FREE Sample Here - We can offer most test bank and
... What might each of these theories say about the infinite possibility of influence? Compare an individual’s influence on his/her environment to the ripples made by a single stone cast into a lake. How then does the lake influence the stone? What other factors might play a role? ...
... What might each of these theories say about the infinite possibility of influence? Compare an individual’s influence on his/her environment to the ripples made by a single stone cast into a lake. How then does the lake influence the stone? What other factors might play a role? ...
Reinforcement Learning Leads to Risk Averse Behavior
... in period t is Exp ( Sy i ,t ) /[∑ Exp ( Sy j ,t )] . ...
... in period t is Exp ( Sy i ,t ) /[∑ Exp ( Sy j ,t )] . ...
AP PSYCH E04
... 2. Students present their approach to a free-response question to the class. This holds students accountable demonstrating the ability to dissect freeresponse questions and for developing an outline to answer the question. The focus is on students’ learning to answer the question asked. 3. Have stu ...
... 2. Students present their approach to a free-response question to the class. This holds students accountable demonstrating the ability to dissect freeresponse questions and for developing an outline to answer the question. The focus is on students’ learning to answer the question asked. 3. Have stu ...
(TSWs) File
... 2. Students present their approach to a free-response question to the class. This holds students accountable demonstrating the ability to dissect freeresponse questions and for developing an outline to answer the question. The focus is on students’ learning to answer the question asked. 3. Have stu ...
... 2. Students present their approach to a free-response question to the class. This holds students accountable demonstrating the ability to dissect freeresponse questions and for developing an outline to answer the question. The focus is on students’ learning to answer the question asked. 3. Have stu ...
Animal Behavior
... will facilitate handling, reduce stress, and improve both handler safety and animal welfare. Large animals can seriously injure handlers and/or themselves if they become excited or agitated. • Stockman, farm manager, animal transporter, and designer of animal houses have to be aware of farm animal b ...
... will facilitate handling, reduce stress, and improve both handler safety and animal welfare. Large animals can seriously injure handlers and/or themselves if they become excited or agitated. • Stockman, farm manager, animal transporter, and designer of animal houses have to be aware of farm animal b ...
Introduction to Learning Theory and Behavioral Psychology
... The researchers first recorded baseline, or normally occurring, frequencies of the behaviors. Then they gave the patients a token every time the proper behavior was performed. The tokens could be exchanged for food and personal items at the hospital drugstore. The patients significantly increased th ...
... The researchers first recorded baseline, or normally occurring, frequencies of the behaviors. Then they gave the patients a token every time the proper behavior was performed. The tokens could be exchanged for food and personal items at the hospital drugstore. The patients significantly increased th ...
Learning - Villanova University
... Operant conditioning B. F. Skinner • The organism behaves in a certain way in order to change the environment » not merely a passive recipient of the conditioned stimulus » behaviors repeat because they have been reinforced » consequence of behavior matters ...
... Operant conditioning B. F. Skinner • The organism behaves in a certain way in order to change the environment » not merely a passive recipient of the conditioned stimulus » behaviors repeat because they have been reinforced » consequence of behavior matters ...
classical conditioning - Warren County Public Schools
... (strengthened) and remembered forever and utilized in future similar situations. This is the basis of the theory known as the law of effect which states behaviors resulting in rewards are strengthened while behaviors that do no result in rewards are weakened. Thorndike described this kind of learnin ...
... (strengthened) and remembered forever and utilized in future similar situations. This is the basis of the theory known as the law of effect which states behaviors resulting in rewards are strengthened while behaviors that do no result in rewards are weakened. Thorndike described this kind of learnin ...
Classical and Operant Conditioning
... Conditioned Stimulus (CS) an initially neutral stimulus that comes to produce a new response because it is associated with the UCS (BELL) Conditioned Response (CR) the response that results due to the association formed between the UCS & the CS (SALIVATION PRODUCED ...
... Conditioned Stimulus (CS) an initially neutral stimulus that comes to produce a new response because it is associated with the UCS (BELL) Conditioned Response (CR) the response that results due to the association formed between the UCS & the CS (SALIVATION PRODUCED ...
1 4.0 learning - eduNEPAL.info
... Reinforcement: The learned behavior will eventually disappear if reinforcement do not arrive, Reinforcement hence, is another primary component of learning. Classical Conditioning Theory of Learning It is a type of conditioning where an individual respond to some stimulus that would not invariably p ...
... Reinforcement: The learned behavior will eventually disappear if reinforcement do not arrive, Reinforcement hence, is another primary component of learning. Classical Conditioning Theory of Learning It is a type of conditioning where an individual respond to some stimulus that would not invariably p ...
MOLECULES and BEHAVIOR
... Instrumental Conditioning • Both Occur Simultaneously • Instrumental (operant) conditioning ResponseReward contingency – but, Stimulus-Reward contingency is also being tracked ...
... Instrumental Conditioning • Both Occur Simultaneously • Instrumental (operant) conditioning ResponseReward contingency – but, Stimulus-Reward contingency is also being tracked ...
Lecture Outline Learning
... Classical Conditioning Issues Q Interstimulus interval (ISI) between CS and UCS is important for conditioning • ISI’s longer than 2 sec produce poor conditioning ...
... Classical Conditioning Issues Q Interstimulus interval (ISI) between CS and UCS is important for conditioning • ISI’s longer than 2 sec produce poor conditioning ...
Chapter 11: Behaviorism (18921956) Detailed Summary Notes New
... ○ It could still be used to determine the processes connecting stimulus and response. Haggerty agreed with Watson that behavior could be reduced to “physical terms” and that consciousness was therefore no longer needed to explain thinking. ● Yerkes did not agree with the idea of discarding the me ...
... ○ It could still be used to determine the processes connecting stimulus and response. Haggerty agreed with Watson that behavior could be reduced to “physical terms” and that consciousness was therefore no longer needed to explain thinking. ● Yerkes did not agree with the idea of discarding the me ...
EXAMINATION REVISION GUIDE FIRST: READ THE UNIT
... the majority of behaviour is learned from the environment after birth. Psychology should investigate the laws and products of learning. Behaviour is determined by the environment, since we are the total of all our past learning experiences, free will is an illusion. Only observable behaviours ...
... the majority of behaviour is learned from the environment after birth. Psychology should investigate the laws and products of learning. Behaviour is determined by the environment, since we are the total of all our past learning experiences, free will is an illusion. Only observable behaviours ...
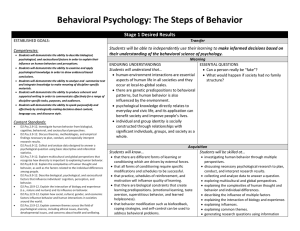
BEHAVIORAL PSYCH The Steps of Behavior
... • human-environment interactions are essential • What would happen if society had no family aspects of human life in all societies and they structure? occur at local-to-global scales. • there are genetic predispositions to behavioral patterns, but human behavior is also influenced by the environment ...
... • human-environment interactions are essential • What would happen if society had no family aspects of human life in all societies and they structure? occur at local-to-global scales. • there are genetic predispositions to behavioral patterns, but human behavior is also influenced by the environment ...
Course 21 - Evaeducation
... attention to others, they will remain focused on themselves. – pampering. Many children are taught, by the actions of others, that they can take without giving. – neglect. They learn inferiority because they are told and shown every day that they are of no value; They learn selfishness because they ...
... attention to others, they will remain focused on themselves. – pampering. Many children are taught, by the actions of others, that they can take without giving. – neglect. They learn inferiority because they are told and shown every day that they are of no value; They learn selfishness because they ...
FREE Sample Here
... What might each of these theories say about the infinite possibility of influence? Compare an individual’s influence on his/her environment to the ripples made by a single stone cast into a lake. How then does the lake influence the stone? What other factors might play a role? ...
... What might each of these theories say about the infinite possibility of influence? Compare an individual’s influence on his/her environment to the ripples made by a single stone cast into a lake. How then does the lake influence the stone? What other factors might play a role? ...
Ch 5 Lab Conditioning
... Situation #4 Johnny has developed a habit of yelling “BYE MOM!” and then slamming the door very loudly in his hurry to leave for school in the morning. The door slam causes his mother to flinch. After several days of the procedure, Johnny’s mother begins to flinch at the sound of her son’s words, ‘ ...
... Situation #4 Johnny has developed a habit of yelling “BYE MOM!” and then slamming the door very loudly in his hurry to leave for school in the morning. The door slam causes his mother to flinch. After several days of the procedure, Johnny’s mother begins to flinch at the sound of her son’s words, ‘ ...
Learning Notes I think this is a fun lesson! Anyone with
... B.F. Skinner proposed the theory of operant conditioning (instrumental conditioning), a form of learning in which the consequences of behavior produce changes in behavior. A reward of some kind will increase a behavior; a punishment will reduce a behavior. The subject (person, pet, etc.) can CHOOSE ...
... B.F. Skinner proposed the theory of operant conditioning (instrumental conditioning), a form of learning in which the consequences of behavior produce changes in behavior. A reward of some kind will increase a behavior; a punishment will reduce a behavior. The subject (person, pet, etc.) can CHOOSE ...
Media:oreilly_genpsych_midterm1_study
... There is only a consensus among those who choose to believe in the power of reproducible scientific experiments and the data they generate, to establish certain facts, that we can then generally accept, even if we can’t all quite agree ...
... There is only a consensus among those who choose to believe in the power of reproducible scientific experiments and the data they generate, to establish certain facts, that we can then generally accept, even if we can’t all quite agree ...
CNCR Mouse Behavior Course
... regard to psychopathology models. Behavioral methods need to be complemented by electrophysiological and autonomic techniques for an improved understanding of underlying mechanisms. The importance of the use of a broader method spectrum and experimental limitations will be discussed in the course. B ...
... regard to psychopathology models. Behavioral methods need to be complemented by electrophysiological and autonomic techniques for an improved understanding of underlying mechanisms. The importance of the use of a broader method spectrum and experimental limitations will be discussed in the course. B ...
1. An event that decreases the behavior that precedes it
... A) consistently used reinforcement in combination with punishment to shape their children's moral behavior. B) modeled a strong moral or humanitarian concern. C) consistently used psychological punishment rather than physical punishment in shaping their children's behavior. D) consistently used perm ...
... A) consistently used reinforcement in combination with punishment to shape their children's moral behavior. B) modeled a strong moral or humanitarian concern. C) consistently used psychological punishment rather than physical punishment in shaping their children's behavior. D) consistently used perm ...