Lab: Measuring the Monstrous Digestive System
... You feel hungry because your brain receives signals that your cells need energy. But eating is only the beginning of the story. You body mush change a meal into substances that you can use. Your digestive system is a group of organs that work together to digest food so that it can be used by the bod ...
... You feel hungry because your brain receives signals that your cells need energy. But eating is only the beginning of the story. You body mush change a meal into substances that you can use. Your digestive system is a group of organs that work together to digest food so that it can be used by the bod ...
B. True or False/Edit
... ___ 44. The absorption of carbohydrates, lipids, amino acids, calcium, and iron occurs primarily in the duodenum and jejunum of the small intestine. ___ 45. Electron microscopic foldings of the apical plasma membrane of epithelial cells lining the small intestine are called villi. ___ 46. At the bas ...
... ___ 44. The absorption of carbohydrates, lipids, amino acids, calcium, and iron occurs primarily in the duodenum and jejunum of the small intestine. ___ 45. Electron microscopic foldings of the apical plasma membrane of epithelial cells lining the small intestine are called villi. ___ 46. At the bas ...
Human Nutrition Question Bank
... 1. Which substances in the small intestine of humans serve to increase the surface area for absorption? (a.) intestinal glands (b.) villi (c.) pseudopodia (d.) cilia (e.) flagella 2. The chemical digestion of proteins in humans begins in the (a.) mouth (b.) esophagus (c.) stomach (d.) liver (e.) sma ...
... 1. Which substances in the small intestine of humans serve to increase the surface area for absorption? (a.) intestinal glands (b.) villi (c.) pseudopodia (d.) cilia (e.) flagella 2. The chemical digestion of proteins in humans begins in the (a.) mouth (b.) esophagus (c.) stomach (d.) liver (e.) sma ...
Lab 8: Digestive System
... Breaks up food Moves food through the GI tract (Peristalsis) Mixes with digestive enzymes Release of enzymes and hormones for chemical digestion and regulation ...
... Breaks up food Moves food through the GI tract (Peristalsis) Mixes with digestive enzymes Release of enzymes and hormones for chemical digestion and regulation ...
Document
... breaks the starch into molecules called maltose; then an enzyme in the lining of the small intestine (maltase) splits the maltose into glucose molecules that can be absorbed into the blood. Glucose is carried through the bloodstream to the liver, where it is stored or used to provide energy for the ...
... breaks the starch into molecules called maltose; then an enzyme in the lining of the small intestine (maltase) splits the maltose into glucose molecules that can be absorbed into the blood. Glucose is carried through the bloodstream to the liver, where it is stored or used to provide energy for the ...
Chapter 46: Bowel Elimination
... – Infants: small stomach capacity; less secretion of digestive enzymes; rapid peristalsis; lack neuromuscular development so cannot control bowels – Older adults: arteriosclerosis which causes decreased mesenteric blood flow, decreasing absorption in small intestine; decrease in peristalsis; loose m ...
... – Infants: small stomach capacity; less secretion of digestive enzymes; rapid peristalsis; lack neuromuscular development so cannot control bowels – Older adults: arteriosclerosis which causes decreased mesenteric blood flow, decreasing absorption in small intestine; decrease in peristalsis; loose m ...
19 Digestive System Mt SAC
... needed to absorb vitamin B12, which is needed to make red blood cells. ...
... needed to absorb vitamin B12, which is needed to make red blood cells. ...
The Digestive System
... food into a soft pulp that is easy to swallow. – Chewing mixes the food with saliva, from salivary glands around the mouth and face, to make it moist and easy to ...
... food into a soft pulp that is easy to swallow. – Chewing mixes the food with saliva, from salivary glands around the mouth and face, to make it moist and easy to ...
8646EPPO - Arp ISD HOME
... The stomach of non-ruminants is located just beyond the diaphragm on the left side of the body. The “true” stomach has folds in the epithelial lining that creates gastric pits. Glands are located throughout the stomach and secrete digestive fluids into the pits, including hydrochloric acid, pepsin, ...
... The stomach of non-ruminants is located just beyond the diaphragm on the left side of the body. The “true” stomach has folds in the epithelial lining that creates gastric pits. Glands are located throughout the stomach and secrete digestive fluids into the pits, including hydrochloric acid, pepsin, ...
Advances in Environmental Biology (ITM)
... rheumatology,(17) it is needed that this criteria help recognition and treatment of the functional disorders based on signs.(7) Numerous limitations exist for using the criteria based on the signs. In recent years, histology findings determined that there is no difference between the functional and ...
... rheumatology,(17) it is needed that this criteria help recognition and treatment of the functional disorders based on signs.(7) Numerous limitations exist for using the criteria based on the signs. In recent years, histology findings determined that there is no difference between the functional and ...
Digestive System
... journals, summaries, oral reports, and technology-based reports; 130.206(c)(3)(A) in all fields of science, analyze, evaluate, and critique scientific explanations by using empirical evidence, logical reasoning, and experimental and observational testing, including examining all sides of scientific ...
... journals, summaries, oral reports, and technology-based reports; 130.206(c)(3)(A) in all fields of science, analyze, evaluate, and critique scientific explanations by using empirical evidence, logical reasoning, and experimental and observational testing, including examining all sides of scientific ...
PowerPoint lecture - Lower Cape May Regional School District
... blocks for assembling essential body components. • Nutritional guidelines are periodically revised in light of new research. Current guidelines call for most calories to come from complex carbohydrates, rather than simple sugars. They also favor fat and protein sources that are low in saturated and ...
... blocks for assembling essential body components. • Nutritional guidelines are periodically revised in light of new research. Current guidelines call for most calories to come from complex carbohydrates, rather than simple sugars. They also favor fat and protein sources that are low in saturated and ...
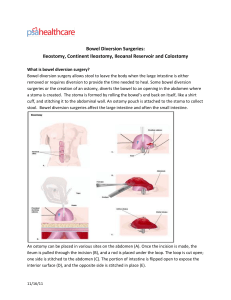
Bowel Diversion Surgeries
... A conventional ileostomy, also called a Brooke ileostomy, a small incision is made through the abdominal wall (usually on the lower right side) to which the cut end of the ileum is sutured. The il ...
... A conventional ileostomy, also called a Brooke ileostomy, a small incision is made through the abdominal wall (usually on the lower right side) to which the cut end of the ileum is sutured. The il ...
Human Digestive System
... lactose, maltose, and glucose are all sugars. A person should consume only about 40 grams of sugar a day. 16. carbohydrates – Carbohydrates are another name for starches. Complex carbs is a term given to starches that have not been processed. Whole grains are an example of complex carbohydrates. Sim ...
... lactose, maltose, and glucose are all sugars. A person should consume only about 40 grams of sugar a day. 16. carbohydrates – Carbohydrates are another name for starches. Complex carbs is a term given to starches that have not been processed. Whole grains are an example of complex carbohydrates. Sim ...
Digestive system
... food into molecules that can be absorbed and utilized by the cells of the body. Food is broken down, bit by bit, until the molecules are small enough to be absorbed and the waste products are eliminated. The digestive tract, also called the alimentary canal or gastrointestinal (GI) tract, consists o ...
... food into molecules that can be absorbed and utilized by the cells of the body. Food is broken down, bit by bit, until the molecules are small enough to be absorbed and the waste products are eliminated. The digestive tract, also called the alimentary canal or gastrointestinal (GI) tract, consists o ...
digestion….
... Digestive Disorders Disorders of the digestive system and its accessory organs include: ...
... Digestive Disorders Disorders of the digestive system and its accessory organs include: ...
Chapter 3 - HCC Learning Web
... The esophageal stage begins when the bolus enters the esophagus. During this stage the peristalsis movers the bolus from the esophagus to the stomach. Table 24.2 summarizes the digestion related activities of the pharynx and ...
... The esophageal stage begins when the bolus enters the esophagus. During this stage the peristalsis movers the bolus from the esophagus to the stomach. Table 24.2 summarizes the digestion related activities of the pharynx and ...
Chapter 6.2 ppt
... Digestive Disorders Disorders of the digestive system and its accessory organs include: ...
... Digestive Disorders Disorders of the digestive system and its accessory organs include: ...
RoseMarie Pierce, B.Sc.Pharm Stomach Acid
... Situations such as illness, stress, very low-salt diets (low chloride), gall bladder removal, chronic use of antacids and acid-reducing drugs, H. pylori infection, as well as normal aging, contribute to insufficient secretion of stomach acid. This process is exacerbated by diets high in red meat, da ...
... Situations such as illness, stress, very low-salt diets (low chloride), gall bladder removal, chronic use of antacids and acid-reducing drugs, H. pylori infection, as well as normal aging, contribute to insufficient secretion of stomach acid. This process is exacerbated by diets high in red meat, da ...
19 Digestive System MtSAC
... needed to absorb vitamin B12, which is needed to make red blood cells. ...
... needed to absorb vitamin B12, which is needed to make red blood cells. ...