Blood
... – Electrolytes most abundant solutes by number – Plasma proteins most abundant solutes by mass • Remain in blood; not taken up by cells • Proteins produced mostly by liver • 60% albumin; 36% globulins; 4% fibrinogen © 2013 Pearson Education, Inc. ...
... – Electrolytes most abundant solutes by number – Plasma proteins most abundant solutes by mass • Remain in blood; not taken up by cells • Proteins produced mostly by liver • 60% albumin; 36% globulins; 4% fibrinogen © 2013 Pearson Education, Inc. ...
Allegany County Sheriff`s Department Title: Infectious Disease Control
... sputum, vomit, sweat, tears, urine, or saliva (except when blood is visible) E. Exposure- direct contact with body fluids on open cuts, breaks in the skin, or mucous membranes such as the mouth or eyes F. Universal Precautions- procedures used by personnel which assumes that any other person has a c ...
... sputum, vomit, sweat, tears, urine, or saliva (except when blood is visible) E. Exposure- direct contact with body fluids on open cuts, breaks in the skin, or mucous membranes such as the mouth or eyes F. Universal Precautions- procedures used by personnel which assumes that any other person has a c ...
Blood Clotting - Meridian Kinesiology
... Blood Clotting is necessary for the repair of damaged Blood Vessels (as occurs during Bleeding) but is detrimental when it occurs in the absence of damage to the Blood Vessels - hence the term Abnormal Blood Clotting. Biology of Blood Clots Cardiovascular System During bleeding, Platelets flow throu ...
... Blood Clotting is necessary for the repair of damaged Blood Vessels (as occurs during Bleeding) but is detrimental when it occurs in the absence of damage to the Blood Vessels - hence the term Abnormal Blood Clotting. Biology of Blood Clots Cardiovascular System During bleeding, Platelets flow throu ...
The fetal circulation - Pitt Honors Human Physiology
... The fetal circulation (Fig. 1) is markedly different from the adult circulation. In the fetus, gas exchange does not occur in the lungs but in the placenta. The placenta must therefore receive deoxygenated blood from the fetal systemic organs and return its oxygen rich venous drainage to the fetal s ...
... The fetal circulation (Fig. 1) is markedly different from the adult circulation. In the fetus, gas exchange does not occur in the lungs but in the placenta. The placenta must therefore receive deoxygenated blood from the fetal systemic organs and return its oxygen rich venous drainage to the fetal s ...
Body Fluids
... Blood Clotting When body tissues are damaged, the blood flow must be stopped or else enough of it will pour out to cause death. The mechanism used by the body to stem leaks in the blood vessels is clotting. This complicated process involves many factors. Here we mention only a few important steps. W ...
... Blood Clotting When body tissues are damaged, the blood flow must be stopped or else enough of it will pour out to cause death. The mechanism used by the body to stem leaks in the blood vessels is clotting. This complicated process involves many factors. Here we mention only a few important steps. W ...
The fetal circulation
... The fetal circulation (Fig. 1) is markedly different from the adult circulation. In the fetus, gas exchange does not occur in the lungs but in the placenta. The placenta must therefore receive deoxygenated blood from the fetal systemic organs and return its oxygen rich venous drainage to the fetal s ...
... The fetal circulation (Fig. 1) is markedly different from the adult circulation. In the fetus, gas exchange does not occur in the lungs but in the placenta. The placenta must therefore receive deoxygenated blood from the fetal systemic organs and return its oxygen rich venous drainage to the fetal s ...
Moving on from voluntary nonremunerated donors: who is the best
... donors is that they are volunteer donors and they are unpaid. Furthermore, they are benevolent, but their altruistic move is limited towards people they know and love instead of being directed towards unknown people. It is true, however, that they are under pressure to donate, particularly when the ...
... donors is that they are volunteer donors and they are unpaid. Furthermore, they are benevolent, but their altruistic move is limited towards people they know and love instead of being directed towards unknown people. It is true, however, that they are under pressure to donate, particularly when the ...
Urinary System
... bicarbonate, and phosphates are regulated by the amount that the kidney excretes. Regulation of plasma osmolarity. The kidneys regulate osmolarity because they have direct control over how many ions and how much water a person excretes. Regulation of plasma volume. Your kidneys are so important they ...
... bicarbonate, and phosphates are regulated by the amount that the kidney excretes. Regulation of plasma osmolarity. The kidneys regulate osmolarity because they have direct control over how many ions and how much water a person excretes. Regulation of plasma volume. Your kidneys are so important they ...
ch_19_lecture_outline_a
... • Function in absorption or filtrate formation (small intestines, endocrine glands, and kidneys) ...
... • Function in absorption or filtrate formation (small intestines, endocrine glands, and kidneys) ...
Obtaining Coagulation Blood Samples From Central Venous Access
... they are widely used in other specialty populations as well. During the course of treatment, many patients will require the use of CVADs, including peripherally inserted central catheters (PICCs), tunneled catheters, or implanted ports. These devices are used for medication administration, blood pro ...
... they are widely used in other specialty populations as well. During the course of treatment, many patients will require the use of CVADs, including peripherally inserted central catheters (PICCs), tunneled catheters, or implanted ports. These devices are used for medication administration, blood pro ...
Neonatal sepsis early detection and antibiotics choice
... Clinical signs of sepsis in VLBW infants NICHD network study ...
... Clinical signs of sepsis in VLBW infants NICHD network study ...
Document
... Background • There is a high global burden of Inf. Dis. in the very young. • Immunity is not static; it changes with age, with many distinctive features in early life. • Newborns and young infants have distinct immune ontogeny and responses to microbes. Dowling & Levy. Trend in Immunology 2014 35(7 ...
... Background • There is a high global burden of Inf. Dis. in the very young. • Immunity is not static; it changes with age, with many distinctive features in early life. • Newborns and young infants have distinct immune ontogeny and responses to microbes. Dowling & Levy. Trend in Immunology 2014 35(7 ...
14.3 The heart
... Question 2: What do you observe when carbon dioxide is bubbled through the blood? Explain. Answer 2: The blood turns purplish red when carbon dioxide is bubbled through it because oxyhaemoglobin gives up oxygen and is changed back into haemoglobin when the carbon dioxide concentrations is high. ...
... Question 2: What do you observe when carbon dioxide is bubbled through the blood? Explain. Answer 2: The blood turns purplish red when carbon dioxide is bubbled through it because oxyhaemoglobin gives up oxygen and is changed back into haemoglobin when the carbon dioxide concentrations is high. ...
Insulin Delivery
... pancreatic beta cells, the only cells that make insulin. Low levels of insulin production cannot adequately regulate blood sugar levels Can be caused by autoimmune, genetic, or environmental factors Patients must administer insulin multiple times daily, especially before meal times ...
... pancreatic beta cells, the only cells that make insulin. Low levels of insulin production cannot adequately regulate blood sugar levels Can be caused by autoimmune, genetic, or environmental factors Patients must administer insulin multiple times daily, especially before meal times ...
rajiv gandhi university of health sciences, bangalore, karnataka
... patients’ weight. Initial dose of 10-15 ml/kg body weight is usually given. As this is an empirical dose, laboratory test should be used to monitor the efficacy and the result of these tests as well as the patients’ clinical response should guide any further dosing requirement. ABO compatible FFP sh ...
... patients’ weight. Initial dose of 10-15 ml/kg body weight is usually given. As this is an empirical dose, laboratory test should be used to monitor the efficacy and the result of these tests as well as the patients’ clinical response should guide any further dosing requirement. ABO compatible FFP sh ...
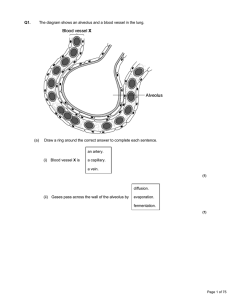
Q1. The diagram shows an alveolus and a blood vessel in the lung
... The student then did some exercise for two minutes. The volume breathed out in five breaths was again measured. This time there was 9000 cm3 of air in the bag. What does this tell you about the effect of exercise on breathing? ...
... The student then did some exercise for two minutes. The volume breathed out in five breaths was again measured. This time there was 9000 cm3 of air in the bag. What does this tell you about the effect of exercise on breathing? ...
Rh-Mediated Isoimmune Hemolytic Disease
... Define Rh-isoimmune disease as it relates to a newborn Review abnormal indices in Rh-isoimmune disease Discuss therapies for hyperbilirubinemia Review complications of exchange transfusion Identify complications of phototherapy ...
... Define Rh-isoimmune disease as it relates to a newborn Review abnormal indices in Rh-isoimmune disease Discuss therapies for hyperbilirubinemia Review complications of exchange transfusion Identify complications of phototherapy ...
Respiratory System
... • Hb + O2 HbO2 – at cells where O2 is being used and plasma PO2 decreases, O2 detaches from Hb and enters the cell • HbO2 → Hb + O2 • Overall the binding of oxygen to hemoglobin is reversible and is expressed as Hb + O2 ↔ HbO2 – if O2 increases, then reaction shifts to the right – if O2 decreases, t ...
... • Hb + O2 HbO2 – at cells where O2 is being used and plasma PO2 decreases, O2 detaches from Hb and enters the cell • HbO2 → Hb + O2 • Overall the binding of oxygen to hemoglobin is reversible and is expressed as Hb + O2 ↔ HbO2 – if O2 increases, then reaction shifts to the right – if O2 decreases, t ...
ANTIGEN – ANTIBODY REACTIONS
... Immunoflourescence (IF) is a technique based on the antigen-antibody reaction for detection of particular molecule that uses antibodies labeled with fluorescent dye (fluorochrome). Fluorescence is the emission of light by a substance that has absorbed light or other electromagnetic radiation (It is ...
... Immunoflourescence (IF) is a technique based on the antigen-antibody reaction for detection of particular molecule that uses antibodies labeled with fluorescent dye (fluorochrome). Fluorescence is the emission of light by a substance that has absorbed light or other electromagnetic radiation (It is ...
Blood Type Diet Tutorial Is this diet right for you?
... Rh negative. About 90 to 95 percent of African Americans and 98 to 99 percent of Asians are Rh-positive. Also, since pathologist Karl Landsteiner identified the four blood groups early in the twentieth century, 276 discrete red-cell antigens have been discovered. Maybe D'Adamo should have 276 discre ...
... Rh negative. About 90 to 95 percent of African Americans and 98 to 99 percent of Asians are Rh-positive. Also, since pathologist Karl Landsteiner identified the four blood groups early in the twentieth century, 276 discrete red-cell antigens have been discovered. Maybe D'Adamo should have 276 discre ...
Blood type
A blood type (also called a blood group) is a classification of blood based on the presence or absence of inherited antigenic substances on the surface of red blood cells (RBCs). These antigens may be proteins, carbohydrates, glycoproteins, or glycolipids, depending on the blood group system. Some of these antigens are also present on the surface of other types of cells of various tissues. Several of these red blood cell surface antigens can stem from one allele (or an alternative version of a gene) and collectively form a blood group system.Blood types are inherited and represent contributions from both parents. A total of 35 human blood group systems are now recognized by the International Society of Blood Transfusion (ISBT). The two most important ones are ABO and the RhD antigen; they determine someone's blood type (A, B, AB and O, with +, − or Null denoting RhD status).Many pregnant women carry a fetus with a blood type which is different from their own, which is not a problem. What can matter is whether the baby is RhD positive or negative. Mothers who are RhD- and carry a RhD+ baby can form antibodies against fetal RBCs. Sometimes these maternal antibodies are IgG, a small immunoglobulin, which can cross the placenta and cause hemolysis of fetal RBCs, which in turn can lead to hemolytic disease of the newborn called erythroblastosis fetalis, an illness of low fetal blood counts that ranges from mild to severe. Sometimes this is lethal for the fetus; in these cases it is called hydrops fetalis.