File
... • Behaviors with favorable consequences will occur more frequently. • Behaviors with unfavorable consequences will occur less frequently. • Developed into Operant Conditioning • Created puzzle boxes for research on cats ...
... • Behaviors with favorable consequences will occur more frequently. • Behaviors with unfavorable consequences will occur less frequently. • Developed into Operant Conditioning • Created puzzle boxes for research on cats ...
Learning - Stephen F. Austin State University
... in a special area away from the attention of others. Essentially, the organism is being “removed” from any possibility of positive reinforcement in the form of attention. Applied behavior analysis (ABA) – modern term for a form of behavior modification that uses shaping techniques to mold a desi ...
... in a special area away from the attention of others. Essentially, the organism is being “removed” from any possibility of positive reinforcement in the form of attention. Applied behavior analysis (ABA) – modern term for a form of behavior modification that uses shaping techniques to mold a desi ...
Learning
... • Behavior modification - the use of operant conditioning techniques to bring about desired changes in behavior. • Token economy - type of behavior modification in which desired behavior is rewarded with tokens. • Time-out - a form of mild punishment by removal in which a misbehaving animal, child, ...
... • Behavior modification - the use of operant conditioning techniques to bring about desired changes in behavior. • Token economy - type of behavior modification in which desired behavior is rewarded with tokens. • Time-out - a form of mild punishment by removal in which a misbehaving animal, child, ...
Slide 1
... Aristotle: what are correct arguments/thought processes? Several Greek schools developed various forms of logic: notation and rules of derivation for thoughts; may or may not have proceeded to the idea of mechanization Direct line through mathematics and philosophy to modern AI ...
... Aristotle: what are correct arguments/thought processes? Several Greek schools developed various forms of logic: notation and rules of derivation for thoughts; may or may not have proceeded to the idea of mechanization Direct line through mathematics and philosophy to modern AI ...
Notes: Classical Conditioning
... 1. Classical- The process by which a once neutral stimulus acquires the capacity to elicit a response due to becoming linked with something that automatically evokes a strong response. *Define this in your own words:_________________________________ __________________________________________________ ...
... 1. Classical- The process by which a once neutral stimulus acquires the capacity to elicit a response due to becoming linked with something that automatically evokes a strong response. *Define this in your own words:_________________________________ __________________________________________________ ...
中原大學 95 學年度 碩士班入學考試
... 18. Ethologists challenge the basic assumption of behaviorism that a. human learning is based on associations. b. learning of rats is influenced by reward and punishment. c. learning is best understood by studying internal associations. d. laws of learning are the same for all organisms. 19. A commo ...
... 18. Ethologists challenge the basic assumption of behaviorism that a. human learning is based on associations. b. learning of rats is influenced by reward and punishment. c. learning is best understood by studying internal associations. d. laws of learning are the same for all organisms. 19. A commo ...
lifesmart-1st-edition-fiore-solution-manual
... What might each of these theories say about the infinite possibility of influence? Compare an individual’s influence on his/her environment to the ripples made by a single stone cast into a lake. How then does the lake influence the stone? What other factors might play a role? ...
... What might each of these theories say about the infinite possibility of influence? Compare an individual’s influence on his/her environment to the ripples made by a single stone cast into a lake. How then does the lake influence the stone? What other factors might play a role? ...
chp 1
... Types of Behavioral Learning Theories Classical Conditioning: a stimulus that elicits a response is paired with ...
... Types of Behavioral Learning Theories Classical Conditioning: a stimulus that elicits a response is paired with ...
3. Final - Psychology
... Evolution works by natural selection: A key concept in his theory. Because more members of a species are born than environmental resources can support, nature selects those with characteristics most conducive to survival under the circumstances to continue living and to reproduce. Darwin defined fit ...
... Evolution works by natural selection: A key concept in his theory. Because more members of a species are born than environmental resources can support, nature selects those with characteristics most conducive to survival under the circumstances to continue living and to reproduce. Darwin defined fit ...
Chapter 1 online
... psychological traits and self-identity. • Looks at importance of social relationships Emphasis is on the ego, or sense of self • Physical maturation contributes to development • Mastery of developmental task/s at each stage needed to move to next stage • Early experiences of parent/child relations ...
... psychological traits and self-identity. • Looks at importance of social relationships Emphasis is on the ego, or sense of self • Physical maturation contributes to development • Mastery of developmental task/s at each stage needed to move to next stage • Early experiences of parent/child relations ...
AP Psychology
... _________________________ 5. Margaret was given a standing ovation after singing karaoke. Now she goes to sing karaoke almost every other day. _________________________ 6. Oliver does his laundry frequently so that his room no longer smells. _________________________ 7. You study for math tests in o ...
... _________________________ 5. Margaret was given a standing ovation after singing karaoke. Now she goes to sing karaoke almost every other day. _________________________ 6. Oliver does his laundry frequently so that his room no longer smells. _________________________ 7. You study for math tests in o ...
Learning: Classical and Operant Conditioning Chapter 7
... What if we could not distinguish between stimuli that were ...
... What if we could not distinguish between stimuli that were ...
Name: Date: ______ Period: ______ Points: +______ Chapter 8
... 43. Gambling is reinforced according to which schedule? A) fixed-interval B) fixed-ratio C) variable-interval D) variable-ratio 44. From a casino owner's viewpoint, which of the following jackpot payout schedules would be the most desirable for reinforcing customer use of a slot machine? A) variabl ...
... 43. Gambling is reinforced according to which schedule? A) fixed-interval B) fixed-ratio C) variable-interval D) variable-ratio 44. From a casino owner's viewpoint, which of the following jackpot payout schedules would be the most desirable for reinforcing customer use of a slot machine? A) variabl ...
Sample summary
... Systematic study and EBM add to intuition, or those “gut feelings” about “why I do what I do” and “what makes others tick”. Since one tends to overestimate the accuracy of what we think we know, the limits of relying on intuition are made worse. One should enhance the intuitive views of behavior wit ...
... Systematic study and EBM add to intuition, or those “gut feelings” about “why I do what I do” and “what makes others tick”. Since one tends to overestimate the accuracy of what we think we know, the limits of relying on intuition are made worse. One should enhance the intuitive views of behavior wit ...
Learning Chapter 6 - Mrs. Short`s AP Psychology Class
... – varied depending upon the type of animal and the experimental variables. – chamber that includes at least one lever, bar, or key that the animal can manipulate • lever is pressed, food, water, or some other type of reinforcement might be dispensed ...
... – varied depending upon the type of animal and the experimental variables. – chamber that includes at least one lever, bar, or key that the animal can manipulate • lever is pressed, food, water, or some other type of reinforcement might be dispensed ...
Learning
... The rising curve (simplified here) shows that the CR rapidly grows stronger as the NS becomes a CS as it is repeatedly paired with the US (acquisition). The CS weakens when it is presented alone (extinction). After a pause, the CR reappears (spontaneous recovery). ...
... The rising curve (simplified here) shows that the CR rapidly grows stronger as the NS becomes a CS as it is repeatedly paired with the US (acquisition). The CS weakens when it is presented alone (extinction). After a pause, the CR reappears (spontaneous recovery). ...
Module 10: Operant & Cognitive Approaches
... behavior, and the following consequence (reward or punishment) increases or decreases the chance that an animal or human will again perform that same behavior. Behavior being repeated depends on whether the ...
... behavior, and the following consequence (reward or punishment) increases or decreases the chance that an animal or human will again perform that same behavior. Behavior being repeated depends on whether the ...
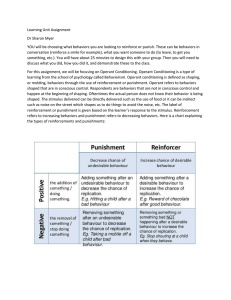
Learning Unit Assignment Dr Sharon Myer YOU will be choosing
... YOU will be choosing what behaviors you are looking to reinforce or punish. These can be behaviors in conversation (reinforce a smile for example), what you want someone to do (to leave, to get you something, etc.). You will have about 25 minutes to design this with your group. Then you will need to ...
... YOU will be choosing what behaviors you are looking to reinforce or punish. These can be behaviors in conversation (reinforce a smile for example), what you want someone to do (to leave, to get you something, etc.). You will have about 25 minutes to design this with your group. Then you will need to ...
Cognitive Flexibility - University of Arkansas
... The ability to predict and explain human behavior in terms of mental states such as intentions, emotions, desires, beliefs and states of knowledge and ignorance (Astington, 1993) Cognitive skill that typically develops around age 4-5yrs. Around ages 3-5 children start making links between the behavi ...
... The ability to predict and explain human behavior in terms of mental states such as intentions, emotions, desires, beliefs and states of knowledge and ignorance (Astington, 1993) Cognitive skill that typically develops around age 4-5yrs. Around ages 3-5 children start making links between the behavi ...
Preview from Notesale.co.uk Page 1 of 4
... an organism. CS- a stimulus that elicits a conditioned response in an organism. CR- the response that is elicited by a conditioned stimulus. Stimulus generalization versus stimulus discrimination Stimulus generalization is responding in a like fashion to similar stimuli while stimulus discriminati ...
... an organism. CS- a stimulus that elicits a conditioned response in an organism. CR- the response that is elicited by a conditioned stimulus. Stimulus generalization versus stimulus discrimination Stimulus generalization is responding in a like fashion to similar stimuli while stimulus discriminati ...
Classical Conditioning
... species – Only overt behaviors can be reinforced by the environment – Principle of the selection is based in the behavioral discrepancy ...
... species – Only overt behaviors can be reinforced by the environment – Principle of the selection is based in the behavioral discrepancy ...
CB4 - FA1 IIPM
... present when the dog was presented with meat powder, then this stimulus would become associated with food and cause salivation on its own. In his initial experiment, Pavlov used a bell to call the dogs to their food and, after a few repetitions, the dogs started to salivate in response to the bell R ...
... present when the dog was presented with meat powder, then this stimulus would become associated with food and cause salivation on its own. In his initial experiment, Pavlov used a bell to call the dogs to their food and, after a few repetitions, the dogs started to salivate in response to the bell R ...