Type II hypersensitivity target tissues
... Trai-Ming Yeh, Ph.D. Department of Medical Laboratory Science and Biotechnology College of Medicine National Cheng Kung University ...
... Trai-Ming Yeh, Ph.D. Department of Medical Laboratory Science and Biotechnology College of Medicine National Cheng Kung University ...
File
... Toxins produced by pathogens Dead pathogens These all act as antigens – when injected into the body, they stimulate white blood cells to produce antibodies against the pathogen ...
... Toxins produced by pathogens Dead pathogens These all act as antigens – when injected into the body, they stimulate white blood cells to produce antibodies against the pathogen ...
Anaplasma
... rounded nucleus. By finding Ehrlichia inside certain types of white blood cells, one could get a better idea for which type of Ehrlichia one was seeing. Or so we foolishly thought. ...
... rounded nucleus. By finding Ehrlichia inside certain types of white blood cells, one could get a better idea for which type of Ehrlichia one was seeing. Or so we foolishly thought. ...
337: Alternatives to Blood Transfusions Part 1 of 2
... their willingness to depart from tradition.” It is possible that as more medical professionals are trained in bloodless alternatives, patients who do not consent to blood transfusions will meet less resistance. Many patients view it not as a last resort but as a preferred treatment. Stephen Geoffrey ...
... their willingness to depart from tradition.” It is possible that as more medical professionals are trained in bloodless alternatives, patients who do not consent to blood transfusions will meet less resistance. Many patients view it not as a last resort but as a preferred treatment. Stephen Geoffrey ...
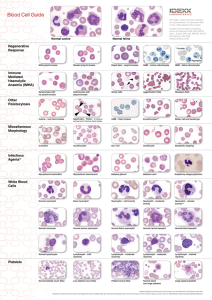
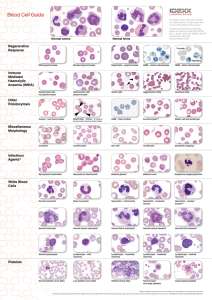
Blood Cell Guide
... parasite attachment and immune response by the host results in increased red blood cell (RBC) destruction and anaemia.2 There are three haemotropic mycoplasmas that have been identified in cats: Mycoplasma haemofelis, Candidatus Mycoplasma haemominutum and most recently Candidatus Mycoplasma turicen ...
... parasite attachment and immune response by the host results in increased red blood cell (RBC) destruction and anaemia.2 There are three haemotropic mycoplasmas that have been identified in cats: Mycoplasma haemofelis, Candidatus Mycoplasma haemominutum and most recently Candidatus Mycoplasma turicen ...
Blood Cell Guide - IDEXX Laboratories
... parasite attachment and immune response by the host results in increased red blood cell (RBC) destruction and anaemia. There are three haemotropic mycoplasmas that have been identified in cats: Mycoplasma haemofelis, Candidatus Mycoplasma haemominutum and most recently Candidatus Mycoplasma turicens ...
... parasite attachment and immune response by the host results in increased red blood cell (RBC) destruction and anaemia. There are three haemotropic mycoplasmas that have been identified in cats: Mycoplasma haemofelis, Candidatus Mycoplasma haemominutum and most recently Candidatus Mycoplasma turicens ...
Platelets
... Subcutaneous hemorrhage Plonged bleeding time Vitamin k deficiency vit K is important for formation of factors II,VII, ,IX, X in the liver It is a fat soluble vitamin & is formed by intestinal flora Its absorption is decreased in obstruction of bile duct ...
... Subcutaneous hemorrhage Plonged bleeding time Vitamin k deficiency vit K is important for formation of factors II,VII, ,IX, X in the liver It is a fat soluble vitamin & is formed by intestinal flora Its absorption is decreased in obstruction of bile duct ...
Transport in animals
... • 2. Layer of fat around the heart which is spongy acts as shock absorber/ cushions and protects the heart. • 3. Pulmonary vein and vena cava blood vessels have wide lumen and valves to ensure flow of blood to the heart right auricle and left auricle respectively. • 4. The aorta and pulmonary artery ...
... • 2. Layer of fat around the heart which is spongy acts as shock absorber/ cushions and protects the heart. • 3. Pulmonary vein and vena cava blood vessels have wide lumen and valves to ensure flow of blood to the heart right auricle and left auricle respectively. • 4. The aorta and pulmonary artery ...
Designing with Heart
... setting can promote blood clot formation — reverse flows and vortices are undesirable. The CFD results found that a smooth and gradual transition in the secondary flow velocity was present at the curvature of one inflow and outflow cannula geometry. This graduation helps to prevent separation and re ...
... setting can promote blood clot formation — reverse flows and vortices are undesirable. The CFD results found that a smooth and gradual transition in the secondary flow velocity was present at the curvature of one inflow and outflow cannula geometry. This graduation helps to prevent separation and re ...
Circulatory, Respiratory and Excretory Unit packet
... Circulatory system: body system that transports wastes and nutrients throughout the body. Heart: multi-chambered, muscular organ that pumps blood throughout the body Interstitial fluid: fluid found between cells Lymph: fluid similar to interstitial fluid that circulates in the lymphatic system Vein: ...
... Circulatory system: body system that transports wastes and nutrients throughout the body. Heart: multi-chambered, muscular organ that pumps blood throughout the body Interstitial fluid: fluid found between cells Lymph: fluid similar to interstitial fluid that circulates in the lymphatic system Vein: ...
WHAT SHOULD I KNOW FOR THE TEST
... What is the difference between homozygous/heterozygous? Dominant/recessive? Pure/hybrid? allele/trait? genetics/heredity? Genotype/phenotype? What molecule found on the surface of cells is responsible for A, B,O blood types? What would cells from each of the blood types look like? What combination o ...
... What is the difference between homozygous/heterozygous? Dominant/recessive? Pure/hybrid? allele/trait? genetics/heredity? Genotype/phenotype? What molecule found on the surface of cells is responsible for A, B,O blood types? What would cells from each of the blood types look like? What combination o ...
Antigens and Antibodies
... What seems to happen when an antibody comes in contact with an antigen? ...
... What seems to happen when an antibody comes in contact with an antigen? ...
Zika Virus - ascls-nd
... CD38 is a transmembrane glycoprotein expressed on the surface of hematopoietic cells. Daratumumab binds to CD38 and inhibits the growth of CD38 expressing tumor cells by inducing apoptosis directly through Fc mediated crosslinking as well as by immune-mediated tumor cell lysis through complement dep ...
... CD38 is a transmembrane glycoprotein expressed on the surface of hematopoietic cells. Daratumumab binds to CD38 and inhibits the growth of CD38 expressing tumor cells by inducing apoptosis directly through Fc mediated crosslinking as well as by immune-mediated tumor cell lysis through complement dep ...
Sickle Cell Donor Brochure
... used to cut grass or wheat, sickle cells become hard and sticky, and clog blood flow as they move through the small blood tubes, often causing extreme pain. Abnormal hemoglobin—inherited from both parents who either carry the sickle cell trait or have the disease—results in deformed, crescentshaped ...
... used to cut grass or wheat, sickle cells become hard and sticky, and clog blood flow as they move through the small blood tubes, often causing extreme pain. Abnormal hemoglobin—inherited from both parents who either carry the sickle cell trait or have the disease—results in deformed, crescentshaped ...
EDU-Thiede_SuppMaterials
... You’re in the park on a hot afternoon. Without warning, dark clouds form. Suddenly, there’s a flash of lightning. You hear loud thunder. Someone screams, you jump and everyone runs for cover. Your heart is pounding. Your body’s reaction to the sudden storm is caused by your endocrine system. The end ...
... You’re in the park on a hot afternoon. Without warning, dark clouds form. Suddenly, there’s a flash of lightning. You hear loud thunder. Someone screams, you jump and everyone runs for cover. Your heart is pounding. Your body’s reaction to the sudden storm is caused by your endocrine system. The end ...
Immunology - PharmaEuphoria
... Antigen types Based upon the ability of antigens to carry out their functions, antigens are of two types complete antigens Incomplete antigens (haptens) A complete antigen is able to induce antibody formation & produce a specific and observable reaction with the antibody so produced. Haptens are su ...
... Antigen types Based upon the ability of antigens to carry out their functions, antigens are of two types complete antigens Incomplete antigens (haptens) A complete antigen is able to induce antibody formation & produce a specific and observable reaction with the antibody so produced. Haptens are su ...
Blood ppt1 - John Bowne High School
... Type O people are universal donors for transfusions, but they can receive only type O blood themselves. Those with type AB blood do not make any ABO antibodies. Their blood does not discriminate against any other ABO type. Type AB people are universal receivers for transfusions, but their blood will ...
... Type O people are universal donors for transfusions, but they can receive only type O blood themselves. Those with type AB blood do not make any ABO antibodies. Their blood does not discriminate against any other ABO type. Type AB people are universal receivers for transfusions, but their blood will ...
CHAPTER 16: LYMPHATIC SYSTEM AND IMMUNITY OBJECTIVES
... Discuss the general structure of an antibody (immunoglobulin [Ig]). Resemble a Y, with 4 amino acid chains; 2 heavy chains, and 2 light chains. ...
... Discuss the general structure of an antibody (immunoglobulin [Ig]). Resemble a Y, with 4 amino acid chains; 2 heavy chains, and 2 light chains. ...
Methodological Instruction to Practical Lesson № 5
... 1. What is hemostasis pathology. With the help of the system of hemostasis blood carriers out one of its most significant functions –keeping itself in a liquid state and coagulation in case of a vessel’s wall injury and, this way, stopping the bleeding and keeping the initial volume and composition ...
... 1. What is hemostasis pathology. With the help of the system of hemostasis blood carriers out one of its most significant functions –keeping itself in a liquid state and coagulation in case of a vessel’s wall injury and, this way, stopping the bleeding and keeping the initial volume and composition ...
Blood Vessels
... heart failure, vascular disease, renal failure, and stroke • Primary or essential hypertension – 90% of hypertensive conditions – Due to several risk factors including heredity, diet, obesity, age, stress, diabetes mellitus, and smoking ...
... heart failure, vascular disease, renal failure, and stroke • Primary or essential hypertension – 90% of hypertensive conditions – Due to several risk factors including heredity, diet, obesity, age, stress, diabetes mellitus, and smoking ...
CP-72 – Blood/Body Fluid (BBF) Exposures in Employees
... exposure are defined in Attachment A. Evaluation includes screening and preventive intervention for hepatitis B and C and/or HIV-infected BBF based on the type and extent of exposure 3 following current Centers for Disease Control recommendations. Source patients may be screened for the above bloodb ...
... exposure are defined in Attachment A. Evaluation includes screening and preventive intervention for hepatitis B and C and/or HIV-infected BBF based on the type and extent of exposure 3 following current Centers for Disease Control recommendations. Source patients may be screened for the above bloodb ...
AACC JALMTalk Transcript Document
... And with over several million blood donations performed each year, there certainly continues to be a lot of debate in adding universal hemoglobinopathy screening. Getting back your question, when discussing this topic, I commonly come across several arguments, such as the extra added cost to screen ...
... And with over several million blood donations performed each year, there certainly continues to be a lot of debate in adding universal hemoglobinopathy screening. Getting back your question, when discussing this topic, I commonly come across several arguments, such as the extra added cost to screen ...
No Slide Title
... • Appear 2 to 8 months after birth; maximum concentration by 10 years of age – Antibody-A and/or antibody-B (both or none) are found in plasma • You do not form antibodies against your antigens ...
... • Appear 2 to 8 months after birth; maximum concentration by 10 years of age – Antibody-A and/or antibody-B (both or none) are found in plasma • You do not form antibodies against your antigens ...
Blood type
A blood type (also called a blood group) is a classification of blood based on the presence or absence of inherited antigenic substances on the surface of red blood cells (RBCs). These antigens may be proteins, carbohydrates, glycoproteins, or glycolipids, depending on the blood group system. Some of these antigens are also present on the surface of other types of cells of various tissues. Several of these red blood cell surface antigens can stem from one allele (or an alternative version of a gene) and collectively form a blood group system.Blood types are inherited and represent contributions from both parents. A total of 35 human blood group systems are now recognized by the International Society of Blood Transfusion (ISBT). The two most important ones are ABO and the RhD antigen; they determine someone's blood type (A, B, AB and O, with +, − or Null denoting RhD status).Many pregnant women carry a fetus with a blood type which is different from their own, which is not a problem. What can matter is whether the baby is RhD positive or negative. Mothers who are RhD- and carry a RhD+ baby can form antibodies against fetal RBCs. Sometimes these maternal antibodies are IgG, a small immunoglobulin, which can cross the placenta and cause hemolysis of fetal RBCs, which in turn can lead to hemolytic disease of the newborn called erythroblastosis fetalis, an illness of low fetal blood counts that ranges from mild to severe. Sometimes this is lethal for the fetus; in these cases it is called hydrops fetalis.