2.3 Animal Transport
... substantial reduction from aortic pressure. Their pressure depends on whether they are dilated or contracted. 16. There is an even greater resistance in the capillaries with a larger crosssectional area. 17. The velocity of blood of blood flow is directly related to pressure. In the capillary beds t ...
... substantial reduction from aortic pressure. Their pressure depends on whether they are dilated or contracted. 16. There is an even greater resistance in the capillaries with a larger crosssectional area. 17. The velocity of blood of blood flow is directly related to pressure. In the capillary beds t ...
Hemoglobin - Medico Tutorials
... Types of Haemoglobin • HbA ( Alpha2 Beta2) • HbA2 ( Alpha2 Delta2) • Hb A1c ...
... Types of Haemoglobin • HbA ( Alpha2 Beta2) • HbA2 ( Alpha2 Delta2) • Hb A1c ...
Save as PDF - Stiftung Tierärztliche Hochschule Hannover
... (APP) expression with real-time reverse transcriptase-polymerase chain reaction (real-time RT-PCR). Cytokines are messengers, initiating and regulating the immune response. Furthermore it is possible to distinguish certain immune cells (T-helpercells) on the basis of their cytokine expression. T-hel ...
... (APP) expression with real-time reverse transcriptase-polymerase chain reaction (real-time RT-PCR). Cytokines are messengers, initiating and regulating the immune response. Furthermore it is possible to distinguish certain immune cells (T-helpercells) on the basis of their cytokine expression. T-hel ...
Blood as a Soil on Surgical Instruments: Chemical Profile, Cleaning
... Unfolding of the polypeptide chain detracts in most cases from solubility. In the case of blood proteins on a surface, this process results in hardening (coagulation) due to the formation of high-molecular aggregates. Temperatures between 60-70o C suffice for complete denaturation. An important con ...
... Unfolding of the polypeptide chain detracts in most cases from solubility. In the case of blood proteins on a surface, this process results in hardening (coagulation) due to the formation of high-molecular aggregates. Temperatures between 60-70o C suffice for complete denaturation. An important con ...
Blood Composition, Vessels, and The Lymphatic System Reading
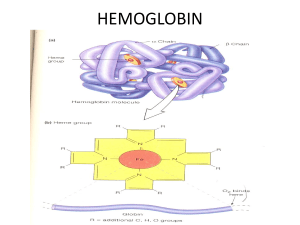
... Blood Composition, Vessels, and The Lymphatic System Reading Blood Composition Your blood contains cells called erythrocytes or red blood cells (RBCs). Red blood cells are packed full of a protein molecule called hemoglobin. The heme in the hemoglobin is red in color. Each molecule of hemoglobin con ...
... Blood Composition, Vessels, and The Lymphatic System Reading Blood Composition Your blood contains cells called erythrocytes or red blood cells (RBCs). Red blood cells are packed full of a protein molecule called hemoglobin. The heme in the hemoglobin is red in color. Each molecule of hemoglobin con ...
Lymphatic System Structures
... • To control flow of lymph fluid • To produce lymph system components • To filter lymph fluid and blood ...
... • To control flow of lymph fluid • To produce lymph system components • To filter lymph fluid and blood ...
CFR482.27 - Laboratory services
... more specific) test or other follow-up testing required by FDA is positive, the hospital must— (A) Dispose of the blood and blood components; and (B) Notify the transfusion beneficiaries as set forth in paragraph (b)(6) of this section. (iii) If the blood collecting establishment notifies the hospit ...
... more specific) test or other follow-up testing required by FDA is positive, the hospital must— (A) Dispose of the blood and blood components; and (B) Notify the transfusion beneficiaries as set forth in paragraph (b)(6) of this section. (iii) If the blood collecting establishment notifies the hospit ...
document
... • Agranular leukocytes lack granules; their nuclei are rounded or kidney-shaped • Lymphocytes fight infections; some produce antibodies, others directly attack invaders such as bacteria or viruses • Monocytes are phagocytes that migrate from blood into tissues during an infection; they differentiate ...
... • Agranular leukocytes lack granules; their nuclei are rounded or kidney-shaped • Lymphocytes fight infections; some produce antibodies, others directly attack invaders such as bacteria or viruses • Monocytes are phagocytes that migrate from blood into tissues during an infection; they differentiate ...
Glossary P2 - Skills Commons
... Howell-Jolly body- nuclear remnant remaining in red blood cells after the nucleus is lost and commonly seen in pernicious anemia and hemolytic anemias Keratocyte- a red blood cell deformed by mechanical trauma Leukemia- a cancer of white blood cells characterized by an abnormal increase of white bl ...
... Howell-Jolly body- nuclear remnant remaining in red blood cells after the nucleus is lost and commonly seen in pernicious anemia and hemolytic anemias Keratocyte- a red blood cell deformed by mechanical trauma Leukemia- a cancer of white blood cells characterized by an abnormal increase of white bl ...
The Endocrine System
... How is the endocrine system different from the nervous system? The endocrine system works with the nervous system to help regulate and control different bodily functions. The endocrine system acts more slowly than the nervous system because hormones are transported by blood while the nervous system ...
... How is the endocrine system different from the nervous system? The endocrine system works with the nervous system to help regulate and control different bodily functions. The endocrine system acts more slowly than the nervous system because hormones are transported by blood while the nervous system ...
Forensic Biology by Richard Li
... binding to the subsequently produced antibodies. Antigens are generally proteins or polysaccharides, but other substances such as nucleic acids can also be antigens. ...
... binding to the subsequently produced antibodies. Antigens are generally proteins or polysaccharides, but other substances such as nucleic acids can also be antigens. ...
Blood Notes Packet
... you are Type A, and transfused with Type B, your body will mobilize a massive immune response against the "invading" blood. This will cause coagulation of blood and death. ----- AGGLUTINATION (the clumping of red blood cells following a transfusion reaction; fatal ...
... you are Type A, and transfused with Type B, your body will mobilize a massive immune response against the "invading" blood. This will cause coagulation of blood and death. ----- AGGLUTINATION (the clumping of red blood cells following a transfusion reaction; fatal ...
Sijie
... A. The role of the skin in providing nonspecific defenses against infection. - Impenetrable barrier to most pathogens - Oil and sweat glands form an acidic environment which kills many bacteria Other: saliva, sweat, tears, stomach acid kill bacteria, mucus and hair trap pathogens Inflammatory respon ...
... A. The role of the skin in providing nonspecific defenses against infection. - Impenetrable barrier to most pathogens - Oil and sweat glands form an acidic environment which kills many bacteria Other: saliva, sweat, tears, stomach acid kill bacteria, mucus and hair trap pathogens Inflammatory respon ...
1 Searching for the Lost Children
... blood of an Rh-positive fetus if blood from the fetus crosses the placenta into the mother’s circulatory system. Since the immune response develops over time, it usually does not lead to problems until a second pregnancy with an Rh-positive fetus. In the second pregnancy, the mother’s immune system ...
... blood of an Rh-positive fetus if blood from the fetus crosses the placenta into the mother’s circulatory system. Since the immune response develops over time, it usually does not lead to problems until a second pregnancy with an Rh-positive fetus. In the second pregnancy, the mother’s immune system ...
Molecular genetic blood group typing by the use of
... he molecular genetic basis of almost all blood group systems has been investigated and described in the literature. Deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) typing is possible for many of the blood group antigens that are defined by single amino acid polymorphisms. An increased frequency of scientific literature ...
... he molecular genetic basis of almost all blood group systems has been investigated and described in the literature. Deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) typing is possible for many of the blood group antigens that are defined by single amino acid polymorphisms. An increased frequency of scientific literature ...
Chapter 18
... • Appear 2 to 8 months after birth; maximum concentration by 10 years of age – Antibody-A and/or antibody-B (both or none) are found in plasma • You do not form antibodies against your antigens ...
... • Appear 2 to 8 months after birth; maximum concentration by 10 years of age – Antibody-A and/or antibody-B (both or none) are found in plasma • You do not form antibodies against your antigens ...
healthinfo - Haldimand
... other times when your hands are likely to come in contact with blood, body fluids, excretions and secretions, mucous membranes or broken skin. Wear gloves when handling soiled items or surfaces. Clean properly: Be careful when you handle soiled materials and equipment so that you don't soil other th ...
... other times when your hands are likely to come in contact with blood, body fluids, excretions and secretions, mucous membranes or broken skin. Wear gloves when handling soiled items or surfaces. Clean properly: Be careful when you handle soiled materials and equipment so that you don't soil other th ...
2.3 Page 1 - csfcbiology
... Organs are not in direct contact with the blood. Respiratory gases are transported in the blood. 4. Mammals have a circulatory system comprising closed, double circulation and a heart with two atria and ventricles. 5. The major blood vessels of the heart include: aorta, vena cava, pulmonary veins, p ...
... Organs are not in direct contact with the blood. Respiratory gases are transported in the blood. 4. Mammals have a circulatory system comprising closed, double circulation and a heart with two atria and ventricles. 5. The major blood vessels of the heart include: aorta, vena cava, pulmonary veins, p ...
Transport Systems
... – Network of tubes or body spaces through which fluid can flow – Means of driving fluid through these spaces (pump) ...
... – Network of tubes or body spaces through which fluid can flow – Means of driving fluid through these spaces (pump) ...
Blood Transfusion - Patient Education Institute
... Red blood cells carry oxygen from the lungs to organs and tissues. You may need a red blood cell transfusion if you’ve lost blood from an injury, surgery, or have anemia. Red blood cells are the most common part of the blood that is used in transfusions. Anemia is a low count of red blood cells. It ...
... Red blood cells carry oxygen from the lungs to organs and tissues. You may need a red blood cell transfusion if you’ve lost blood from an injury, surgery, or have anemia. Red blood cells are the most common part of the blood that is used in transfusions. Anemia is a low count of red blood cells. It ...
HASPI Blood Types and Transfusions
... chicken pox, caused by a virus that has antigens on it’s surface, your body now contains antibodies made to recognize the antigens on the virus. This makes it easier for your body to recognize the chicken pox virus if it ever infects you again, and start to attack the virus faster. So fast in fact, ...
... chicken pox, caused by a virus that has antigens on it’s surface, your body now contains antibodies made to recognize the antigens on the virus. This makes it easier for your body to recognize the chicken pox virus if it ever infects you again, and start to attack the virus faster. So fast in fact, ...
MCB 181 (Nov 4 – Dec 4) Information and Heredity
... production after initial exposure to an antigen (e.g. flu shot). • Notice that upon second exposure (second peak of the blue line) to the same antigen the production of antibodies is both faster and dramatically larger (log scale). • The reason for the rapid and dramatic response upon second exposur ...
... production after initial exposure to an antigen (e.g. flu shot). • Notice that upon second exposure (second peak of the blue line) to the same antigen the production of antibodies is both faster and dramatically larger (log scale). • The reason for the rapid and dramatic response upon second exposur ...
Blood type
A blood type (also called a blood group) is a classification of blood based on the presence or absence of inherited antigenic substances on the surface of red blood cells (RBCs). These antigens may be proteins, carbohydrates, glycoproteins, or glycolipids, depending on the blood group system. Some of these antigens are also present on the surface of other types of cells of various tissues. Several of these red blood cell surface antigens can stem from one allele (or an alternative version of a gene) and collectively form a blood group system.Blood types are inherited and represent contributions from both parents. A total of 35 human blood group systems are now recognized by the International Society of Blood Transfusion (ISBT). The two most important ones are ABO and the RhD antigen; they determine someone's blood type (A, B, AB and O, with +, − or Null denoting RhD status).Many pregnant women carry a fetus with a blood type which is different from their own, which is not a problem. What can matter is whether the baby is RhD positive or negative. Mothers who are RhD- and carry a RhD+ baby can form antibodies against fetal RBCs. Sometimes these maternal antibodies are IgG, a small immunoglobulin, which can cross the placenta and cause hemolysis of fetal RBCs, which in turn can lead to hemolytic disease of the newborn called erythroblastosis fetalis, an illness of low fetal blood counts that ranges from mild to severe. Sometimes this is lethal for the fetus; in these cases it is called hydrops fetalis.