JPD@Muon potential
... • Multi-detectors supporting broad physics communities • Large time (15 ms) between bunch crossings ...
... • Multi-detectors supporting broad physics communities • Large time (15 ms) between bunch crossings ...
Handout
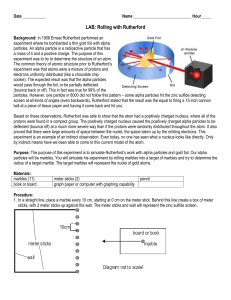
... Based on these observations, Rutherford was able to show that the atom had a positively charged nucleus, where all of the protons were found in a compact group. The positively charged nucleus caused the positively charged alpha particles to be deflected (bounce off) at a much more severe way than if ...
... Based on these observations, Rutherford was able to show that the atom had a positively charged nucleus, where all of the protons were found in a compact group. The positively charged nucleus caused the positively charged alpha particles to be deflected (bounce off) at a much more severe way than if ...
What is mass?
... Some may claim that matter is anything that occupies space and has rest mass. Under this definition one will not consider photons – particles of light – as particles of matter, because they are massless. For the same reason they do not consider as matter the electromagnetic field. It is not quite cl ...
... Some may claim that matter is anything that occupies space and has rest mass. Under this definition one will not consider photons – particles of light – as particles of matter, because they are massless. For the same reason they do not consider as matter the electromagnetic field. It is not quite cl ...
VIII
... becomes smaller than critical for some reason, the repelling forces between particles become too small to prevent their sticking together. For most soles the critical value of -potential is around 30 mV, under which the aggregative stability is lost. Electro kinetic potential is always a part of th ...
... becomes smaller than critical for some reason, the repelling forces between particles become too small to prevent their sticking together. For most soles the critical value of -potential is around 30 mV, under which the aggregative stability is lost. Electro kinetic potential is always a part of th ...
Document
... present limit from the CHOOZ experiment, expected sensitivity from the MINOS experiment, 0.75 MW JHF to super Kamiokande with an off-axis narrow-band beam, Superbeam: 4 MW CERN-SPL to a 400 kton water Cerenkov in Fréjus from a Neutrino Factory with 40 kton large magnetic detector. INCLUDING SYSTEMAT ...
... present limit from the CHOOZ experiment, expected sensitivity from the MINOS experiment, 0.75 MW JHF to super Kamiokande with an off-axis narrow-band beam, Superbeam: 4 MW CERN-SPL to a 400 kton water Cerenkov in Fréjus from a Neutrino Factory with 40 kton large magnetic detector. INCLUDING SYSTEMAT ...
Baryon femtoscopy considering residual correlations as a tool to
... These proceedings are based on [1] where all the relevant details may be found. Femtoscopy, the study of particle-correlations at low relative momentum, is a powerful tool extensively used in heavy-ion, proton-nucleus and proton-proton collisions. Such correlations arise due to Quantum Statistics (i ...
... These proceedings are based on [1] where all the relevant details may be found. Femtoscopy, the study of particle-correlations at low relative momentum, is a powerful tool extensively used in heavy-ion, proton-nucleus and proton-proton collisions. Such correlations arise due to Quantum Statistics (i ...
Atomic Structure
... multiple proportions. This law states that if two elements form more than one compound between them, then the ratios of the masses of the second element that combine with a fixed mass of the first element will be ratios of small whole numbers. ...
... multiple proportions. This law states that if two elements form more than one compound between them, then the ratios of the masses of the second element that combine with a fixed mass of the first element will be ratios of small whole numbers. ...
Atomic Structure
... multiple proportions. This law states that if two elements form more than one compound between them, then the ratios of the masses of the second element that combine with a fixed mass of the first element will be ratios of small whole numbers. ...
... multiple proportions. This law states that if two elements form more than one compound between them, then the ratios of the masses of the second element that combine with a fixed mass of the first element will be ratios of small whole numbers. ...
Microsoft Word Format - University of Toronto Physics
... The goal of particle physics is to understand the basic building blocks of the universe and how they interact. We currently believe that the basic constituents are quarks and leptons, and these fundamental fermions interact via forces mediated by gauge bosons corresponding to fundamental symmetries ...
... The goal of particle physics is to understand the basic building blocks of the universe and how they interact. We currently believe that the basic constituents are quarks and leptons, and these fundamental fermions interact via forces mediated by gauge bosons corresponding to fundamental symmetries ...
Chapter 6 Stability of Colloidal Suspensions
... integration for the case of a semi-infinite solid and a point. Equation (6.4) reduces in this case to one single volume integral, over the semi-infinite body. If we indicate with d the distance between the point (named 1) and the surface of the semi-infinite body, and we define a coordinate system w ...
... integration for the case of a semi-infinite solid and a point. Equation (6.4) reduces in this case to one single volume integral, over the semi-infinite body. If we indicate with d the distance between the point (named 1) and the surface of the semi-infinite body, and we define a coordinate system w ...
Document
... Computational Methods in Particle Physics: On-Shell Methods in Field Theory, Zurich, Jan 31–Feb 14, 2007 ...
... Computational Methods in Particle Physics: On-Shell Methods in Field Theory, Zurich, Jan 31–Feb 14, 2007 ...
Dynamic light scattering and application to proteins in solutions
... To interpret light scattering experiments, we begin with a discussion of light scattering theories. Classical light scattering theory was derived by Lord Rayleigh and is now called Rayleigh theory. Rayleigh developed theory for particles much smaller than the wavelength of light (tipically we take s ...
... To interpret light scattering experiments, we begin with a discussion of light scattering theories. Classical light scattering theory was derived by Lord Rayleigh and is now called Rayleigh theory. Rayleigh developed theory for particles much smaller than the wavelength of light (tipically we take s ...
Radioactivity from last time…
... The half-life of 14C is 5,730 years. What is the approximate age of the fossil? ...
... The half-life of 14C is 5,730 years. What is the approximate age of the fossil? ...
physics/9902034 PDF
... ether till his death. Even today there are physicists who still question the foundations of special relativity (ref. 23). Some of the most disturbing results from SR include the abolishment of the ether and the relative nature of 4D space-time. In SR, it still is not understood why our universe has ...
... ether till his death. Even today there are physicists who still question the foundations of special relativity (ref. 23). Some of the most disturbing results from SR include the abolishment of the ether and the relative nature of 4D space-time. In SR, it still is not understood why our universe has ...
Parity Violation in Chiral Molecules
... distinguished by the indices 1, 2, and 3. To every elementary particle, there exists a corresponding anti-particle which has the same spin and mass (within CPT symmetry) but opposite electric charge. It is common to collect the elementary particles in families: the first family (second column in Tab ...
... distinguished by the indices 1, 2, and 3. To every elementary particle, there exists a corresponding anti-particle which has the same spin and mass (within CPT symmetry) but opposite electric charge. It is common to collect the elementary particles in families: the first family (second column in Tab ...
Aspects of Heavy-Ion Collisions with the FOPI detector at SIS Energies
... – Pion spectra provides an information of the Coulomb interaction and the modification of the delta-spectral function. – Kaon yields and spectra favor the in-medium modification of kaon masses (it also favors a soft EoS). ...
... – Pion spectra provides an information of the Coulomb interaction and the modification of the delta-spectral function. – Kaon yields and spectra favor the in-medium modification of kaon masses (it also favors a soft EoS). ...
Uses Of Electrostatics
... What is EDS? Electrostatic discharge (ESD) is the release of static electricity when two objects come into contact. Familiar examples of ESD include the shock we receive when we walk across a carpet and touch a metal doorknob and the static electricity we feel after drying clothes in clothes dryer. ...
... What is EDS? Electrostatic discharge (ESD) is the release of static electricity when two objects come into contact. Familiar examples of ESD include the shock we receive when we walk across a carpet and touch a metal doorknob and the static electricity we feel after drying clothes in clothes dryer. ...
Fish mouths as engineering structures for vortical cross-step filtration ARTICLE S. Laurie Sanderson
... identical dimensions for the gape, total mesh area and mesh pore size. Removal of 2.8% of the mesh from the standard crossflow model (Fig. 5c,d) caused a significant reduction of 21.0% in the dry mass of particles retained (Fig. 5e; two-way ANOVA with Tukey’s post-hoc test; Po0.0001; n ¼ 5 models for ...
... identical dimensions for the gape, total mesh area and mesh pore size. Removal of 2.8% of the mesh from the standard crossflow model (Fig. 5c,d) caused a significant reduction of 21.0% in the dry mass of particles retained (Fig. 5e; two-way ANOVA with Tukey’s post-hoc test; Po0.0001; n ¼ 5 models for ...
Standard Model
The Standard Model of particle physics is a theory concerning the electromagnetic, weak, and strong nuclear interactions, as well as classifying all the subatomic particles known. It was developed throughout the latter half of the 20th century, as a collaborative effort of scientists around the world. The current formulation was finalized in the mid-1970s upon experimental confirmation of the existence of quarks. Since then, discoveries of the top quark (1995), the tau neutrino (2000), and more recently the Higgs boson (2013), have given further credence to the Standard Model. Because of its success in explaining a wide variety of experimental results, the Standard Model is sometimes regarded as a ""theory of almost everything"".Although the Standard Model is believed to be theoretically self-consistent and has demonstrated huge and continued successes in providing experimental predictions, it does leave some phenomena unexplained and it falls short of being a complete theory of fundamental interactions. It does not incorporate the full theory of gravitation as described by general relativity, or account for the accelerating expansion of the universe (as possibly described by dark energy). The model does not contain any viable dark matter particle that possesses all of the required properties deduced from observational cosmology. It also does not incorporate neutrino oscillations (and their non-zero masses).The development of the Standard Model was driven by theoretical and experimental particle physicists alike. For theorists, the Standard Model is a paradigm of a quantum field theory, which exhibits a wide range of physics including spontaneous symmetry breaking, anomalies, non-perturbative behavior, etc. It is used as a basis for building more exotic models that incorporate hypothetical particles, extra dimensions, and elaborate symmetries (such as supersymmetry) in an attempt to explain experimental results at variance with the Standard Model, such as the existence of dark matter and neutrino oscillations.




![Assemblage: Exercises in Statistical Mechanics ====== [A] Ensemble Theory - classical gases](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/008930193_1-b370c417d56cac9a0859542b76e2a6e4-300x300.png)