Enzymes & Digestion
... through the wall of the small intestine into the bloodstream (where they are carried around the body to where they are needed) Only small, soluble substances can pass across the wall of the small intestine Large insoluble substances cannot pass through - this is why we need enzymes! ...
... through the wall of the small intestine into the bloodstream (where they are carried around the body to where they are needed) Only small, soluble substances can pass across the wall of the small intestine Large insoluble substances cannot pass through - this is why we need enzymes! ...
Figure from: Martini, Anatomy & Physiology
... Actions of Cholecystokinin (CCK) on Digestion Figure adapted from: Barrett, K., Gastrointestinal Physiology, Lange, ...
... Actions of Cholecystokinin (CCK) on Digestion Figure adapted from: Barrett, K., Gastrointestinal Physiology, Lange, ...
Lab 11 - Digestive Anatomy
... 1. Identify the esophagus in the thoracic cavity. It is directly behind the trachea. Note that it connects to the stomach in the abdominopelvic cavity. 2. Push aside the greater omentum. It is a double membrane filled with fat and serves as a protective cover for the abdominal organs. 3. The small i ...
... 1. Identify the esophagus in the thoracic cavity. It is directly behind the trachea. Note that it connects to the stomach in the abdominopelvic cavity. 2. Push aside the greater omentum. It is a double membrane filled with fat and serves as a protective cover for the abdominal organs. 3. The small i ...
Chapter 2 – Digestion and Absorption
... To digest food, the 13.____________________ glands, stomach, pancreas, liver (via the 14.____________________), and small intestine deliver fluids and digestive 15.____________________. The many 16.____________________ and 17.____________________ of the small intestine dramatically increase its surf ...
... To digest food, the 13.____________________ glands, stomach, pancreas, liver (via the 14.____________________), and small intestine deliver fluids and digestive 15.____________________. The many 16.____________________ and 17.____________________ of the small intestine dramatically increase its surf ...
doc 2012 Digestion Study Guide
... period of the BER. These are coupled to contraction of the stomach. Stimulated by local stretch or Ach. Ca2+ dependent. Spreads from cell to cell myogenically. Interstitial Cells of Cajal – non-neuronal, non-muscle cells located between the muscle layers and enteric plexuses. May be implicated in t ...
... period of the BER. These are coupled to contraction of the stomach. Stimulated by local stretch or Ach. Ca2+ dependent. Spreads from cell to cell myogenically. Interstitial Cells of Cajal – non-neuronal, non-muscle cells located between the muscle layers and enteric plexuses. May be implicated in t ...
Chapter 17
... b. Liver—lies just below the diaphragm on the right side of the body. c. Gallbladder—lies on posterior side of the liver. d. Pancreas—located behind the stomach, attached to the duodenum. 17.2 General Characteristics of the Alimentary Canal 3. Contrast the composition of the four layers in the wall ...
... b. Liver—lies just below the diaphragm on the right side of the body. c. Gallbladder—lies on posterior side of the liver. d. Pancreas—located behind the stomach, attached to the duodenum. 17.2 General Characteristics of the Alimentary Canal 3. Contrast the composition of the four layers in the wall ...
Livestock Evaluation
... As a result of the small size, the rate of flow of feed material in the digestive tract through the stomach is relatively fast. Because gastric emptying is dependent upon volume, large meals can be expected to pass more quickly than feed eaten continuously in small amounts. Studies have shown the ma ...
... As a result of the small size, the rate of flow of feed material in the digestive tract through the stomach is relatively fast. Because gastric emptying is dependent upon volume, large meals can be expected to pass more quickly than feed eaten continuously in small amounts. Studies have shown the ma ...
FUNCTION of the SMALL INTESTINE
... Thin weblike tissue that holds the small intestines together ...
... Thin weblike tissue that holds the small intestines together ...
Digestion
... organic catalysts that speed up the digestive process. Salivary amylase changes starch to ...
... organic catalysts that speed up the digestive process. Salivary amylase changes starch to ...
Peptic Ulcer Basics - Digestive Disease Associates
... The doctor may give you an X-ray test called an upper-GI (gastrointestinal) series. You will be given a contrast liquid to drink called barium, a thick, white, milkshake-like liquid. Barium coats the inside lining of the esophagus, stomach and small intestine, and makes them easier to see clearly on ...
... The doctor may give you an X-ray test called an upper-GI (gastrointestinal) series. You will be given a contrast liquid to drink called barium, a thick, white, milkshake-like liquid. Barium coats the inside lining of the esophagus, stomach and small intestine, and makes them easier to see clearly on ...
Unit B3-1
... HS-LS1-2 Develop and use a model to illustrate the hierarchical organization of interacting systems that provide specific functions within multicellular organisms. [Clarification Statement: Emphasis is on functions at the organism system level such as nutrient uptake, water delivery, and organism mo ...
... HS-LS1-2 Develop and use a model to illustrate the hierarchical organization of interacting systems that provide specific functions within multicellular organisms. [Clarification Statement: Emphasis is on functions at the organism system level such as nutrient uptake, water delivery, and organism mo ...
Large Intestine - cloudfront.net
... Enzymes from the liver, gallbladder, pancreas released to aid digestion – Mechanical digestion: Muscular contractions mix & churn the chyme • Peristalsis pushes the chyme ...
... Enzymes from the liver, gallbladder, pancreas released to aid digestion – Mechanical digestion: Muscular contractions mix & churn the chyme • Peristalsis pushes the chyme ...
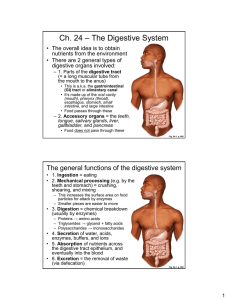
Ch. 24 – The Digestive System
... Functions of saliva: moisten and lubricate food, rinse/flush the mouth, dissolve chemicals for taste bud stimulation, initiate the chemical digestion of complex carbos (by salivary amylase) Composition: saliva is 99.4% water; the rest is solutes, including ions, salivary amylase, buffers (so pH ~ 7. ...
... Functions of saliva: moisten and lubricate food, rinse/flush the mouth, dissolve chemicals for taste bud stimulation, initiate the chemical digestion of complex carbos (by salivary amylase) Composition: saliva is 99.4% water; the rest is solutes, including ions, salivary amylase, buffers (so pH ~ 7. ...
Alkaline Water and Stomach Acid
... water, since tap water is almost neutral. When the stomach pH value gets higher than 4, the stomach knows what to do to lower it. However, if the pH value goes below 4, for any reason, the stomach doesn't know what to do. That's why we take Alka-Seltzer, which is alkaline, to relieve acidic stomach ...
... water, since tap water is almost neutral. When the stomach pH value gets higher than 4, the stomach knows what to do to lower it. However, if the pH value goes below 4, for any reason, the stomach doesn't know what to do. That's why we take Alka-Seltzer, which is alkaline, to relieve acidic stomach ...
Ch. 41 - Ltcconline.net
... b. enzymes trypsin and chymotripsin split polypeptides into smaller chains after pepsin starts the process c. aminopeptidase and carboxypeptidase split off one amino acid at a time, working from the ends of the polypeptides. d. dipeptidase hydrolyzes fragments only 2 or 3 aminos long e. they all wor ...
... b. enzymes trypsin and chymotripsin split polypeptides into smaller chains after pepsin starts the process c. aminopeptidase and carboxypeptidase split off one amino acid at a time, working from the ends of the polypeptides. d. dipeptidase hydrolyzes fragments only 2 or 3 aminos long e. they all wor ...
Frog External Anatomy
... object that serves as a holding area for blood, where harmful particles can be filtered out for the immune system. • Esophagus--where the stomach gets smaller at the bottom of the esophagus. The esophagus is the tube that leads from the frog’s mouth to the stomach. Stomach & Intestine The texture an ...
... object that serves as a holding area for blood, where harmful particles can be filtered out for the immune system. • Esophagus--where the stomach gets smaller at the bottom of the esophagus. The esophagus is the tube that leads from the frog’s mouth to the stomach. Stomach & Intestine The texture an ...
B. Feeding, digestion, nutrition
... simple molecules involves use of acids, enzymes Absorption - taking molecules into blood diffusion into mucosal cells phagocytosis/pinocytosis by mucosal ...
... simple molecules involves use of acids, enzymes Absorption - taking molecules into blood diffusion into mucosal cells phagocytosis/pinocytosis by mucosal ...
Digestive system notes http://www
... anus - the opening at the end of the digestive system from which feces exit the body. appendix - a small sac located near the start of the large intestine. esophagus - the long tube between the mouth and the stomach. It uses rhythmic muscle movements (called peristalsis) to force food from the throa ...
... anus - the opening at the end of the digestive system from which feces exit the body. appendix - a small sac located near the start of the large intestine. esophagus - the long tube between the mouth and the stomach. It uses rhythmic muscle movements (called peristalsis) to force food from the throa ...
PowerPoint
... HS-LS1-2 Develop and use a model to illustrate the hierarchical organization of interacting systems that provide specific functions within multicellular organisms. [Clarification Statement: Emphasis is on functions at the organism system level such as nutrient uptake, water delivery, and organism mo ...
... HS-LS1-2 Develop and use a model to illustrate the hierarchical organization of interacting systems that provide specific functions within multicellular organisms. [Clarification Statement: Emphasis is on functions at the organism system level such as nutrient uptake, water delivery, and organism mo ...
14_01aLectureNotes
... Two important nerve plexuses serve the alimentary canal Both are part of the autonomic nervous system ...
... Two important nerve plexuses serve the alimentary canal Both are part of the autonomic nervous system ...
Digestive System
... – “Mixing bowl” that receives chyme from stomach and digestive secretions from pancreas and liver – Neutralizes acids before they can damage the absorptive surfaces of the small intestine ...
... – “Mixing bowl” that receives chyme from stomach and digestive secretions from pancreas and liver – Neutralizes acids before they can damage the absorptive surfaces of the small intestine ...
4. Auricular Points for lose weight
... Points for Losing Weight Clinically, most patients’ hungry feeling can be reduced by pressing the ear points before meals or when feel hungry. With the treatment the patients feel relaxed in the body and the weight can be reduced. The practice proves that to lose weight with ear-therapy is a simple ...
... Points for Losing Weight Clinically, most patients’ hungry feeling can be reduced by pressing the ear points before meals or when feel hungry. With the treatment the patients feel relaxed in the body and the weight can be reduced. The practice proves that to lose weight with ear-therapy is a simple ...
The Digestive System - Valhalla High School
... the rest of the S.I., they begin to be absorbed into the blood stream. Absorption is carried out by special finger-like extensions in the walls of the S.I. called villi. The villi’s shape greatly increases the surface area of the S.I., allowing it to absorb nutrients at a much faster rate. By the ti ...
... the rest of the S.I., they begin to be absorbed into the blood stream. Absorption is carried out by special finger-like extensions in the walls of the S.I. called villi. The villi’s shape greatly increases the surface area of the S.I., allowing it to absorb nutrients at a much faster rate. By the ti ...