Unit 5
... which Pavlov stated that classical conditioning occurred because the conditioned stimulus became a substitute for the unconditioned stimulus by being paired closely together. Cognitive perspective - modern theory in which classical conditioning is seen to occur because the conditioned stimulus pro ...
... which Pavlov stated that classical conditioning occurred because the conditioned stimulus became a substitute for the unconditioned stimulus by being paired closely together. Cognitive perspective - modern theory in which classical conditioning is seen to occur because the conditioned stimulus pro ...
HANDOUT Chapter 6 – Behavioral Views of Learning
... Unconditioned Stimulus (US) - event that automatically produces an emotional or physical response Unconditioned Response (UR) - naturally occurring emotional or physical response Neutral Stimulus (NS) - stimulus not connected to a response Conditioned Stimulus (CS) - stimulus that evokes a response ...
... Unconditioned Stimulus (US) - event that automatically produces an emotional or physical response Unconditioned Response (UR) - naturally occurring emotional or physical response Neutral Stimulus (NS) - stimulus not connected to a response Conditioned Stimulus (CS) - stimulus that evokes a response ...
Behaviorism - cepd410104
... 10. True or False. Positive Reinforcement allows students to receive a reward or treat when doing something right by the teacher. ...
... 10. True or False. Positive Reinforcement allows students to receive a reward or treat when doing something right by the teacher. ...
File - Oscar H. Suarez
... Operant conditioning is a form of learning in which the consequences of behavior are strengthen, suppressed or weaken. Behaviors are influenced by different stimulus, and they determine the likelihood that they will occur. Reinforcement and punishment could be considered as opposite forms of learnin ...
... Operant conditioning is a form of learning in which the consequences of behavior are strengthen, suppressed or weaken. Behaviors are influenced by different stimulus, and they determine the likelihood that they will occur. Reinforcement and punishment could be considered as opposite forms of learnin ...
Study Guide - DocShare.tips
... • Delay of reward: the longer you delay, the less effective it becomes; immediate is best. • Conditioning somatic (voluntary) behavior versus autonomic (involuntary) behaviors. Somatic is easier to donation then autonomic. • Deprivation level: learning is faster and stronger when learned is deprive ...
... • Delay of reward: the longer you delay, the less effective it becomes; immediate is best. • Conditioning somatic (voluntary) behavior versus autonomic (involuntary) behaviors. Somatic is easier to donation then autonomic. • Deprivation level: learning is faster and stronger when learned is deprive ...
Classical vs. Operant Conditioning
... An example of the ABC approach to understanding behavior can be found in the scenario of a family where the parents constantly fight. This fighting is very disturbing the couple’s child who does whatever it takes to stop parental arguments. As soon as an argument begins the child starts to misbehave ...
... An example of the ABC approach to understanding behavior can be found in the scenario of a family where the parents constantly fight. This fighting is very disturbing the couple’s child who does whatever it takes to stop parental arguments. As soon as an argument begins the child starts to misbehave ...
Behaviouristic learning theory
... • They believe that children came into this world with a clean slate (Tabula Rasa) and their behaviour are then shaped by the environment whether it is positive or negative reinforcement. ...
... • They believe that children came into this world with a clean slate (Tabula Rasa) and their behaviour are then shaped by the environment whether it is positive or negative reinforcement. ...
File
... inspired by the work of Charles Darwin and applies his ideas of natural selection to the mind. Natural selection is the nonrandom process by which biological traits become more or less common in a population as a function of differential reproduction of their bearers. It is a key mechanism of evolut ...
... inspired by the work of Charles Darwin and applies his ideas of natural selection to the mind. Natural selection is the nonrandom process by which biological traits become more or less common in a population as a function of differential reproduction of their bearers. It is a key mechanism of evolut ...
Chapter Five Practice Quiz 2 Name: Schedule of reinforcement in
... 5. Development of nausea or aversive response to a particular taste because that taste was followed by a nausea reaction, occurring after only one association. Conditioned taste aversion 6. Modern theory in which classical conditioning is seen to occur because the conditioned stimulus provides infor ...
... 5. Development of nausea or aversive response to a particular taste because that taste was followed by a nausea reaction, occurring after only one association. Conditioned taste aversion 6. Modern theory in which classical conditioning is seen to occur because the conditioned stimulus provides infor ...
PSYC 120 Conditioning Homework Name
... 5. Mikey cried after receiving a painful vaccination from a nurse in a white jacket. The next week his mother couldn't understand why Mikey burst out in tears when the barber (in a white jacket) welcomed them to his shop. UCS ____________________________ UCR ____________________________ ...
... 5. Mikey cried after receiving a painful vaccination from a nurse in a white jacket. The next week his mother couldn't understand why Mikey burst out in tears when the barber (in a white jacket) welcomed them to his shop. UCS ____________________________ UCR ____________________________ ...
Human Cognitive Processes
... – 2. figuring out how they are organized – 3. understanding why they are organized in a particular manner given a conscious experience. ...
... – 2. figuring out how they are organized – 3. understanding why they are organized in a particular manner given a conscious experience. ...
PSYCH-UNIT-2-0 -NOTES-BIO-INTRO
... accident in which a large iron rod was driven completely through his head. ★ Much of his left frontal lobe was destroyed. ★ The reported effects were personality & behaviorally based. ★ Over the succeeding 12 years - effects so profound that for a time (at least) his friends reported that they say h ...
... accident in which a large iron rod was driven completely through his head. ★ Much of his left frontal lobe was destroyed. ★ The reported effects were personality & behaviorally based. ★ Over the succeeding 12 years - effects so profound that for a time (at least) his friends reported that they say h ...
File - Ms. G`s Classroom
... Behavioral Approach Focuses on measuring and recording observable behavior in relation to the environment. Behavior mainly determined by an organism’s experiences and its environment rather than by genetics. Ivan Pavlov: Russian physiologist famous for experiments in the early 1900s training d ...
... Behavioral Approach Focuses on measuring and recording observable behavior in relation to the environment. Behavior mainly determined by an organism’s experiences and its environment rather than by genetics. Ivan Pavlov: Russian physiologist famous for experiments in the early 1900s training d ...
Chapter 6 Quiz
... 6. Watson and Rayner’s classical conditioning of “Little Albert” was helpful in explaining that a) some conditioned stimuli do not generalize b) human emotions such as fear are subject to classical conditioning c) drug dependency is subject to classical as well as operant conditioning d) small chil ...
... 6. Watson and Rayner’s classical conditioning of “Little Albert” was helpful in explaining that a) some conditioned stimuli do not generalize b) human emotions such as fear are subject to classical conditioning c) drug dependency is subject to classical as well as operant conditioning d) small chil ...
Course Outline - South Central College eCatalog
... Demonstrate an understanding of the key components of social psychology and how this subspecialty describes behavior and mental processes. Learning Objectives Name and describe some of the key studies in social psychology and discuss their significance in expanding our knowledge of social influences ...
... Demonstrate an understanding of the key components of social psychology and how this subspecialty describes behavior and mental processes. Learning Objectives Name and describe some of the key studies in social psychology and discuss their significance in expanding our knowledge of social influences ...
MSWord review handout (partial)
... helplessness is failure to take steps to avoid or escape from an unpleasant or aversive stimulus that occurs as the result of previous exposure to unavoidable painful stimuli (M197-198) Biological constraints on learning researchers have found animals will not perform certain behaviors that go again ...
... helplessness is failure to take steps to avoid or escape from an unpleasant or aversive stimulus that occurs as the result of previous exposure to unavoidable painful stimuli (M197-198) Biological constraints on learning researchers have found animals will not perform certain behaviors that go again ...
Learning - Blue Valley Schools
... Extinction is the gradual disappearance of a conditioned response when the conditioned stimulus is repeatedly presented without the unconditioned stimulus. Spontaneous recovery is when after a rest period, the conditioned response may reappear when the conditioned stimulus is presented again ...
... Extinction is the gradual disappearance of a conditioned response when the conditioned stimulus is repeatedly presented without the unconditioned stimulus. Spontaneous recovery is when after a rest period, the conditioned response may reappear when the conditioned stimulus is presented again ...
Theories of Learning
... Three major laws of learning were developed by Thorndike: (1) the law of readiness— when a “conduction” unit is ready to conduct, to do so is satisfying and not to do so is annoying; (2) the law of exercise—a connection is strengthened in proportion to the number of times it occurs, and in proportio ...
... Three major laws of learning were developed by Thorndike: (1) the law of readiness— when a “conduction” unit is ready to conduct, to do so is satisfying and not to do so is annoying; (2) the law of exercise—a connection is strengthened in proportion to the number of times it occurs, and in proportio ...
Learning - Mr. Hunsaker`s Classes
... How do we learn? • Two types of associative learning: – Classical Conditioning – Operant Conditioning • Other types of learning: – Cognitive learning – Observational learning ...
... How do we learn? • Two types of associative learning: – Classical Conditioning – Operant Conditioning • Other types of learning: – Cognitive learning – Observational learning ...
The Major Theorists
... based upon the idea that all behaviors are acquired through conditioning. Conditioning occurs through interaction with the environment. Behaviorists believe that our responses to environmental stimuli shape our behaviors. ...
... based upon the idea that all behaviors are acquired through conditioning. Conditioning occurs through interaction with the environment. Behaviorists believe that our responses to environmental stimuli shape our behaviors. ...
UNIT VI Notes File
... Pavlov’s work was the foundation of much of the work of psychologist John B. Watson – Watson believed psychology should focus on how organisms respond to stimuli in the environment (Behaviorism) – today most psychologists agree that classical conditioning is the basic form of learning by which all o ...
... Pavlov’s work was the foundation of much of the work of psychologist John B. Watson – Watson believed psychology should focus on how organisms respond to stimuli in the environment (Behaviorism) – today most psychologists agree that classical conditioning is the basic form of learning by which all o ...
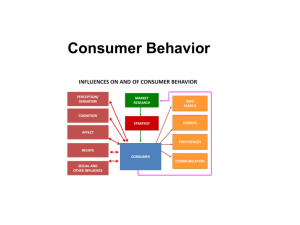
CB Lecture
... Consumer behavior: consists of the actions a person takes in purchasing and using products and services, including the mental and social processes that come before and after these actions. ...
... Consumer behavior: consists of the actions a person takes in purchasing and using products and services, including the mental and social processes that come before and after these actions. ...
Learning - McMurray VMC
... Tendency to respond to stimuli similar to the CS is called generalization. (Pavlov’s dog salivates to any kind of bell) ...
... Tendency to respond to stimuli similar to the CS is called generalization. (Pavlov’s dog salivates to any kind of bell) ...