Chapter 12 - The Blood
... determines how easily blood can flow through vessels and how easily plasma can pass trough blood vessel walls to the interstitial fluid ...
... determines how easily blood can flow through vessels and how easily plasma can pass trough blood vessel walls to the interstitial fluid ...
Blood Web Quest Name Go to the following Web site: http://health
... 5. List 4 characteristics of red blood cells. 6. What is the function of red blood cells? 7. List the 6 main types of white blood cells and the percentages of each type in the blood. ...
... 5. List 4 characteristics of red blood cells. 6. What is the function of red blood cells? 7. List the 6 main types of white blood cells and the percentages of each type in the blood. ...
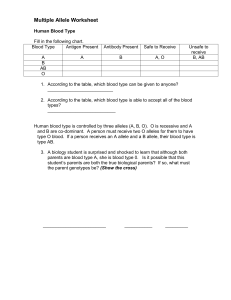
Multiple Allele Worksheet
... Human Blood Type Fill in the following chart. Blood Type Antigen Present A B AB O ...
... Human Blood Type Fill in the following chart. Blood Type Antigen Present A B AB O ...
THE CIRCULATORY SYSTEM
... Is a liquid viscuous, dense and red circulating in the blood vessels. Is formed by one liquid part called plasma. In the plasma there are three kinds of cells: erythrocytes, leukocytes and platelets. ...
... Is a liquid viscuous, dense and red circulating in the blood vessels. Is formed by one liquid part called plasma. In the plasma there are three kinds of cells: erythrocytes, leukocytes and platelets. ...
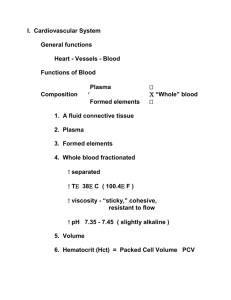
Cardiovascular System
... 1. A fluid connective tissue 2. Plasma 3. Formed elements 4. Whole blood fractionated separated T 38 C ( 100.4 F ) viscosity - “sticky,” cohesive, resistant to flow pH 7.35 - 7.45 ( slightly alkaline ) 5. Volume 6. Hematocrit (Hct) = Packed Cell Volume PCV ...
... 1. A fluid connective tissue 2. Plasma 3. Formed elements 4. Whole blood fractionated separated T 38 C ( 100.4 F ) viscosity - “sticky,” cohesive, resistant to flow pH 7.35 - 7.45 ( slightly alkaline ) 5. Volume 6. Hematocrit (Hct) = Packed Cell Volume PCV ...
Ch 12 Blood Cells
... EPO, or erythropoietin (pronounced, ahrith-ro-poy-tin), is a hormone produced by the liver and kidneys. In the first part of a twonight interview broadcast in January, ...
... EPO, or erythropoietin (pronounced, ahrith-ro-poy-tin), is a hormone produced by the liver and kidneys. In the first part of a twonight interview broadcast in January, ...
11.1 Blood Antigens
... Another antigen found on red blood cells. Individuals are referred to as “rhesuspositive” if they have rhesus factor antigen on their red blood cells. (Rh+) Individuals are referred to as “rhesusnegative” if they lack rhesus factor antigen on their red blood cells. (Rh-) ...
... Another antigen found on red blood cells. Individuals are referred to as “rhesuspositive” if they have rhesus factor antigen on their red blood cells. (Rh+) Individuals are referred to as “rhesusnegative” if they lack rhesus factor antigen on their red blood cells. (Rh-) ...
Body Systems Review Sheet
... 2. What is the function of antibodies? Mark bacteria and viruses for distruction Immobilize bacteria and viruses Cover virus protein receptors so they cannot infect host cells 3. What does the body do when a person gets a vaccine? Explain the entire process. The vaccine has dead or weakened viruse a ...
... 2. What is the function of antibodies? Mark bacteria and viruses for distruction Immobilize bacteria and viruses Cover virus protein receptors so they cannot infect host cells 3. What does the body do when a person gets a vaccine? Explain the entire process. The vaccine has dead or weakened viruse a ...
PowerPoint
... 1. Reduce pain events by one half, 2. Reduce hospital admissions by one half, 3. Reduced the need for transfused blood, 4. Raised the patient's hemoglobin on average by one gram. ...
... 1. Reduce pain events by one half, 2. Reduce hospital admissions by one half, 3. Reduced the need for transfused blood, 4. Raised the patient's hemoglobin on average by one gram. ...
Blood Composition: Red Blood Cells, White Blood Cells, Platelets
... Liver and spleen destroy damaged red cells by macrophages a. RBC usually live for 120 days ...
... Liver and spleen destroy damaged red cells by macrophages a. RBC usually live for 120 days ...
The-Circulatory
... • Vertebrates only have one heart • The heart is divided into closed spaces called chambers. • The atria are chambers that receive blood that returns to the heart. • The ventricles are chambers that pump blood out of the heart. ...
... • Vertebrates only have one heart • The heart is divided into closed spaces called chambers. • The atria are chambers that receive blood that returns to the heart. • The ventricles are chambers that pump blood out of the heart. ...
The Circulatory System
... Some white blood cells surround and consume harmful microbes. Some produce chemicals called antibodies that fight infection. ...
... Some white blood cells surround and consume harmful microbes. Some produce chemicals called antibodies that fight infection. ...
Name______________________________________
... child will be a girl? 39. What is the cause of chromosomal disorders? When does this happen? 40. What happens to the chromosome number of the gametes? 41. What is the genotype of a hemophilia carrier? 42. If this person has a child with a non-hemophiliac, what is the chance that the child will be a ...
... child will be a girl? 39. What is the cause of chromosomal disorders? When does this happen? 40. What happens to the chromosome number of the gametes? 41. What is the genotype of a hemophilia carrier? 42. If this person has a child with a non-hemophiliac, what is the chance that the child will be a ...
Power Point Notes
... – We also have antibodies that fight substances that don’t look like our bodies own antigens ...
... – We also have antibodies that fight substances that don’t look like our bodies own antigens ...
12.2 Notes - Techniques - Trimble County Schools
... Uses drugs with radioactive tags Neither EMIT or RIA are drug specific and must be used with a reliable confirmation test ...
... Uses drugs with radioactive tags Neither EMIT or RIA are drug specific and must be used with a reliable confirmation test ...
Blood Analysis: Activity 4: Blood Typing Lab Report Pre
... 2. Which blood sample contained the rarest blood type? Your answer: AB- is the rarest blood type and it was found in sample 3. 3. Which blood sample contained the universal donor? Your answer: Sample 4 contained the universal donor, type O-. 4. Which blood sample contained the universal recipient? Y ...
... 2. Which blood sample contained the rarest blood type? Your answer: AB- is the rarest blood type and it was found in sample 3. 3. Which blood sample contained the universal donor? Your answer: Sample 4 contained the universal donor, type O-. 4. Which blood sample contained the universal recipient? Y ...
Blood - BrownsBiology
... ◦ Thrombocytopenia – not enough platelets ◦ Hemophilia – hereditary disorder resulting in lack of any of the factors needed for clotting ...
... ◦ Thrombocytopenia – not enough platelets ◦ Hemophilia – hereditary disorder resulting in lack of any of the factors needed for clotting ...
Cardiovascular System Test Study Guide
... 23. Draw a diagram of the heart from memory, labeling the four chambers, septum, and valves. Show the direction of blood flow to and from the lungs and body. Also, show which sections are oxygen-rich and which are oxygen-poor. ...
... 23. Draw a diagram of the heart from memory, labeling the four chambers, septum, and valves. Show the direction of blood flow to and from the lungs and body. Also, show which sections are oxygen-rich and which are oxygen-poor. ...
Blood Groups PPT
... weakness, shock and eventually death. • Loss of over 30% of a person’s total blood volume can be fatal unless treated with a whole blood transfusion. • Whole blood transfusion is also used to treat chronic health conditions such as anemia or thrombocytopenia. • When giving a blood transfusion, it is ...
... weakness, shock and eventually death. • Loss of over 30% of a person’s total blood volume can be fatal unless treated with a whole blood transfusion. • Whole blood transfusion is also used to treat chronic health conditions such as anemia or thrombocytopenia. • When giving a blood transfusion, it is ...
Document
... Veins (To the heart) • There is less blood pressure & some veins have to fight gravity so they have valves to prevent backflow • Walls are also thinner & are collapsible (less rigid shape) • Most carry deoxygenated blood (except pulmonary veins coming back from the lungs) ...
... Veins (To the heart) • There is less blood pressure & some veins have to fight gravity so they have valves to prevent backflow • Walls are also thinner & are collapsible (less rigid shape) • Most carry deoxygenated blood (except pulmonary veins coming back from the lungs) ...
Blood type
A blood type (also called a blood group) is a classification of blood based on the presence or absence of inherited antigenic substances on the surface of red blood cells (RBCs). These antigens may be proteins, carbohydrates, glycoproteins, or glycolipids, depending on the blood group system. Some of these antigens are also present on the surface of other types of cells of various tissues. Several of these red blood cell surface antigens can stem from one allele (or an alternative version of a gene) and collectively form a blood group system.Blood types are inherited and represent contributions from both parents. A total of 35 human blood group systems are now recognized by the International Society of Blood Transfusion (ISBT). The two most important ones are ABO and the RhD antigen; they determine someone's blood type (A, B, AB and O, with +, − or Null denoting RhD status).Many pregnant women carry a fetus with a blood type which is different from their own, which is not a problem. What can matter is whether the baby is RhD positive or negative. Mothers who are RhD- and carry a RhD+ baby can form antibodies against fetal RBCs. Sometimes these maternal antibodies are IgG, a small immunoglobulin, which can cross the placenta and cause hemolysis of fetal RBCs, which in turn can lead to hemolytic disease of the newborn called erythroblastosis fetalis, an illness of low fetal blood counts that ranges from mild to severe. Sometimes this is lethal for the fetus; in these cases it is called hydrops fetalis.