Unit 2
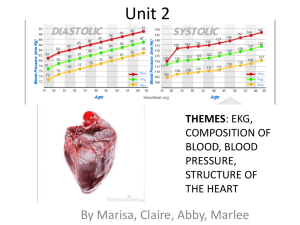
... • High blood pressure- heart disease, kidney failure. • Low blood pressure- kidney failure and chest pain. • Systolic- pumping pressure measured in your arteries(higher number) • Diastolic- hearts resting pressure measured in your arteries(lower number) ...
... • High blood pressure- heart disease, kidney failure. • Low blood pressure- kidney failure and chest pain. • Systolic- pumping pressure measured in your arteries(higher number) • Diastolic- hearts resting pressure measured in your arteries(lower number) ...
LOYOLA COLLEGE (AUTONOMOUS), CHENNAI – 600 034
... 02. Define the term: universal donor. 03. What is occult blood? 04. Distinguish type 1 from type 2 Diabetes mellitus. 05. What is meant by storage lesion. 06. Distinguish leucopenia from polycythemia. 07. Write the procedure for the detection of bile salts in urine sample. 08. Give the names of any ...
... 02. Define the term: universal donor. 03. What is occult blood? 04. Distinguish type 1 from type 2 Diabetes mellitus. 05. What is meant by storage lesion. 06. Distinguish leucopenia from polycythemia. 07. Write the procedure for the detection of bile salts in urine sample. 08. Give the names of any ...
Ch 4 Les 1 SG Master
... What component of the air is needed by all of the body’s cells? ____________________________________________________________________________ ____________________________________________________________________________ ____________________________________________________________________________ ...
... What component of the air is needed by all of the body’s cells? ____________________________________________________________________________ ____________________________________________________________________________ ____________________________________________________________________________ ...
Unit B3, B3.2.1 - GCSE Biology Revision
... A ventricle fills with blood by the contraction of .................................................. . When a ventricle contracts, blood is forced into .................................................... . When a ventricle relaxes, the backflow of blood into it is prevented by the closing of ...
... A ventricle fills with blood by the contraction of .................................................. . When a ventricle contracts, blood is forced into .................................................... . When a ventricle relaxes, the backflow of blood into it is prevented by the closing of ...
Unit B3, B3.2.1
... A ventricle fills with blood by the contraction of .................................................. . When a ventricle contracts, blood is forced into .................................................... . When a ventricle relaxes, the backflow of blood into it is prevented by the closing of ...
... A ventricle fills with blood by the contraction of .................................................. . When a ventricle contracts, blood is forced into .................................................... . When a ventricle relaxes, the backflow of blood into it is prevented by the closing of ...
Answers to WHAT DID YOU LEARN questions
... blood type A would not be successful. The person with blood type A has anti-B antibodies and would react to the B surface antigens in the donor’s blood, causing the blood to agglutinate. ...
... blood type A would not be successful. The person with blood type A has anti-B antibodies and would react to the B surface antigens in the donor’s blood, causing the blood to agglutinate. ...
ch 8 diagnostic review
... 15. Type (A +) blood would show “clumping” (as pictured in “b”) when combined with: anti-A anti-B anti-Rh all of the above none of the above 16. Red stains that have tested positive for blood would then be subjected to this monoclonal-antibody based test to determine whether it is from a human or an ...
... 15. Type (A +) blood would show “clumping” (as pictured in “b”) when combined with: anti-A anti-B anti-Rh all of the above none of the above 16. Red stains that have tested positive for blood would then be subjected to this monoclonal-antibody based test to determine whether it is from a human or an ...
Circulatory & Respiratory System Flashcards
... Which type of circulation carries blood from the heart to the rest of the body? ...
... Which type of circulation carries blood from the heart to the rest of the body? ...
Incorporating the Review and Assessment SIOP Component into an
... Directions: Complete the paragraph by providing the correct term from the word bank. Each term may only be used once. plasma ...
... Directions: Complete the paragraph by providing the correct term from the word bank. Each term may only be used once. plasma ...
ABO AND RH SYSTEM (Blood Grouping) • LEARNING OBJECTIVE
... • When blood type of parents known possible genotypes can be predicted • Blood type of child matching with father is used for proving the parental father. ...
... • When blood type of parents known possible genotypes can be predicted • Blood type of child matching with father is used for proving the parental father. ...
Quiz 2 - Delmar
... Multiple Choice 1. _____ is the most abundant of the plasma proteins. a. Fibrinogen b. Albumin c. Globulin d. Prothrombin 2. _____ is vital to the function of the red blood cell, helping it transport oxygen to the tissues and some carbon dioxide away from tissues. a. Hemoglobin b. Albumin c. Fibrino ...
... Multiple Choice 1. _____ is the most abundant of the plasma proteins. a. Fibrinogen b. Albumin c. Globulin d. Prothrombin 2. _____ is vital to the function of the red blood cell, helping it transport oxygen to the tissues and some carbon dioxide away from tissues. a. Hemoglobin b. Albumin c. Fibrino ...
Blood and Oxygen - science-teachers
... This is a banned process where an athlete receives a blood transfusion of red blood cells (usually their own, collected at an earlier time) to increase the oxygen carrying capacity of their blood. ...
... This is a banned process where an athlete receives a blood transfusion of red blood cells (usually their own, collected at an earlier time) to increase the oxygen carrying capacity of their blood. ...
Circulatory System: Blood system transporting materials in the body
... Blood: Red Blood Cells: carries O2 & CO2 White Blood Cells: fight off disease Plasma: carries food, protein, & nitrogen wastes Blood Vessels: Arteries: always carry blood away from heart; thick walls, generally high in O2 Veins: always carry blood to the heart; thinner walls, generally low in O2 Ca ...
... Blood: Red Blood Cells: carries O2 & CO2 White Blood Cells: fight off disease Plasma: carries food, protein, & nitrogen wastes Blood Vessels: Arteries: always carry blood away from heart; thick walls, generally high in O2 Veins: always carry blood to the heart; thinner walls, generally low in O2 Ca ...
ABO Blood Types
... important blood types are in the ABO group. They were discovered in 1900 and 1901 at the University of Vienna by Karl Landsteiner in the process of trying to learn why blood transfusions sometimes cause death and at other times save a patient. In 1930, he belatedly received the Nobel Prize for his d ...
... important blood types are in the ABO group. They were discovered in 1900 and 1901 at the University of Vienna by Karl Landsteiner in the process of trying to learn why blood transfusions sometimes cause death and at other times save a patient. In 1930, he belatedly received the Nobel Prize for his d ...
Haemolytic Anaemias due to Extrinsic Factors
... but at the time of delivery fetal RBCs pass to maternal circulation and the mother may become sensitized ( produces anti-D antibodies ), the second baby will usually have severe anaemia with severe jaundice ( 2nd or 3rd day ) and may develop kernicterus with severe neurological defects unless prompt ...
... but at the time of delivery fetal RBCs pass to maternal circulation and the mother may become sensitized ( produces anti-D antibodies ), the second baby will usually have severe anaemia with severe jaundice ( 2nd or 3rd day ) and may develop kernicterus with severe neurological defects unless prompt ...
IV Blood – delivers oxygen, hormones and nutrients to cells and
... B. Red Blood Cells (RBC) – carry oxygen from the lungs to the body. a. Hemoglobin – responsible for giving blood it’s red tint. b. RBC – carry CO2 (Carbon Dioxide) the lungs so it can be exhaled from the body. C. White Blood Cells (WBC) – responsible for fighting infections. a. T-cells and B-cells b ...
... B. Red Blood Cells (RBC) – carry oxygen from the lungs to the body. a. Hemoglobin – responsible for giving blood it’s red tint. b. RBC – carry CO2 (Carbon Dioxide) the lungs so it can be exhaled from the body. C. White Blood Cells (WBC) – responsible for fighting infections. a. T-cells and B-cells b ...
Review of Blood type and Rh
... Rh isoimmunization Rh isoimmunization occurs when an Rh negative mother has an Rh positive child causes the destruction of the infant’s red blood cells (anemia) during pregnancy and after birth ...
... Rh isoimmunization Rh isoimmunization occurs when an Rh negative mother has an Rh positive child causes the destruction of the infant’s red blood cells (anemia) during pregnancy and after birth ...
Blood type
A blood type (also called a blood group) is a classification of blood based on the presence or absence of inherited antigenic substances on the surface of red blood cells (RBCs). These antigens may be proteins, carbohydrates, glycoproteins, or glycolipids, depending on the blood group system. Some of these antigens are also present on the surface of other types of cells of various tissues. Several of these red blood cell surface antigens can stem from one allele (or an alternative version of a gene) and collectively form a blood group system.Blood types are inherited and represent contributions from both parents. A total of 35 human blood group systems are now recognized by the International Society of Blood Transfusion (ISBT). The two most important ones are ABO and the RhD antigen; they determine someone's blood type (A, B, AB and O, with +, − or Null denoting RhD status).Many pregnant women carry a fetus with a blood type which is different from their own, which is not a problem. What can matter is whether the baby is RhD positive or negative. Mothers who are RhD- and carry a RhD+ baby can form antibodies against fetal RBCs. Sometimes these maternal antibodies are IgG, a small immunoglobulin, which can cross the placenta and cause hemolysis of fetal RBCs, which in turn can lead to hemolytic disease of the newborn called erythroblastosis fetalis, an illness of low fetal blood counts that ranges from mild to severe. Sometimes this is lethal for the fetus; in these cases it is called hydrops fetalis.