Psychology
... Functionalists had very different ideas about nature of consciousness and how it should be studied. ...
... Functionalists had very different ideas about nature of consciousness and how it should be studied. ...
UNIT 6: LEARNING
... One of the great ethical concerns raised by Watson's work was the wellbeing of his human subject. We do not know if Little Albert continued these phobic (intense, irrational fear) responses throughout his adult life. We do know that Watson did not report any deconditioning work on his subject. ...
... One of the great ethical concerns raised by Watson's work was the wellbeing of his human subject. We do not know if Little Albert continued these phobic (intense, irrational fear) responses throughout his adult life. We do know that Watson did not report any deconditioning work on his subject. ...
Psychology - Jay School Corporation
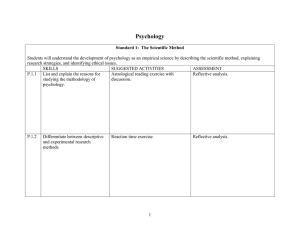
... Differentiate between descriptive and experimental research ...
... Differentiate between descriptive and experimental research ...
File
... Cognitive Factors in Learning • Cognitive psychologists focus on the mental aspects of learning and are interested in what people or animals know, not just what they do. ...
... Cognitive Factors in Learning • Cognitive psychologists focus on the mental aspects of learning and are interested in what people or animals know, not just what they do. ...
3. Classical Conditioning
... E.g. Bite from a particular type of dog doesn’t cause fear for other breeds of dog. ...
... E.g. Bite from a particular type of dog doesn’t cause fear for other breeds of dog. ...
Learning
... Cognitive Factors in Learning • Cognitive psychologists focus on the mental aspects of learning and are interested in what people or animals know, not just what they do. ...
... Cognitive Factors in Learning • Cognitive psychologists focus on the mental aspects of learning and are interested in what people or animals know, not just what they do. ...
... helping the dog to overcome most types of fears, including fear of people, noises, and new places. One of the great advantages of using classical conditioning to overcome a dog's fears is that you don't have to know why the dog is afraid. You just need to figure out what she is afraid of and then co ...
Learning
... • Expanded on Thorndike’s law of effect • Organisms don’t simply respond to the environment, but rather they exert influence (or “operate”) on it • Behaviours that are followed by favourable consequences will likely be repeated ...
... • Expanded on Thorndike’s law of effect • Organisms don’t simply respond to the environment, but rather they exert influence (or “operate”) on it • Behaviours that are followed by favourable consequences will likely be repeated ...
AP Psychology Challenge - District 196 e
... 5. In its early years, psychology focused on the study of ___, but from the 1920’s into the 1960’s they focused on: • A) environmental influences; hereditary influences. • B) maladaptive behavior; adaptive behavior. • C) unconscious motives; conscious thoughts and feelings. • D) mental processes; o ...
... 5. In its early years, psychology focused on the study of ___, but from the 1920’s into the 1960’s they focused on: • A) environmental influences; hereditary influences. • B) maladaptive behavior; adaptive behavior. • C) unconscious motives; conscious thoughts and feelings. • D) mental processes; o ...
Learning Learning Habituation Sensitization
... • Typically highintensity stimuli • Nonspecific generalization • > neurotransmitter ...
... • Typically highintensity stimuli • Nonspecific generalization • > neurotransmitter ...
Psychological and economic considerations of rewards programs
... specific to context of the study. Therefore a more comprehensive framework may be required under which one may be able to examine the effectiveness of different types of rewards programs. In order to better understand the nature of rewards programs, a review of how rewards affect behavior and/or moti ...
... specific to context of the study. Therefore a more comprehensive framework may be required under which one may be able to examine the effectiveness of different types of rewards programs. In order to better understand the nature of rewards programs, a review of how rewards affect behavior and/or moti ...
II - NIOS
... pairs of words. Psychologists study how various procedures like serial learning and paired associates learning are used. Concept Learning This is about developing categories of objects and events. It is very important in our life that we should discriminate between things on the basis of some criter ...
... pairs of words. Psychologists study how various procedures like serial learning and paired associates learning are used. Concept Learning This is about developing categories of objects and events. It is very important in our life that we should discriminate between things on the basis of some criter ...
The Neural Foundations of Reaction and Action in Aversive Motivation
... the current state of research on these behaviors, we will briefly review the history of this field. In aversive conditioning a neutral conditioned stimulus (CS), such as a tone, is repeatedly paired with an aversive unconditioned stimulus (US), usually an electric shock. Following this episode, the C ...
... the current state of research on these behaviors, we will briefly review the history of this field. In aversive conditioning a neutral conditioned stimulus (CS), such as a tone, is repeatedly paired with an aversive unconditioned stimulus (US), usually an electric shock. Following this episode, the C ...
Electrical Activity of a Membrane Resting Potential
... • Voltage-Sensitive Ion Channels – Gated protein channel that opens or closes only at specific membrane voltages – Sodium (Na+) and potassium (K+) – Closed at membrane’s resting potential – Na+ channels are more sensitive than K+ channels and therefore open sooner ...
... • Voltage-Sensitive Ion Channels – Gated protein channel that opens or closes only at specific membrane voltages – Sodium (Na+) and potassium (K+) – Closed at membrane’s resting potential – Na+ channels are more sensitive than K+ channels and therefore open sooner ...
Chapter 2 Intrinsic Dynamics of an Excitatory
... in discrete time intervals, is one of the simplest systems capable of showing chaotic behavior. This has guided the choiceof this system for extensive study in this thesis. The present chapter examines the discrete-time dynamics of such coupled neuron pairs with four different types of nonlinear act ...
... in discrete time intervals, is one of the simplest systems capable of showing chaotic behavior. This has guided the choiceof this system for extensive study in this thesis. The present chapter examines the discrete-time dynamics of such coupled neuron pairs with four different types of nonlinear act ...
lecture without notes - Doral Academy Preparatory
... Unconditioned Response (UCR) Conditioned Response (CR) ...
... Unconditioned Response (UCR) Conditioned Response (CR) ...
Introduction to Reinforcement Learning
... A Bit of History: From Psychology to Machine Learning The Reinforcement Learning Model ...
... A Bit of History: From Psychology to Machine Learning The Reinforcement Learning Model ...
an opponent-process theory of motivation: i. temporal
... and aversive. The opponent processes for most hedonic states are strengthened by use and are weakened by disuse. These simple assumptions lead to deductions of many known facts about acquired motivation. In addition, the theory suggests several new lines of research on motivation. It argues that the ...
... and aversive. The opponent processes for most hedonic states are strengthened by use and are weakened by disuse. These simple assumptions lead to deductions of many known facts about acquired motivation. In addition, the theory suggests several new lines of research on motivation. It argues that the ...
Cate hears a funny ticking sound when she presses the gas pedal in
... In learning theory, when a behavioural response becomes weaker after an individual observes a model being punished for the same behaviour, the process at work is referred to as: ...
... In learning theory, when a behavioural response becomes weaker after an individual observes a model being punished for the same behaviour, the process at work is referred to as: ...
Psychology of Learning
... A technique that uses classical conditioning to treat phobias Person learns to relax in presence of stimulus that used to be upsetting ...
... A technique that uses classical conditioning to treat phobias Person learns to relax in presence of stimulus that used to be upsetting ...
20-Limbic
... important role on the mediation and control of major affective activities like friendship, love and affection, on the expression of mood and, mainly, on fear, anger and violent behavior. The amygdala, being the center for identification of danger. When triggered, it gives rise to fear and anxiety wh ...
... important role on the mediation and control of major affective activities like friendship, love and affection, on the expression of mood and, mainly, on fear, anger and violent behavior. The amygdala, being the center for identification of danger. When triggered, it gives rise to fear and anxiety wh ...
PDF
... Several important theories have previously been advanced to explain decision-making deficits in addiction. These hypotheses can be grouped into two main classes. The first class proposes that a drug-induced deficit in prefrontal cortical function results in a loss of control over behavior. Jentsch a ...
... Several important theories have previously been advanced to explain decision-making deficits in addiction. These hypotheses can be grouped into two main classes. The first class proposes that a drug-induced deficit in prefrontal cortical function results in a loss of control over behavior. Jentsch a ...
Reward and punishment act as distinct factors in guiding behavior
... from zero over the subjects (p < 0:0001; t 53 ¼ 16:41, twosided t-test). Thus, the click difference was a significant factor in guiding the subjects’ responses. The amount of information in the stimulus may influence the time it takes to produce a response, the reaction time (RT). We indeed found th ...
... from zero over the subjects (p < 0:0001; t 53 ¼ 16:41, twosided t-test). Thus, the click difference was a significant factor in guiding the subjects’ responses. The amount of information in the stimulus may influence the time it takes to produce a response, the reaction time (RT). We indeed found th ...
CHILDHOOD AND GROWING UP
... Each card will be shown for a second. We have to say how many dots there are in each card. The maximum number of dots you can notice is your span of attention. 1.13.2 INATTENTION& DISTRACTION Inattention means, not paying attention to a particular stimulus or to any stimulus. We do not pay attention ...
... Each card will be shown for a second. We have to say how many dots there are in each card. The maximum number of dots you can notice is your span of attention. 1.13.2 INATTENTION& DISTRACTION Inattention means, not paying attention to a particular stimulus or to any stimulus. We do not pay attention ...