9 free IB Chem labs (sent to OCC) - VicPark-IBRoundtable-2009
... 6. When you are ready with the stopwatch and the tubing, place the Mg inside the flask. Immediately start timing, cover the flask with the bung and hold the tubing inside the cylinder. 2 people should be operating the apparatus and 1 person should be recording data. 7. Take volume measurements every ...
... 6. When you are ready with the stopwatch and the tubing, place the Mg inside the flask. Immediately start timing, cover the flask with the bung and hold the tubing inside the cylinder. 2 people should be operating the apparatus and 1 person should be recording data. 7. Take volume measurements every ...
No Slide Title
... • Therefore the regime where Butler-Volmer equation is valid is the charge-transfer-limiting regime • Here, most of the driving force is spent in overcoming the activation energy barrier of the charge transfer process • Therefore, the overpotential in this regime is termed activation overpotential • ...
... • Therefore the regime where Butler-Volmer equation is valid is the charge-transfer-limiting regime • Here, most of the driving force is spent in overcoming the activation energy barrier of the charge transfer process • Therefore, the overpotential in this regime is termed activation overpotential • ...
Chapter 19: Phenomena
... If the t2g orbital is closer in energy to the bonding orbital, the two orbitals will interact and the electron in the filled orbitals will enter the lower energy molecular orbital therefore the electrons in the d-metal will have to occupy the higher energy molecular orbital which will decrease the o ...
... If the t2g orbital is closer in energy to the bonding orbital, the two orbitals will interact and the electron in the filled orbitals will enter the lower energy molecular orbital therefore the electrons in the d-metal will have to occupy the higher energy molecular orbital which will decrease the o ...
Uranium solution chemistry
... Net charge 2.43 for UO2(H2O)52+, 3.2 for fluoride systems Net negative 0.43 on oxygens Lewis bases * Can vary with ligand in equatorial plane * Responsible for cation-cation interaction * O=U=O- - -M * Pentavalent U yl oxygens more basic • Small changes in U=O bond distance with variation in equ ...
... Net charge 2.43 for UO2(H2O)52+, 3.2 for fluoride systems Net negative 0.43 on oxygens Lewis bases * Can vary with ligand in equatorial plane * Responsible for cation-cation interaction * O=U=O- - -M * Pentavalent U yl oxygens more basic • Small changes in U=O bond distance with variation in equ ...
Welcome to AP Chemistry! AP Chemistry is
... add the suffix, -ic acid. For example, HBr is hydrobromic acid. 2. Oxyacids contain polyatomic anions such as nitrite, carbonate, etc. To name an acid with an anion ending with the -ite suffix, drop the -ite suffix and add the suffix, -ous acid. For example, HNO2 , would be name as nitrous acid. To ...
... add the suffix, -ic acid. For example, HBr is hydrobromic acid. 2. Oxyacids contain polyatomic anions such as nitrite, carbonate, etc. To name an acid with an anion ending with the -ite suffix, drop the -ite suffix and add the suffix, -ous acid. For example, HNO2 , would be name as nitrous acid. To ...
Chemistry 12 - hrsbstaff.ednet.ns.ca
... 40. What effect does a catalyst have? A. increases the reaction rate by decreasing the heat of reaction B. increases the reaction rate by increasing the activation energy of the reverse reaction C. increases the reaction rate by lowering the activation energy of the forward reaction only D. increase ...
... 40. What effect does a catalyst have? A. increases the reaction rate by decreasing the heat of reaction B. increases the reaction rate by increasing the activation energy of the reverse reaction C. increases the reaction rate by lowering the activation energy of the forward reaction only D. increase ...
Article - Max Planck Institut für Festkörperforschung
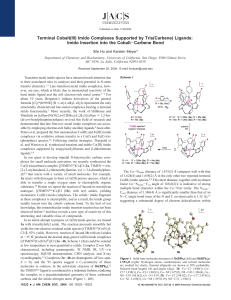
... accounts for deprotonation of carboxylic groups of TMA molecules, which provides three carboxylate ligands per molecule. TMA molecules lie flat on the surface and are resolved as equilateral triangles in STM data.20 As shown in Figure 1a, flower-shaped arrangements where a central protrusion is deco ...
... accounts for deprotonation of carboxylic groups of TMA molecules, which provides three carboxylate ligands per molecule. TMA molecules lie flat on the surface and are resolved as equilateral triangles in STM data.20 As shown in Figure 1a, flower-shaped arrangements where a central protrusion is deco ...
equilibrium - TeacherWeb
... EQUILIBRIUM Le Chatelier’s Principle – If a system at equilibrium is disturbed by a change in temperature, pressure or the concentration of one of the components, the system will shift its equilibrium position so as to counteract the effect of the disturbance. 3 ways that a chemical equilibrium can ...
... EQUILIBRIUM Le Chatelier’s Principle – If a system at equilibrium is disturbed by a change in temperature, pressure or the concentration of one of the components, the system will shift its equilibrium position so as to counteract the effect of the disturbance. 3 ways that a chemical equilibrium can ...
PDF
... soil colloids tends to reduce its concentration in solution (i.e. less than 1% of the copper added to these soils remained in solution). On the other hand, soluble complexing agents compete with adsorption sites for free Cu2+ and thereby prevent its adsorption. Hence complexing is thought to be resp ...
... soil colloids tends to reduce its concentration in solution (i.e. less than 1% of the copper added to these soils remained in solution). On the other hand, soluble complexing agents compete with adsorption sites for free Cu2+ and thereby prevent its adsorption. Hence complexing is thought to be resp ...
Soquids Answers M/C 58. C 68. C 27. E 54. A 21. A 49. C 50. B 51
... Consider three unlabeled bottles, each contain small pieces of one of the following metals. - Magnesium - Sodium - Silver The following reagents are used for identifying the metals. - Pure water - A solution of 1.0 molar HCl - A solution of concentrated HNO3 (a) Which metal can be easily identified ...
... Consider three unlabeled bottles, each contain small pieces of one of the following metals. - Magnesium - Sodium - Silver The following reagents are used for identifying the metals. - Pure water - A solution of 1.0 molar HCl - A solution of concentrated HNO3 (a) Which metal can be easily identified ...
Sabina4_V10 - Universidade de Vigo
... contain bands attributed to d-d transitions of metal atoms (Table S2) in 1b–d and 2c in addition to bands with CT (charge transfer) or IL (intra-ligand) character that are common to all of the complexes. The thermal stability of compounds 1a–d, 2a and 2c was studied by thermogravimetric analysis (Fi ...
... contain bands attributed to d-d transitions of metal atoms (Table S2) in 1b–d and 2c in addition to bands with CT (charge transfer) or IL (intra-ligand) character that are common to all of the complexes. The thermal stability of compounds 1a–d, 2a and 2c was studied by thermogravimetric analysis (Fi ...
Syntheses, spectral characterization, thermal properties and DNA
... ligands L1/L2 or L3 to give the corresponding metal complexes. The elemental analysis data for ligands and complexes is given in Table.1. All the compounds show the analytical results close to the theoretical values indicating the presence of two types of ligands. 3.2. IR Spectra The IR spectral dat ...
... ligands L1/L2 or L3 to give the corresponding metal complexes. The elemental analysis data for ligands and complexes is given in Table.1. All the compounds show the analytical results close to the theoretical values indicating the presence of two types of ligands. 3.2. IR Spectra The IR spectral dat ...
Chemistry 115 Lecture Number Seventeen Test Two Review April 2
... Note from Dr. Sevian: These notes were based on the material covered in Lecture 17, but also augmented from the student’s own notes, so there is much more detail than what was covered in lecture. Thank you to the student [sk] who put together these notes! They are an excellent review to help with pr ...
... Note from Dr. Sevian: These notes were based on the material covered in Lecture 17, but also augmented from the student’s own notes, so there is much more detail than what was covered in lecture. Thank you to the student [sk] who put together these notes! They are an excellent review to help with pr ...
Chapter 24 Chemistry of Coordination Compounds
... Werner proposed putting all molecules and ions within the sphere in brackets and those “free” anions (that dissociate from the complex ion when dissolved in water) outside the brackets. ...
... Werner proposed putting all molecules and ions within the sphere in brackets and those “free” anions (that dissociate from the complex ion when dissolved in water) outside the brackets. ...
Coordination Compounds - Madison Public Schools
... Werner proposed putting all molecules and ions within the sphere in brackets and those “free” anions (that dissociate from the complex ion when dissolved in water) outside the brackets. ...
... Werner proposed putting all molecules and ions within the sphere in brackets and those “free” anions (that dissociate from the complex ion when dissolved in water) outside the brackets. ...