Study Guide for Exam II
... How can you tell the difference between a monocot and a dicot? Name the 3 tissue types for plants and name their functions. Name the 3 organ types for plants and describe their function. What is the difference between xylem and phloem? What organ are stomata found on and what do they do? Why are sto ...
... How can you tell the difference between a monocot and a dicot? Name the 3 tissue types for plants and name their functions. Name the 3 organ types for plants and describe their function. What is the difference between xylem and phloem? What organ are stomata found on and what do they do? Why are sto ...
Karl Landsteiner - OldForensics 2012-2013
... discovered the Rh factor, which helped save the lives of many fetuses with mismatched Rh factors from their mothers. ...
... discovered the Rh factor, which helped save the lives of many fetuses with mismatched Rh factors from their mothers. ...
Worksheet 13 Multiple choice Which of these statements is false? A
... 98% of Oxygen from the alveoli is carried by hemoglobin in red blood cells At the lungs, O2 comes in, diffuses through pulmonary capillary wall, into red blood cell’s cytoplasm O2 binds to Hb. This binding releases H+ from hemoglobin. H+ then reacts with the bicarbonate in red blood cell to form car ...
... 98% of Oxygen from the alveoli is carried by hemoglobin in red blood cells At the lungs, O2 comes in, diffuses through pulmonary capillary wall, into red blood cell’s cytoplasm O2 binds to Hb. This binding releases H+ from hemoglobin. H+ then reacts with the bicarbonate in red blood cell to form car ...
Lesson 5 - saddlespace.org
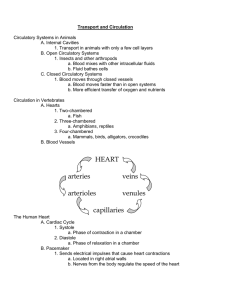
... • arteries carry blood away from the heart to various organs • veins carry blood from various parts of the body back to the heart • Capillaries are very small tubes that connect arteries and veins. Some capillaries are so small you need a microscope to see them. ...
... • arteries carry blood away from the heart to various organs • veins carry blood from various parts of the body back to the heart • Capillaries are very small tubes that connect arteries and veins. Some capillaries are so small you need a microscope to see them. ...
life processes
... blood, blood vessels and heart • Blood: blood is a liquid connective tissue. It consists of a fluid matrix called plasma and solid constituents such as red blood corpuscles, white blood corpuscles and platelets. ...
... blood, blood vessels and heart • Blood: blood is a liquid connective tissue. It consists of a fluid matrix called plasma and solid constituents such as red blood corpuscles, white blood corpuscles and platelets. ...
HemaSpot™: Advanced Blood Sampling Introduction HemaSpot Design
... finger stick to collect and dry blood within a protective cartridge. Once dried, the sample is stable at ambient temperature and can be safely and easily shipped to a diagnostic test site for analysis. Based on dried blood spot technology and leveraging the phenomenal success of newborn blood screen ...
... finger stick to collect and dry blood within a protective cartridge. Once dried, the sample is stable at ambient temperature and can be safely and easily shipped to a diagnostic test site for analysis. Based on dried blood spot technology and leveraging the phenomenal success of newborn blood screen ...
Human Blood Typing Lab
... 2. Describe the appearance of agglutinated blood. 3. Explain how to determine a human blood type. 4. Using data, determine the blood type for each person. ...
... 2. Describe the appearance of agglutinated blood. 3. Explain how to determine a human blood type. 4. Using data, determine the blood type for each person. ...
Circulatory Quiz
... 7. Name the largest vein in the body and its division. 8. What are the components of blood, as discussed in class. ...
... 7. Name the largest vein in the body and its division. 8. What are the components of blood, as discussed in class. ...
Chapter 14 Forensic Serology CHAPTER OVERVIEW • Serology
... Serology involves a broad scope of laboratory tests that use specific antigen and serum antibody reactions. ...
... Serology involves a broad scope of laboratory tests that use specific antigen and serum antibody reactions. ...
Blood typing
... • A man with type AB blood is married to a woman with type O blood. They have two natural children, and one adopted child. The children's blood types are: A, B, and O. Which child was adopted? ...
... • A man with type AB blood is married to a woman with type O blood. They have two natural children, and one adopted child. The children's blood types are: A, B, and O. Which child was adopted? ...
Unit 6: Human Health And Physiology
... • Veins- generally move blood toward the heart. Have thinner walls and interior valves to prevent backflow. • Arteries- generally move blood away from the heart. Have thick walls but no interior valves. • Capillaries- bridges between arteries and veins. Capillary tissue is only 1 cell width thick, e ...
... • Veins- generally move blood toward the heart. Have thinner walls and interior valves to prevent backflow. • Arteries- generally move blood away from the heart. Have thick walls but no interior valves. • Capillaries- bridges between arteries and veins. Capillary tissue is only 1 cell width thick, e ...
Blood
... In addition to the four blood types, there is a positive and negative component in the blood, known as the Rh factor. Rh+ (positive) blood contains this factor, and Rh- (negative) blood does not. The Rh factor is a type of antigen, or substance that causes the body to produce ...
... In addition to the four blood types, there is a positive and negative component in the blood, known as the Rh factor. Rh+ (positive) blood contains this factor, and Rh- (negative) blood does not. The Rh factor is a type of antigen, or substance that causes the body to produce ...
Blood
... In addition to the four blood types, there is a positive and negative component in the blood, known as the Rh factor. Rh+ (positive) blood contains this factor, and Rh- (negative) blood does not. The Rh factor is a type of antigen, or substance that causes the body to produce ...
... In addition to the four blood types, there is a positive and negative component in the blood, known as the Rh factor. Rh+ (positive) blood contains this factor, and Rh- (negative) blood does not. The Rh factor is a type of antigen, or substance that causes the body to produce ...
HEART arteries veins arterioles venules capillaries
... 2. Nerve signals can make arteries constrict or dilate B. Veins 1. Thinner, less elastic, less muscle than arteries 2. Lower pressure than arteries 3. Valves and gravity aid flow back to the heart C. Capillaries 1. One cell thick 2. Where transfer of gases and nutrients takes place Composition of Bl ...
... 2. Nerve signals can make arteries constrict or dilate B. Veins 1. Thinner, less elastic, less muscle than arteries 2. Lower pressure than arteries 3. Valves and gravity aid flow back to the heart C. Capillaries 1. One cell thick 2. Where transfer of gases and nutrients takes place Composition of Bl ...
Blood Cycle Fact File
... litres of blood in their body A child (36kg) has around 2.352.75 litres of blood in their body Blood travels at 3 feet per second, but slows down as it gets into smaller arteries and capillaries It takes about 1 minute for your blood to go around your body, even faster if you are running Oxy ...
... litres of blood in their body A child (36kg) has around 2.352.75 litres of blood in their body Blood travels at 3 feet per second, but slows down as it gets into smaller arteries and capillaries It takes about 1 minute for your blood to go around your body, even faster if you are running Oxy ...
Document
... 3. Leo has B blood type. His wife Sherri has AB blood. Half of their children have AB blood, and half of their children have B blood. ...
... 3. Leo has B blood type. His wife Sherri has AB blood. Half of their children have AB blood, and half of their children have B blood. ...
SECOND TRIMESTER Unit Two: Human Body Systems Standards
... 3. marrow – soft tissue in center of many bones. Red marrow in end of bones produces blood cells. Yellow marrow in the middle has fat cells. B. Bone connectors 1. cartilage – rubbery tissue between bones; acts as a cushion 2. ligament – strands of tough tissue 3. joints – point at which two bones mo ...
... 3. marrow – soft tissue in center of many bones. Red marrow in end of bones produces blood cells. Yellow marrow in the middle has fat cells. B. Bone connectors 1. cartilage – rubbery tissue between bones; acts as a cushion 2. ligament – strands of tough tissue 3. joints – point at which two bones mo ...
Jeopardy
... that form scabs to stop cuts from bleeding and also prevent blood from leaking through capillaries ...
... that form scabs to stop cuts from bleeding and also prevent blood from leaking through capillaries ...
blood - Yengage
... At the end of the class, student should be able to: 1. Describe composition & functions of blood 2. Define Packed Cell Volume, factors affecting & methods of its determination. 3. Describe plasma proteins – types, concentration, functions and variations. ...
... At the end of the class, student should be able to: 1. Describe composition & functions of blood 2. Define Packed Cell Volume, factors affecting & methods of its determination. 3. Describe plasma proteins – types, concentration, functions and variations. ...
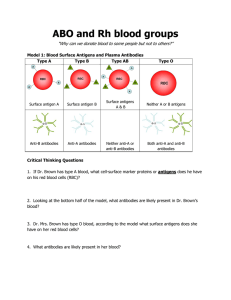
ABO and Rh blood groups
... 7. What reaction occurs between the donor's red blood cells and the recipient's opposing antibodies? a. What process follows agglutination? 8. Blood mis-matches can result in a condition called Acute Hemolytic Reaction. What are the symptoms of this reaction? ...
... 7. What reaction occurs between the donor's red blood cells and the recipient's opposing antibodies? a. What process follows agglutination? 8. Blood mis-matches can result in a condition called Acute Hemolytic Reaction. What are the symptoms of this reaction? ...
Blood type
A blood type (also called a blood group) is a classification of blood based on the presence or absence of inherited antigenic substances on the surface of red blood cells (RBCs). These antigens may be proteins, carbohydrates, glycoproteins, or glycolipids, depending on the blood group system. Some of these antigens are also present on the surface of other types of cells of various tissues. Several of these red blood cell surface antigens can stem from one allele (or an alternative version of a gene) and collectively form a blood group system.Blood types are inherited and represent contributions from both parents. A total of 35 human blood group systems are now recognized by the International Society of Blood Transfusion (ISBT). The two most important ones are ABO and the RhD antigen; they determine someone's blood type (A, B, AB and O, with +, − or Null denoting RhD status).Many pregnant women carry a fetus with a blood type which is different from their own, which is not a problem. What can matter is whether the baby is RhD positive or negative. Mothers who are RhD- and carry a RhD+ baby can form antibodies against fetal RBCs. Sometimes these maternal antibodies are IgG, a small immunoglobulin, which can cross the placenta and cause hemolysis of fetal RBCs, which in turn can lead to hemolytic disease of the newborn called erythroblastosis fetalis, an illness of low fetal blood counts that ranges from mild to severe. Sometimes this is lethal for the fetus; in these cases it is called hydrops fetalis.