Slide 1
... Rh+ means the RBCs carry the Rh antigen. If an Rh- person receives Rh+ blood, their immune system will react to the transfusion and the patient’s antibodies will attack and kill the new blood cells. How could an Rh+ woman became pregnant with an Rhbaby and what would happen to the baby? ...
... Rh+ means the RBCs carry the Rh antigen. If an Rh- person receives Rh+ blood, their immune system will react to the transfusion and the patient’s antibodies will attack and kill the new blood cells. How could an Rh+ woman became pregnant with an Rhbaby and what would happen to the baby? ...
Biology 11 Name Blood Types Crime Lab Purpose: To determine
... Why is it necessary to match the donor’s and the recipient’s blood before a transfusion? (2 mark) ...
... Why is it necessary to match the donor’s and the recipient’s blood before a transfusion? (2 mark) ...
Genetics of Blood
... _________________ is considered to be the _________________ _________________ is considered to be the _________________ ...
... _________________ is considered to be the _________________ _________________ is considered to be the _________________ ...
Object 23: ABO blood types
... Blood transfusion has been practised for hundreds of years but it is only since the mid twentieth century that it has been safe; before that many transfusion recipients died. The reason for this was not understood until the ABO system of blood types was discovered by the Austrian physician Karl Land ...
... Blood transfusion has been practised for hundreds of years but it is only since the mid twentieth century that it has been safe; before that many transfusion recipients died. The reason for this was not understood until the ABO system of blood types was discovered by the Austrian physician Karl Land ...
Chapter 7: Blood
... Vessel injury results in vascular spasms. If that doesn’t seal leak, a platelet plug might. Otherwise, clot formation occurs: This involves a series of chemical reactions which require clotting factors and Vitamin K., resulting in a tangled clot of the protein fibrin. Hemophiliacs lack clotting fact ...
... Vessel injury results in vascular spasms. If that doesn’t seal leak, a platelet plug might. Otherwise, clot formation occurs: This involves a series of chemical reactions which require clotting factors and Vitamin K., resulting in a tangled clot of the protein fibrin. Hemophiliacs lack clotting fact ...
STUDY GUIDE FOR UNIT 11 The Immune System Chapters: 37
... STUDY GUIDE FOR UNIT 11 The Immune System Chapters: 37-2, p 951-954 & 40-2, p 1036-1042 Vocabulary Blood ...
... STUDY GUIDE FOR UNIT 11 The Immune System Chapters: 37-2, p 951-954 & 40-2, p 1036-1042 Vocabulary Blood ...
ABO BLOOD GROUPS
... red blood cells, it will react with the antibody causing clumping or agglutination of the red blood cells ...
... red blood cells, it will react with the antibody causing clumping or agglutination of the red blood cells ...
4/20 - Katy Independent School District
... 1. Carbon Dioxide is picked up by blood cells and released through inhaling ...
... 1. Carbon Dioxide is picked up by blood cells and released through inhaling ...
Hematology Study Guide
... A pus-filled cavity that forms when there is infection below the epidermis is a/an: What blood type is considered to be the universal recipient? Universal donor? Blood type is determined by the presence or absence of a blood protein called: The medical term for platelet is: What two blood proteins a ...
... A pus-filled cavity that forms when there is infection below the epidermis is a/an: What blood type is considered to be the universal recipient? Universal donor? Blood type is determined by the presence or absence of a blood protein called: The medical term for platelet is: What two blood proteins a ...
Hematology Study Guide
... A pus-filled cavity that forms when there is infection below the epidermis is a/an: What blood type is considered to be the universal recipient? Universal donor? Blood type is determined by the presence or absence of a blood protein called: The medical term for platelet is: What two blood proteins a ...
... A pus-filled cavity that forms when there is infection below the epidermis is a/an: What blood type is considered to be the universal recipient? Universal donor? Blood type is determined by the presence or absence of a blood protein called: The medical term for platelet is: What two blood proteins a ...
Blood Groups - Ms. Cole`s Science Center
... • Why is it important for people in a hospital to get the right blood type when they need if for a transfusion? ...
... • Why is it important for people in a hospital to get the right blood type when they need if for a transfusion? ...
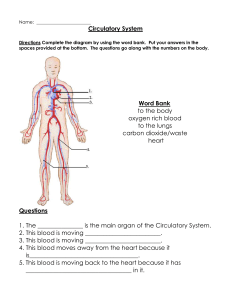
Circulatory System
... Pulmonary- Blood flows between the heart & lungs Systemic- Blood flows between the heart and the cells of the body ...
... Pulmonary- Blood flows between the heart & lungs Systemic- Blood flows between the heart and the cells of the body ...
12.2 Review Questions What happens when serum containing B
... 1. What happens when serum containing B antibodies is added to red blood cells carrying the B antigen? Will the same thing happen if serum containing B antibodies is added to red blood cells containing A antigen? Explain your answer. 2. What is serology and what is its most widespread application? I ...
... 1. What happens when serum containing B antibodies is added to red blood cells carrying the B antigen? Will the same thing happen if serum containing B antibodies is added to red blood cells containing A antigen? Explain your answer. 2. What is serology and what is its most widespread application? I ...
Blood Drop Size
... by a low velocity impact/force to a blood source. blood droplet that looks like this may have been caused by a blunt object and is called a projected bloodstain. ...
... by a low velocity impact/force to a blood source. blood droplet that looks like this may have been caused by a blunt object and is called a projected bloodstain. ...
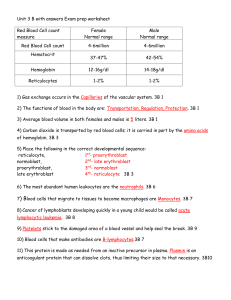
Red Blood Cell count measure Female Normal range Male Normal
... 1) Gas exchange occurs in the Capillaries of the vascular system. 3B 1 2) The functions of blood in the body are: Transportation, Regulation, Protection. 3B 1 3) Average blood volume in both females and males is 5 liters. 3B 1 4) Carbon dioxide is transported by red blood cells; it is carried in par ...
... 1) Gas exchange occurs in the Capillaries of the vascular system. 3B 1 2) The functions of blood in the body are: Transportation, Regulation, Protection. 3B 1 3) Average blood volume in both females and males is 5 liters. 3B 1 4) Carbon dioxide is transported by red blood cells; it is carried in par ...
Serology Notes Blood Volume and Composition Hemocytoblasts
... A. Hemocytoblasts (stem cells) in the red marrow create new blood cells B. Blood Components 1. 45% hematocrit a. 99% erythrocytes (rbc) i. transport gasses; hemoglobin is the O2 carrying molecule ii. millions of antigens on cell surface (A, B, O, and Rh) which may stimulate the production of antibod ...
... A. Hemocytoblasts (stem cells) in the red marrow create new blood cells B. Blood Components 1. 45% hematocrit a. 99% erythrocytes (rbc) i. transport gasses; hemoglobin is the O2 carrying molecule ii. millions of antigens on cell surface (A, B, O, and Rh) which may stimulate the production of antibod ...
RH Factor
... • RH factor is inherited by a simple dominant and recessive relationship where: • R = RH positive (dominant) • r = RH negative (recessive) • Example: – What are the possible blood types (+ or -) of a father who is heterozygous for RH+ and a mother who is RH- ? ...
... • RH factor is inherited by a simple dominant and recessive relationship where: • R = RH positive (dominant) • r = RH negative (recessive) • Example: – What are the possible blood types (+ or -) of a father who is heterozygous for RH+ and a mother who is RH- ? ...
Study Guide
... The items listed below can be found in the powerpoint and assignment article used in this unit. ...
... The items listed below can be found in the powerpoint and assignment article used in this unit. ...
Blood Type Lab
... 9. What is meant by the phrases “universal donor” and “universal receiver”? What determines what blood type a patient can receive? ...
... 9. What is meant by the phrases “universal donor” and “universal receiver”? What determines what blood type a patient can receive? ...
Blood type
A blood type (also called a blood group) is a classification of blood based on the presence or absence of inherited antigenic substances on the surface of red blood cells (RBCs). These antigens may be proteins, carbohydrates, glycoproteins, or glycolipids, depending on the blood group system. Some of these antigens are also present on the surface of other types of cells of various tissues. Several of these red blood cell surface antigens can stem from one allele (or an alternative version of a gene) and collectively form a blood group system.Blood types are inherited and represent contributions from both parents. A total of 35 human blood group systems are now recognized by the International Society of Blood Transfusion (ISBT). The two most important ones are ABO and the RhD antigen; they determine someone's blood type (A, B, AB and O, with +, − or Null denoting RhD status).Many pregnant women carry a fetus with a blood type which is different from their own, which is not a problem. What can matter is whether the baby is RhD positive or negative. Mothers who are RhD- and carry a RhD+ baby can form antibodies against fetal RBCs. Sometimes these maternal antibodies are IgG, a small immunoglobulin, which can cross the placenta and cause hemolysis of fetal RBCs, which in turn can lead to hemolytic disease of the newborn called erythroblastosis fetalis, an illness of low fetal blood counts that ranges from mild to severe. Sometimes this is lethal for the fetus; in these cases it is called hydrops fetalis.