a domain that, until recently, belonged rather to philosophy than to science. It is not the least merit of 20th century physics to hav ...
... quantum theory of fields1 that realizes the merging of quantum physics and restricted relativity. The study of the universe as a whole is the objective of cosmology, a domain that, until recently, belonged rather to philosophy than to science. It is not the least merit of 20th century physics to hav ...
Charging of Dust Particles in Magnetic Field
... becomes smaller than that in the absence of magnetic field due to the Lorentz force, indicating the absorption cross-section larger. In order to investigate the parameter dependence of the electrostatic force and the magnetic field on the electron orbits, the closest radius of an electron is approxi ...
... becomes smaller than that in the absence of magnetic field due to the Lorentz force, indicating the absorption cross-section larger. In order to investigate the parameter dependence of the electrostatic force and the magnetic field on the electron orbits, the closest radius of an electron is approxi ...
retention time =1
... for his assistance on the farm, to Chris Keller for his advice on using dye tracers, and to James Carleton for providing suggestions on investigating reaction rates. This study would not have been possible without funding from the Ohio Agricultural and Research Development Center and generous donati ...
... for his assistance on the farm, to Chris Keller for his advice on using dye tracers, and to James Carleton for providing suggestions on investigating reaction rates. This study would not have been possible without funding from the Ohio Agricultural and Research Development Center and generous donati ...
Definition of Plasma
... will give a more rigorous one. Plasma is often called the fourth state of matter. The various states of matter occur as a substance is heated to temperatures corresponding to thermal energies above the binding energies for particular state of matter. Structured systems placed in a sufficiently hot e ...
... will give a more rigorous one. Plasma is often called the fourth state of matter. The various states of matter occur as a substance is heated to temperatures corresponding to thermal energies above the binding energies for particular state of matter. Structured systems placed in a sufficiently hot e ...
pptx,6Mb - ITEP Lattice Group
... Dynamical decay of chirality observed • Larger volumes to see exponential growth? • Exactly chiral fermions? • Effect of quantum fluctuations (initial ...
... Dynamical decay of chirality observed • Larger volumes to see exponential growth? • Exactly chiral fermions? • Effect of quantum fluctuations (initial ...
Standard Model
The Standard Model of particle physics is a theory concerning the electromagnetic, weak, and strong nuclear interactions, as well as classifying all the subatomic particles known. It was developed throughout the latter half of the 20th century, as a collaborative effort of scientists around the world. The current formulation was finalized in the mid-1970s upon experimental confirmation of the existence of quarks. Since then, discoveries of the top quark (1995), the tau neutrino (2000), and more recently the Higgs boson (2013), have given further credence to the Standard Model. Because of its success in explaining a wide variety of experimental results, the Standard Model is sometimes regarded as a ""theory of almost everything"".Although the Standard Model is believed to be theoretically self-consistent and has demonstrated huge and continued successes in providing experimental predictions, it does leave some phenomena unexplained and it falls short of being a complete theory of fundamental interactions. It does not incorporate the full theory of gravitation as described by general relativity, or account for the accelerating expansion of the universe (as possibly described by dark energy). The model does not contain any viable dark matter particle that possesses all of the required properties deduced from observational cosmology. It also does not incorporate neutrino oscillations (and their non-zero masses).The development of the Standard Model was driven by theoretical and experimental particle physicists alike. For theorists, the Standard Model is a paradigm of a quantum field theory, which exhibits a wide range of physics including spontaneous symmetry breaking, anomalies, non-perturbative behavior, etc. It is used as a basis for building more exotic models that incorporate hypothetical particles, extra dimensions, and elaborate symmetries (such as supersymmetry) in an attempt to explain experimental results at variance with the Standard Model, such as the existence of dark matter and neutrino oscillations.