Chapter 9 Fueling the Functions: The Digestive System
... Whereas the respiratory tract is a two-way street — oxygen flows in and carbon dioxide flows out — the digestive tract is designed to have a one-way flow (although when you’re sick or your body detects something bad in the food you’ve eaten, what goes down sometimes comes ...
... Whereas the respiratory tract is a two-way street — oxygen flows in and carbon dioxide flows out — the digestive tract is designed to have a one-way flow (although when you’re sick or your body detects something bad in the food you’ve eaten, what goes down sometimes comes ...
Histology of GIT I
... Duodenum- The first part of the small intestine which has ducts (tubes) leading into it from the liver/gall bladder and pancreas. Bile and pancreatic enzymes are mixed with food here. Jejuno-ileum- All the small intestine except for the duodenum. Digestion of food is completed here and nutrients are ...
... Duodenum- The first part of the small intestine which has ducts (tubes) leading into it from the liver/gall bladder and pancreas. Bile and pancreatic enzymes are mixed with food here. Jejuno-ileum- All the small intestine except for the duodenum. Digestion of food is completed here and nutrients are ...
Nutrition for Patients with GIST
... – Nutrient maldigestion and other fat soluble vitamin deficiency • 70% - 100% develop some enzyme deficiency (partial vs total gastrectomy) • May or may not be symptomatic Radigan, A. (2004). Post-Gastrectomy: Managing the Nutrition Fall-Out. Practical Gastroenterology, series #18 Smith, B. (2008). ...
... – Nutrient maldigestion and other fat soluble vitamin deficiency • 70% - 100% develop some enzyme deficiency (partial vs total gastrectomy) • May or may not be symptomatic Radigan, A. (2004). Post-Gastrectomy: Managing the Nutrition Fall-Out. Practical Gastroenterology, series #18 Smith, B. (2008). ...
ileum
... The ileum enters the cecum obliquely, and partially invaginates into it, forming the ileocecal valve-consists of two folds, probably delays flow of ileal contents into large intestine A opening of appendix ...
... The ileum enters the cecum obliquely, and partially invaginates into it, forming the ileocecal valve-consists of two folds, probably delays flow of ileal contents into large intestine A opening of appendix ...
Class – XI Biology Chapter – 16 Human
... (a) Villi are finger like structures that absorb the nutrients from digested food in the intestine. The main function of villi is to absorption of nutrients so they are present in small intestine as this is the place where absorption of food takes place. Villi is not present in stomach because the f ...
... (a) Villi are finger like structures that absorb the nutrients from digested food in the intestine. The main function of villi is to absorption of nutrients so they are present in small intestine as this is the place where absorption of food takes place. Villi is not present in stomach because the f ...
Abdominal Viscera
... Pylorus: terminal portion with thickened walls and sphincter opening into the ...
... Pylorus: terminal portion with thickened walls and sphincter opening into the ...
The Digestive System Quiz
... __H___ 10. Small intestine enlargement of the alimentary canal linking the esophagus to the small intestine. __F__ 11. Stomach G) A large organ in the body that stores and metabolizes nutrients destroys toxins and produces bile. ...
... __H___ 10. Small intestine enlargement of the alimentary canal linking the esophagus to the small intestine. __F__ 11. Stomach G) A large organ in the body that stores and metabolizes nutrients destroys toxins and produces bile. ...
Lecture
... • four classes of essential nutrients • 1. essential amino acids: 20 amino acids required by animals to make proteins – most animals have the enzymes required to make half of these – the other half must be taken in through their food – adult humans require 8 amino acids in their diet (infants requir ...
... • four classes of essential nutrients • 1. essential amino acids: 20 amino acids required by animals to make proteins – most animals have the enzymes required to make half of these – the other half must be taken in through their food – adult humans require 8 amino acids in their diet (infants requir ...
Review for Unit Test: The Digestive System
... 8. Be able to label a diagram of an earthworm. Know the function of each of the major parts of the earthworm. 9. Know the six types of nutrients required by the human body. For each nutrient: a) state whether or not it needs to be digested in order to be absorbed b) if it is digested, what are its b ...
... 8. Be able to label a diagram of an earthworm. Know the function of each of the major parts of the earthworm. 9. Know the six types of nutrients required by the human body. For each nutrient: a) state whether or not it needs to be digested in order to be absorbed b) if it is digested, what are its b ...
NIGERIAN VETERINARY JOURNAL
... gastrointestinal tract of the Striped Sand Snake (Psammophis sibilans). Ten snakes (five males and five females) were euthanized and dissected for the study. The gastrointestinal tract appeared as a straight tubular organ from oral cavity to cloaca, owning to the absence of a cecum. The stomach coul ...
... gastrointestinal tract of the Striped Sand Snake (Psammophis sibilans). Ten snakes (five males and five females) were euthanized and dissected for the study. The gastrointestinal tract appeared as a straight tubular organ from oral cavity to cloaca, owning to the absence of a cecum. The stomach coul ...
7b Dig Sy II - Gastro Processes
... into the stomach as zymogens (extra long, inactive polypeptide chains) • Pepsin – an active protein digesting enzyme (converted from pepsinogen through action of HCl and active pepsin) • Rennin (chymosin)– works on digesting milk casein protein in infants The only absorption that occurs in the sto ...
... into the stomach as zymogens (extra long, inactive polypeptide chains) • Pepsin – an active protein digesting enzyme (converted from pepsinogen through action of HCl and active pepsin) • Rennin (chymosin)– works on digesting milk casein protein in infants The only absorption that occurs in the sto ...
Digestive System Notes - Full Version
... 4. Large Intestine 1. Removes water, completes absorption, and manufacture certain vitamins 2. Frames the small intestine; is less than half as long (5 ft.); 2.5” in diameter 3. Haustra – (singular haustrum) of the colon are the small pouches caused by sacculation, which give the colon its segmented ...
... 4. Large Intestine 1. Removes water, completes absorption, and manufacture certain vitamins 2. Frames the small intestine; is less than half as long (5 ft.); 2.5” in diameter 3. Haustra – (singular haustrum) of the colon are the small pouches caused by sacculation, which give the colon its segmented ...
Nasogastric Intubation
... – pH > 6 = may be in lung or pleural space; could be in stomach if patient takes antacids or some medications ...
... – pH > 6 = may be in lung or pleural space; could be in stomach if patient takes antacids or some medications ...
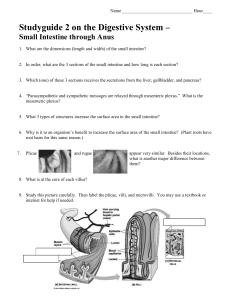
Studyguide 2 on the Digestive System
... 29. Make a diagram listing the following structures and showing how the blood flows in and out of the liver. Use arrows ( ) and the following terms but no pictures in your diagram: descending aorta, hepatic artery, branch of the hepatic artery, hepatic portal vein, branch of the hepatic portal vei ...
... 29. Make a diagram listing the following structures and showing how the blood flows in and out of the liver. Use arrows ( ) and the following terms but no pictures in your diagram: descending aorta, hepatic artery, branch of the hepatic artery, hepatic portal vein, branch of the hepatic portal vei ...
Nerve activates contraction
... • It’s just a 5 Guys cheeseburger • You could eat 2 servings to get your total calories • But would that be balanced? • How much fat? • How much protein? • How many carbs? • How much Vitamin A? • If you ate this, what else should you eat that day? ...
... • It’s just a 5 Guys cheeseburger • You could eat 2 servings to get your total calories • But would that be balanced? • How much fat? • How much protein? • How many carbs? • How much Vitamin A? • If you ate this, what else should you eat that day? ...
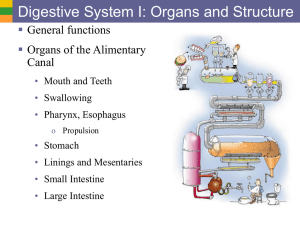
7a DigSys Ia- Organs and Structure
... • Mouth and Teeth • Swallowing • Pharynx, Esophagus o Propulsion ...
... • Mouth and Teeth • Swallowing • Pharynx, Esophagus o Propulsion ...
The structure of Kidney
... Fatty acids and glycerol combined to form fats again in the intestinal epithelium. These fats then pass into the lymphatic system which forms a network all over the body and eventually emptiesits contents into the bloodstream. ...
... Fatty acids and glycerol combined to form fats again in the intestinal epithelium. These fats then pass into the lymphatic system which forms a network all over the body and eventually emptiesits contents into the bloodstream. ...
Chapter 17 - Digestive System
... Bile salts emulsify fats into smaller droplets and aid in the absorption of fatty acids, cholesterol, and certain vitamins. 15.9 Small Intestine (p. 411) A. The lengthy small intestine receives secretions from the pancreas and liver, completes digestion of the nutrients in chyme, absorbs the product ...
... Bile salts emulsify fats into smaller droplets and aid in the absorption of fatty acids, cholesterol, and certain vitamins. 15.9 Small Intestine (p. 411) A. The lengthy small intestine receives secretions from the pancreas and liver, completes digestion of the nutrients in chyme, absorbs the product ...
14 Digestive System - Crestwood Local Schools
... Gastric pits formed by folded mucosa Glands and specialized cells are in the gastric gland region ...
... Gastric pits formed by folded mucosa Glands and specialized cells are in the gastric gland region ...
Learning Targets Explain the importance of enzymes to metabolism
... ● Produces digestive enzymes that are released into the duodenum. ○ Pancreatic amylase (breakdown of carbs.) ○ Trypsin (breakdown of proteins) ○ Lipase (breakdown of lipids) ...
... ● Produces digestive enzymes that are released into the duodenum. ○ Pancreatic amylase (breakdown of carbs.) ○ Trypsin (breakdown of proteins) ○ Lipase (breakdown of lipids) ...
Answers to WHAT DID YOU LEARN questions
... contrasts with gastric juice in that it is alkaline due to the high percentage of bicarbonate. The bicarbonate acts to neutralize the acidic chyme that enters the duodenum from the stomach. Other components of pancreatic juice include mucin and digestive enzymes. ...
... contrasts with gastric juice in that it is alkaline due to the high percentage of bicarbonate. The bicarbonate acts to neutralize the acidic chyme that enters the duodenum from the stomach. Other components of pancreatic juice include mucin and digestive enzymes. ...
unit_ia_digestion_absorption_human
... 3. Liver plays an important role in synthesis of cholesterol and production of triglycerides. 4. Deamination of proteins occurs in the liver. 5. Liver is the chief organ of detoxification of toxic substances that enter the gut along with food. 6. Liver acts as thermoregulatory organ. 7. Liver acts a ...
... 3. Liver plays an important role in synthesis of cholesterol and production of triglycerides. 4. Deamination of proteins occurs in the liver. 5. Liver is the chief organ of detoxification of toxic substances that enter the gut along with food. 6. Liver acts as thermoregulatory organ. 7. Liver acts a ...
The Digestive System (PowerPoint)
... intestine, receptors in the wall of the intestine provide information to the central nervous system which, in turn, prompts a bowel movement. The bowel movement ensures the removal of potentially toxic wastes from the body. Individuals who do not eat sufficient amounts of cellulose (roughage or fibr ...
... intestine, receptors in the wall of the intestine provide information to the central nervous system which, in turn, prompts a bowel movement. The bowel movement ensures the removal of potentially toxic wastes from the body. Individuals who do not eat sufficient amounts of cellulose (roughage or fibr ...