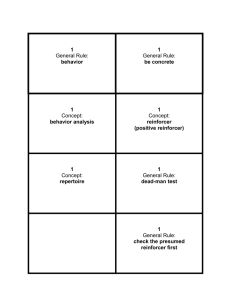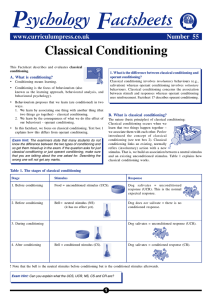
Classical Conditioning
... Describe the basic principles of classical or operant conditioning. Evaluate the role of classical conditioning in human behaviour. In the first section of this question, it asks you to choose between either classical or operant conditioning. Be sure that you know the difference! The basic principle ...
... Describe the basic principles of classical or operant conditioning. Evaluate the role of classical conditioning in human behaviour. In the first section of this question, it asks you to choose between either classical or operant conditioning. Be sure that you know the difference! The basic principle ...
Psychology Vocabulary Matching Exercise: Learning
... stimulus that has no effect on the desired response learning to make an involuntary response to a stimulus other than the natural stimulus that normally produces the reflex sudden perception of relationships among various parts of a problem, allowing the solution to the problem any reinforcer that i ...
... stimulus that has no effect on the desired response learning to make an involuntary response to a stimulus other than the natural stimulus that normally produces the reflex sudden perception of relationships among various parts of a problem, allowing the solution to the problem any reinforcer that i ...
Severe Reduction of Rat Defensive Behavior to a Predator by
... the pattern of hypothalamic activation during the display of innate defensive behavior, five animals were then placed individually for 10 min in a closed, wired-meshed compartment (70 3 16 3 30 cm) located inside a larger arena containing an adult male cat (3 kg). The other five animals served as co ...
... the pattern of hypothalamic activation during the display of innate defensive behavior, five animals were then placed individually for 10 min in a closed, wired-meshed compartment (70 3 16 3 30 cm) located inside a larger arena containing an adult male cat (3 kg). The other five animals served as co ...
Learning - Home | Quincy College
... • Immediate Reinforcement vs. Delayed Punishment • Immediate consequences usually win © 2013 by McGraw-Hill Education. This is proprietary material solely for authorized instructor use. Not authorized for sale or distribution in any manner. This document may not be copied, scanned, duplicated, forwa ...
... • Immediate Reinforcement vs. Delayed Punishment • Immediate consequences usually win © 2013 by McGraw-Hill Education. This is proprietary material solely for authorized instructor use. Not authorized for sale or distribution in any manner. This document may not be copied, scanned, duplicated, forwa ...
think about it
... Pavlov demonstrated that dogs could be conditioned to salivate to a variety of stimuli never before associated with food, as shown in FIGURE 2 (above). During the conditioning process, the researcher would present a neutral stimulus such as a musical tone shortly before placing food powder in the do ...
... Pavlov demonstrated that dogs could be conditioned to salivate to a variety of stimuli never before associated with food, as shown in FIGURE 2 (above). During the conditioning process, the researcher would present a neutral stimulus such as a musical tone shortly before placing food powder in the do ...
Vocab Flashcards
... z A set of responses that either z a) are similar on at least one response dimension, or z b) share the effects of reinforcement and punishment, or z c) serve the same function (produce the same outcome). ...
... z A set of responses that either z a) are similar on at least one response dimension, or z b) share the effects of reinforcement and punishment, or z c) serve the same function (produce the same outcome). ...
Lesions of the Basolateral Amygdala Disrupt Selective Aspects of
... when BLA-lesioned rats are required to use a CS–reward association in higher-order learning tasks such as second-order conditioning and conditioned reinforcement, this association is less effective in modifying behavior. Hatfield et al. (1996) provided further insight into this deficit. They showed ...
... when BLA-lesioned rats are required to use a CS–reward association in higher-order learning tasks such as second-order conditioning and conditioned reinforcement, this association is less effective in modifying behavior. Hatfield et al. (1996) provided further insight into this deficit. They showed ...
Techniques FdSc Canine Behaviour and Training Module Code
... Extinction may be easily understood and implemented by dog owners as it may sometimes be achieved by simply ignoring the problematic behaviour; assuming the reinforcing stimulus is coming from the owner and not elsewhere (Burch and Bailey, 1999). The extinction protocol may be combined with other pr ...
... Extinction may be easily understood and implemented by dog owners as it may sometimes be achieved by simply ignoring the problematic behaviour; assuming the reinforcing stimulus is coming from the owner and not elsewhere (Burch and Bailey, 1999). The extinction protocol may be combined with other pr ...
A Study on First Order and Second Order Conditioning In
... Gorn’s experiment tested on 244 undergraduate students at McGill University on how music affected consumer’s product choices. The subjects were exposed to a neutral CS a pen was used for this, either a light beige or light blue one depending on which group. The CS was paired with liked or disliked m ...
... Gorn’s experiment tested on 244 undergraduate students at McGill University on how music affected consumer’s product choices. The subjects were exposed to a neutral CS a pen was used for this, either a light beige or light blue one depending on which group. The CS was paired with liked or disliked m ...
FREE Sample Here - Find the cheapest test bank for your
... 46. Charles Darwin believed that behaviors, such as the emotional expressions associated with human rage, could be explained by natural selection. Which early psychologist would be most likely to agree with Darwin's assessment? A. William James B. Edward B. Titchener C. Wilhelm Wundt D. John B. Wats ...
... 46. Charles Darwin believed that behaviors, such as the emotional expressions associated with human rage, could be explained by natural selection. Which early psychologist would be most likely to agree with Darwin's assessment? A. William James B. Edward B. Titchener C. Wilhelm Wundt D. John B. Wats ...
Chapter 11: Theories of learning Learning activity suggested answers
... CS (conditioned stimulus): the stimulus that is ‘neutral’ at the start of classical conditioning and does not normally produce the UCR (but eventually becomes associated with the UCS and elicits the CR ...
... CS (conditioned stimulus): the stimulus that is ‘neutral’ at the start of classical conditioning and does not normally produce the UCR (but eventually becomes associated with the UCS and elicits the CR ...
DEPARTMENT OF PSYCHOLOGY (PSY) 211 AYERS HALL
... spirituality, aesthetic appreciation, work satisfaction, self-control, integrity/ethics. Self-assessment and critical thinking are emphasized. 363. Behavior Modification (3). Prerequisites: PSY 220, 221. An introduction to the application of behavioral principles and procedures to the improvement of ...
... spirituality, aesthetic appreciation, work satisfaction, self-control, integrity/ethics. Self-assessment and critical thinking are emphasized. 363. Behavior Modification (3). Prerequisites: PSY 220, 221. An introduction to the application of behavioral principles and procedures to the improvement of ...
File
... - do not use physical punishment - punish the inappropriate behavior immediately - positively reinforce appropriate behavior to take the place of the inappropriate behavior - punish specific behaviors - do not mix punishment with rewards for the same behavior - do not back down © 2012 McGraw-Hill Co ...
... - do not use physical punishment - punish the inappropriate behavior immediately - positively reinforce appropriate behavior to take the place of the inappropriate behavior - punish specific behaviors - do not mix punishment with rewards for the same behavior - do not back down © 2012 McGraw-Hill Co ...
Conditioned Stimulus
... • But he disagreed on what made the CS a useful predictor. It was more complicated than the number of CS-US pairings. ...
... • But he disagreed on what made the CS a useful predictor. It was more complicated than the number of CS-US pairings. ...
Psychology and Life Richard J. Gerrig Twentieth Edition Psychology
... a 1000 hertz tone (Siegel et al., 1968). During an extinction phase, the rabbits were tested on the training tone as well as tones that varied in distance from that tone. Tones more similar to the training tone produced more conditioned responses than those further away. Data from Siegel, S., Hearst ...
... a 1000 hertz tone (Siegel et al., 1968). During an extinction phase, the rabbits were tested on the training tone as well as tones that varied in distance from that tone. Tones more similar to the training tone produced more conditioned responses than those further away. Data from Siegel, S., Hearst ...
- Digital Commons @ Kennesaw State University
... theory proposed by Bandura (1977), which states that human behavior is a result of continuous reciprocal interaction among cognitive, behavioral, and environmental determinants (Latham and Saari, 1979). In other words, as stated by Bandura (1977): “In the social learning view, people are neither dri ...
... theory proposed by Bandura (1977), which states that human behavior is a result of continuous reciprocal interaction among cognitive, behavioral, and environmental determinants (Latham and Saari, 1979). In other words, as stated by Bandura (1977): “In the social learning view, people are neither dri ...
Artificial Intelligence
... • Basic game AI – Decision-making techniques commonly used in almost all games • Basic pathfinding (A*) • Decision trees ...
... • Basic game AI – Decision-making techniques commonly used in almost all games • Basic pathfinding (A*) • Decision trees ...
Lecture 1: Mirroring and Social Cognition
... Bandura also demonstrated that viewing aggression by cartoon characters produces more aggressive behavior than viewing live or ...
... Bandura also demonstrated that viewing aggression by cartoon characters produces more aggressive behavior than viewing live or ...
EXTENDED PRIMARY AND HIGHER ORDER CONDITIONING OF
... With the exception of three studies in the 1930's (Copeland, 1930; Copeland and Brown, 1934; and Raabe, 1939), all research involving Pavlovian conditioning of earthworms has developed since 1959. Perhaps this is attributable, as suggested by Bitterman (1960), to the difficulty of recording classica ...
... With the exception of three studies in the 1930's (Copeland, 1930; Copeland and Brown, 1934; and Raabe, 1939), all research involving Pavlovian conditioning of earthworms has developed since 1959. Perhaps this is attributable, as suggested by Bitterman (1960), to the difficulty of recording classica ...
UNIT 6 LEARNING
... However, despite the theoretical possibility of the widespread applicability of classical conditioning, most modern theorists agree that it represents only a very small part of total human learning. ...
... However, despite the theoretical possibility of the widespread applicability of classical conditioning, most modern theorists agree that it represents only a very small part of total human learning. ...
Slides - NYU Computation and Cognition Lab
... grounded in computational theory, and some neuroscience ...
... grounded in computational theory, and some neuroscience ...