weighing up the risks: hazards of anaemia
... at keeping the DO2 above the DO2CRIT to maintain VO2 and therefore adequate tissue oxygenation. First there is a change in blood flow dynamics caused by the decreased viscosity seen in anaemic blood. This will lead to improved flow characteristics resulting in increased venous return and decreased s ...
... at keeping the DO2 above the DO2CRIT to maintain VO2 and therefore adequate tissue oxygenation. First there is a change in blood flow dynamics caused by the decreased viscosity seen in anaemic blood. This will lead to improved flow characteristics resulting in increased venous return and decreased s ...
Bacterial Antistest
... A single positive result has less significance than the demonstration of a rising or falling antibodies titer as evidence of infection. A clinical diagnosis should not be made on findings of a single test result, but should integrate both clinical and laboratory data. ...
... A single positive result has less significance than the demonstration of a rising or falling antibodies titer as evidence of infection. A clinical diagnosis should not be made on findings of a single test result, but should integrate both clinical and laboratory data. ...
Sentence-Beginnings
... and breaks up the monotony of the sentences. Blood donations must be processed carefully before they can be used. After They being are tested for infectious diseases and identified by blood type., they Theyare broken down into parts, such as red blood cells, platelets, and plasma. ...
... and breaks up the monotony of the sentences. Blood donations must be processed carefully before they can be used. After They being are tested for infectious diseases and identified by blood type., they Theyare broken down into parts, such as red blood cells, platelets, and plasma. ...
Chap 15
... each other. 5. Define pulse and locate the major pulse points on the body. 6. Define hypertension and its associated risk factors and complications. 7. Explain what is meant by the term circulatory shock and describe the major types. Copyright ©2014 by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved. ...
... each other. 5. Define pulse and locate the major pulse points on the body. 6. Define hypertension and its associated risk factors and complications. 7. Explain what is meant by the term circulatory shock and describe the major types. Copyright ©2014 by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved. ...
Chapter 42 Part I Circulatory Systems and the Human
... combination of ‘pulmonary’ and ‘cutaneous’) which carries blood to capillary beds lining both the lungs and the skin for purposes of gas exchange. When amphibians are underwater, they are able to shut off blood flow to their lungs (because they can no longer breath air), and shunt all of their blood ...
... combination of ‘pulmonary’ and ‘cutaneous’) which carries blood to capillary beds lining both the lungs and the skin for purposes of gas exchange. When amphibians are underwater, they are able to shut off blood flow to their lungs (because they can no longer breath air), and shunt all of their blood ...
Molecular genotyping and frequencies of A , A , B, O and O
... scientific point of view, chemical analysis of the group O antigen reveals that from a structural perspective it is the simplest blood group and it serves as the backbone for the synthesis of increasingly complex A, B and AB. These latter blood groups evolved by adding other sugar onto the basic O s ...
... scientific point of view, chemical analysis of the group O antigen reveals that from a structural perspective it is the simplest blood group and it serves as the backbone for the synthesis of increasingly complex A, B and AB. These latter blood groups evolved by adding other sugar onto the basic O s ...
Chemotherapeutic Effects on Hematopoiesis: A Mathematical Model
... that the chemotherapeutic drugs should be administered at integer multiples of the mean cell-cycle length of the normal tissue. They suggest that this method will be successful since the cancer cells have a longer mean cell-cycle time, thus placing them in the more sensitive phase while the normal t ...
... that the chemotherapeutic drugs should be administered at integer multiples of the mean cell-cycle length of the normal tissue. They suggest that this method will be successful since the cancer cells have a longer mean cell-cycle time, thus placing them in the more sensitive phase while the normal t ...
Principles of intravenous infusion/ blood transfusion (CFP)
... Errors can occur : – time of blood sample collection (incorrect labelling, blood taken from the wrong patient) – within the laboratory (use of incorrect sample or patient record; release of wrong unit from the store) – practice settings (administration to the wrong patient) Howard Griffiths, SHS ...
... Errors can occur : – time of blood sample collection (incorrect labelling, blood taken from the wrong patient) – within the laboratory (use of incorrect sample or patient record; release of wrong unit from the store) – practice settings (administration to the wrong patient) Howard Griffiths, SHS ...
LEUKOSES 467KB 06.09.2016
... This is the most common variety of leukaemia, accounting for 30% of cases. The male to female ratio is 2:1 and the median age at presentation is between 65 and 70 years. In this disease B lymphocytes, which would normally respond to antigens by transformation and antibody formation, fail to do so. A ...
... This is the most common variety of leukaemia, accounting for 30% of cases. The male to female ratio is 2:1 and the median age at presentation is between 65 and 70 years. In this disease B lymphocytes, which would normally respond to antigens by transformation and antibody formation, fail to do so. A ...
Factors That Predict Blood Loss After Bernese
... Although strategies to reduce bleeding and avoid allogeneic transfusion have been described, there is controversy about the factors associated with blood loss after Bernese periacetabular osteotomy. This study was conducted to determine risk factors for postoperative blood loss. After institutional ...
... Although strategies to reduce bleeding and avoid allogeneic transfusion have been described, there is controversy about the factors associated with blood loss after Bernese periacetabular osteotomy. This study was conducted to determine risk factors for postoperative blood loss. After institutional ...
Global Theme Article on Poverty and Human
... in many countries means that even a free or inexpensive drug cannot be reliably provided to those in need.36 In addition, whereas the cost of some generic drugs from wholesalers may be low, the price at which the same drug is provided to a patient is often grossly inflated. Moreover, there are often ...
... in many countries means that even a free or inexpensive drug cannot be reliably provided to those in need.36 In addition, whereas the cost of some generic drugs from wholesalers may be low, the price at which the same drug is provided to a patient is often grossly inflated. Moreover, there are often ...
1 - davis.k12.ut.us
... or the loss of the intrinsic factor from the lining of the stomach which prevents the absorption of vitamin B12. Not only is the number of erythrocytes reduced, but those cells that are produced are abnormally large and have fragile cell membranes. It is treated with injections of vitamin B12. 5. He ...
... or the loss of the intrinsic factor from the lining of the stomach which prevents the absorption of vitamin B12. Not only is the number of erythrocytes reduced, but those cells that are produced are abnormally large and have fragile cell membranes. It is treated with injections of vitamin B12. 5. He ...
f869c698c70a3fe
... • Exchanges ultimately occur at the cellular level by crossing the plasma membrane • In unicellular organisms, these exchanges occur directly with the environment ...
... • Exchanges ultimately occur at the cellular level by crossing the plasma membrane • In unicellular organisms, these exchanges occur directly with the environment ...
1 TE The Circulatory, Respiratory, Digestive, and Excretory Systems
... • emphysema: lung disease, usually caused by smoking, in which walls of alveoli break down, so less gas can be exchanged in the lungs • larynx: organ of the respiratory system between the pharynx and trachea that is also called the voice box because it allows the production of vocal sounds • lung: o ...
... • emphysema: lung disease, usually caused by smoking, in which walls of alveoli break down, so less gas can be exchanged in the lungs • larynx: organ of the respiratory system between the pharynx and trachea that is also called the voice box because it allows the production of vocal sounds • lung: o ...
Respiration, Circulation and Excretion
... Ask Does your heart ever stop beating? What does the heart do when we sleep? What does the heart do when we exercise? Have students look at the diagram of the human body. Ask them where the heart is (on the left-hand side of the chest). Tell students that the size of a person’s heart is approximatel ...
... Ask Does your heart ever stop beating? What does the heart do when we sleep? What does the heart do when we exercise? Have students look at the diagram of the human body. Ask them where the heart is (on the left-hand side of the chest). Tell students that the size of a person’s heart is approximatel ...
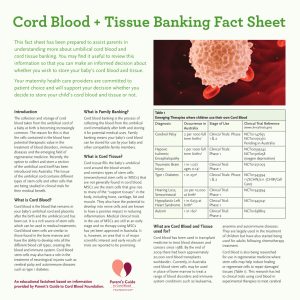
This fact sheet has been prepared to assist parents in
... after the birth of your baby, the umbilical cord is clamped and cut, separating your baby from you and the placenta. The collector will then clean the umbilical cord and collect the cord blood in a sterile collection bag. Cord tissue is collected after the cord blood has been collected. A short sect ...
... after the birth of your baby, the umbilical cord is clamped and cut, separating your baby from you and the placenta. The collector will then clean the umbilical cord and collect the cord blood in a sterile collection bag. Cord tissue is collected after the cord blood has been collected. A short sect ...
Lymphatic system
... causing microorganisms or pathogens, damage from foreign substances and harmful chemicals Lymphocytes B Lymphocytes – humoral (body fluids) immunity; produce antibodies; circulating bacteria and viral infections; attack the invading agents, become plasma cells in the tissues T Lymphocytes – cellul ...
... causing microorganisms or pathogens, damage from foreign substances and harmful chemicals Lymphocytes B Lymphocytes – humoral (body fluids) immunity; produce antibodies; circulating bacteria and viral infections; attack the invading agents, become plasma cells in the tissues T Lymphocytes – cellul ...
19-1 FUNCTIONS OF BLOOD 1. Transportation of gases, nutrients
... A. White blood cells containing large cytoplasmic granules that are easily seen with a light microscope when stained. 1) Neutrophils stain with both basic and acidic dyes. 2) Basophils stain with basic dyes. 3) Eosinophils stain with acidic dyes. B. White blood cells containing small cytoplasmic gra ...
... A. White blood cells containing large cytoplasmic granules that are easily seen with a light microscope when stained. 1) Neutrophils stain with both basic and acidic dyes. 2) Basophils stain with basic dyes. 3) Eosinophils stain with acidic dyes. B. White blood cells containing small cytoplasmic gra ...
Pedigree Powerpoint
... Many people have a Rh factor on the surface of their red blood cells. This is also an antigen and those who have it are called Rh+. Those who haven't are called Rh-. ...
... Many people have a Rh factor on the surface of their red blood cells. This is also an antigen and those who have it are called Rh+. Those who haven't are called Rh-. ...
Rapid identification of pneumococci, enterococci, beta-haemolytic streptococci and S.
... and complementary reports later that same day. The goal was mainly to discriminate among β-haemolytic, non-β-haemolytic streptococci, enterococci, S. aureus and coagulase-negative staphylococci (CoNS). This strategy does not aim to identify all species of gram-positive bacteria, rather a complement ...
... and complementary reports later that same day. The goal was mainly to discriminate among β-haemolytic, non-β-haemolytic streptococci, enterococci, S. aureus and coagulase-negative staphylococci (CoNS). This strategy does not aim to identify all species of gram-positive bacteria, rather a complement ...
ICSI Hypertension Diagnosis and Treatment
... • A standardized blood pressure measurement process is important for correctly classifying blood pressure. • Elevated blood pressure readings should be confirmed. • Self-monitoring of blood pressure should be encouraged in patients with elevated blood pressure. Accurate, reproducible blood pressu ...
... • A standardized blood pressure measurement process is important for correctly classifying blood pressure. • Elevated blood pressure readings should be confirmed. • Self-monitoring of blood pressure should be encouraged in patients with elevated blood pressure. Accurate, reproducible blood pressu ...
1 THE CIRCULATORY SYSTEM Types of Circulatory Systems
... Plasma is the liquid component of the blood. Mammalian blood consists of a liquid (plasma) and a number of cellular and cell fragment components as shown in Figure 21. Plasma is about 60 % of a volume of blood; cells and fragments are 40%. Plasma has 90% water and 10% dissolved materials including p ...
... Plasma is the liquid component of the blood. Mammalian blood consists of a liquid (plasma) and a number of cellular and cell fragment components as shown in Figure 21. Plasma is about 60 % of a volume of blood; cells and fragments are 40%. Plasma has 90% water and 10% dissolved materials including p ...
19-5 White Blood Cells
... may die before delivery or shortly thereafter. A newborn with sever HDN is anemic, and the high concentration of circulating bilirubin produces jaundice. Because the maternal antibodies remain active in the newborn for one to two months after delivery, the infant’s entire blood volume may require re ...
... may die before delivery or shortly thereafter. A newborn with sever HDN is anemic, and the high concentration of circulating bilirubin produces jaundice. Because the maternal antibodies remain active in the newborn for one to two months after delivery, the infant’s entire blood volume may require re ...
Blood type
A blood type (also called a blood group) is a classification of blood based on the presence or absence of inherited antigenic substances on the surface of red blood cells (RBCs). These antigens may be proteins, carbohydrates, glycoproteins, or glycolipids, depending on the blood group system. Some of these antigens are also present on the surface of other types of cells of various tissues. Several of these red blood cell surface antigens can stem from one allele (or an alternative version of a gene) and collectively form a blood group system.Blood types are inherited and represent contributions from both parents. A total of 35 human blood group systems are now recognized by the International Society of Blood Transfusion (ISBT). The two most important ones are ABO and the RhD antigen; they determine someone's blood type (A, B, AB and O, with +, − or Null denoting RhD status).Many pregnant women carry a fetus with a blood type which is different from their own, which is not a problem. What can matter is whether the baby is RhD positive or negative. Mothers who are RhD- and carry a RhD+ baby can form antibodies against fetal RBCs. Sometimes these maternal antibodies are IgG, a small immunoglobulin, which can cross the placenta and cause hemolysis of fetal RBCs, which in turn can lead to hemolytic disease of the newborn called erythroblastosis fetalis, an illness of low fetal blood counts that ranges from mild to severe. Sometimes this is lethal for the fetus; in these cases it is called hydrops fetalis.