BLOOD TYPING
... Blood Typing Genotypes Up to this point, we have talked about only 2 alleles for any gene (for example A or a) In human blood types, there are 3 alleles: ...
... Blood Typing Genotypes Up to this point, we have talked about only 2 alleles for any gene (for example A or a) In human blood types, there are 3 alleles: ...
Blood Web Activity
... http://www.fi.edu/learn/heart/blood/rh.html 20. Scientists discovered a blood protein while studying what animal? ________________________________________________________________________ 21. If a person’s blood does contain the protein, that person is said to be what? _______________________________ ...
... http://www.fi.edu/learn/heart/blood/rh.html 20. Scientists discovered a blood protein while studying what animal? ________________________________________________________________________ 21. If a person’s blood does contain the protein, that person is said to be what? _______________________________ ...
The Blood System Gas Exchange Study Guide
... EI: The blood system continually transports substances to cells and simultaneously collects waste products Arteries convey blood at high pressure from the ventricles to the tissues of the body Arteries have muscle cells and elastic fibers in their walls The muscle and elastic fibers assist in ...
... EI: The blood system continually transports substances to cells and simultaneously collects waste products Arteries convey blood at high pressure from the ventricles to the tissues of the body Arteries have muscle cells and elastic fibers in their walls The muscle and elastic fibers assist in ...
5.3 Lymph and Blood Cells Study Guide by Hisrich
... 5. How do circulating antibodies protect a person from receiving incompatible blood during a transfusion? Antigens are found on the surface of blood cells and platelets and if the antigens trigger an immune response (happens if blood types don’t match), producing antibodies to attack the antigens. T ...
... 5. How do circulating antibodies protect a person from receiving incompatible blood during a transfusion? Antigens are found on the surface of blood cells and platelets and if the antigens trigger an immune response (happens if blood types don’t match), producing antibodies to attack the antigens. T ...
Venepuncture course - blood components pps
... Granular (develop from red bone marrow and are Neutrophils, Basophils and Eosinophils) ...
... Granular (develop from red bone marrow and are Neutrophils, Basophils and Eosinophils) ...
Kidney Transplant - Network of New England
... ABO group HLA (Human Leukocyte Antigen) Proteins located on surface of white blood cells Inherited from parents. PRA (Panel Reactive Antibody) Measurement of anti-HLA antibodies Crossmatch Donor lymphocytes mixed with recipient serum ...
... ABO group HLA (Human Leukocyte Antigen) Proteins located on surface of white blood cells Inherited from parents. PRA (Panel Reactive Antibody) Measurement of anti-HLA antibodies Crossmatch Donor lymphocytes mixed with recipient serum ...
LG Health Blood Donation Parental Consent Form
... eaten within four hours of donation. Approximately 450 cc’s of blood are removed during one donation. That volume of blood does not have any effect on one’s long term health. Various testing of the donated blood will occur for infectious diseases. Any positive or indeterminate test results will be r ...
... eaten within four hours of donation. Approximately 450 cc’s of blood are removed during one donation. That volume of blood does not have any effect on one’s long term health. Various testing of the donated blood will occur for infectious diseases. Any positive or indeterminate test results will be r ...
Nerve activates contraction
... • Loss of 15 to 30 percent causes weakness • Loss of over 30 percent causes shock, which can be fatal Transfusions are the only way to replace blood quickly Transfused blood must be of the same blood group ...
... • Loss of 15 to 30 percent causes weakness • Loss of over 30 percent causes shock, which can be fatal Transfusions are the only way to replace blood quickly Transfused blood must be of the same blood group ...
1 Fertilisation occurs when the (C)
... vein. From here it enters the …(C)…. ventricle and leaves the heart in the …(D)…. to go to the body. From the body……(E)…blood returns via the …(F)….to the …(G)…. atrium, and then leaves the heart in the …(H)…… artery to go to the …(I)…. 7 Which one of the following is not a characteristic of capilla ...
... vein. From here it enters the …(C)…. ventricle and leaves the heart in the …(D)…. to go to the body. From the body……(E)…blood returns via the …(F)….to the …(G)…. atrium, and then leaves the heart in the …(H)…… artery to go to the …(I)…. 7 Which one of the following is not a characteristic of capilla ...
Blood group A
... Low dose helps reduce risk of heart attack Reduces platelet aggregation and plug formation Reduces risks to embolism Heart attack and stroke ...
... Low dose helps reduce risk of heart attack Reduces platelet aggregation and plug formation Reduces risks to embolism Heart attack and stroke ...
Circulatory System
... • Like arteries they have 3 layers that make up the walls. The big difference is that veins aren’t as thick. • They are much thinner. ...
... • Like arteries they have 3 layers that make up the walls. The big difference is that veins aren’t as thick. • They are much thinner. ...
Chapter 17 - Invertebrates Invertebrate – an animal that does not
... Host – an organism that a parasite lives on or in. Is harmed by the parasite. Gills – organ that allows a water-dwelling animal to exchange carbon dioxide for dissolved oxygen in the water. Mollusk – soft bodied, bilaterally symmetrical invertebrate with a large, muscular foot, a mantle, and an open ...
... Host – an organism that a parasite lives on or in. Is harmed by the parasite. Gills – organ that allows a water-dwelling animal to exchange carbon dioxide for dissolved oxygen in the water. Mollusk – soft bodied, bilaterally symmetrical invertebrate with a large, muscular foot, a mantle, and an open ...
The Respiratory System
... The pulmonary arteries split into many branches, forming an intricate network of vessels that carry blood to the lungs’ alveoli. ...
... The pulmonary arteries split into many branches, forming an intricate network of vessels that carry blood to the lungs’ alveoli. ...
Circulatory System - Central High School
... When you walk and your leg muscles squeeze, the venous pump works well. But when you sit or stand, especially for a long time, the blood in your leg veins can pool and the pressure in your veins can increase. If you are a susceptible individual, your veins can stretch if you repeatedly sit or stand ...
... When you walk and your leg muscles squeeze, the venous pump works well. But when you sit or stand, especially for a long time, the blood in your leg veins can pool and the pressure in your veins can increase. If you are a susceptible individual, your veins can stretch if you repeatedly sit or stand ...
THE CIRCULATORY SYSTEM-blood
... other blood type antigens will be considered “non-self” by the body’s immune system • Within the blood plasma there will be ANTIBODIES to the opposite blood type • These antibodies have a complementary shape to the antigen and will bind to it. – eg. A person with antigen A on their red blood cells w ...
... other blood type antigens will be considered “non-self” by the body’s immune system • Within the blood plasma there will be ANTIBODIES to the opposite blood type • These antibodies have a complementary shape to the antigen and will bind to it. – eg. A person with antigen A on their red blood cells w ...
The Circulatory System
... The circulatory system has the job of moving ___blood______ through the entire body. Blood is made up of ____plasma___, white cells, red cells, and __platelets___. White cells fight _infection__, red cells carry __oxygen__, and platelets cause the blood to clot. Blood is the main mover of oxygen, nu ...
... The circulatory system has the job of moving ___blood______ through the entire body. Blood is made up of ____plasma___, white cells, red cells, and __platelets___. White cells fight _infection__, red cells carry __oxygen__, and platelets cause the blood to clot. Blood is the main mover of oxygen, nu ...
Solution - Glencoe
... Your circulatory system supplies all the different parts of your body with nutrients and oxygen. It also carries carbon dioxide and other cellular waste products away from the cells. The heart is the most important organ in the circulatory system. It pumps blood through your body all the time, all y ...
... Your circulatory system supplies all the different parts of your body with nutrients and oxygen. It also carries carbon dioxide and other cellular waste products away from the cells. The heart is the most important organ in the circulatory system. It pumps blood through your body all the time, all y ...
Chapter 9: The Circulatory System
... drops off different substances to ensure that cells have oxygen and carbon dioxide as well as other waste products are properly disposed of ...
... drops off different substances to ensure that cells have oxygen and carbon dioxide as well as other waste products are properly disposed of ...
Body Systems Quiz - ScienceResourceBPSteachers
... 5. Where does most digested food enter your blood? (Circle the one best answer.) A. stomach B. large intestine and colon C. kidneys D. small intestine ...
... 5. Where does most digested food enter your blood? (Circle the one best answer.) A. stomach B. large intestine and colon C. kidneys D. small intestine ...
Artery
... Key Concepts Arteries When blood leaves the heart, it travels through arteries. The walls of arteries are generally very thick. In fact, artery walls consist of three cell layers. Capillaries In the capillaries, materials are exchanged between the blood and the body’s cells. Capillary walls are onl ...
... Key Concepts Arteries When blood leaves the heart, it travels through arteries. The walls of arteries are generally very thick. In fact, artery walls consist of three cell layers. Capillaries In the capillaries, materials are exchanged between the blood and the body’s cells. Capillary walls are onl ...
i: leukocytes, volume, erythrocytes, suspended
... Disorders of volume: ______________1 can cause major blood loss. Damage to the internal organs can cause severe internal bleeding or ______________2. Anemia is a ______________3 of red blood cells and/or hemoglobin; it can require blood ______________4. Several countries have blood ______________5 t ...
... Disorders of volume: ______________1 can cause major blood loss. Damage to the internal organs can cause severe internal bleeding or ______________2. Anemia is a ______________3 of red blood cells and/or hemoglobin; it can require blood ______________4. Several countries have blood ______________5 t ...
Rh NEGATIVE PREGNANCY
... Mechanism of antibody formation in the mother Antibody formation occurs by iso immunization, which is defined as the production of immune antibodies in an individual in response to an antigen derived from another individual of the same species provided first one lacks the antigen. This occurs in tw ...
... Mechanism of antibody formation in the mother Antibody formation occurs by iso immunization, which is defined as the production of immune antibodies in an individual in response to an antigen derived from another individual of the same species provided first one lacks the antigen. This occurs in tw ...
Blood typing lab
... NAME ___________________________ BLOOD TYPING LAB The system used to classify human blood is called the “ABO” system. Dr. Karl Landsteiner, an Austrian physician, received the Nobel Prize in physiology for this discovery in 1930. Surface GLYCOPROTEINS on red blood cells determine an individual’s blo ...
... NAME ___________________________ BLOOD TYPING LAB The system used to classify human blood is called the “ABO” system. Dr. Karl Landsteiner, an Austrian physician, received the Nobel Prize in physiology for this discovery in 1930. Surface GLYCOPROTEINS on red blood cells determine an individual’s blo ...
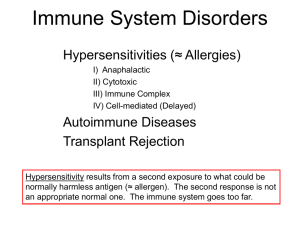
Immune System Disorders (Hypersensitivities ≈ Allergies)
... – AB red blood cell (RBC) antigens & Rh RBC antigen – Drugs (haptens) that bind to blood platelets to become antigenic. ...
... – AB red blood cell (RBC) antigens & Rh RBC antigen – Drugs (haptens) that bind to blood platelets to become antigenic. ...
Blood type
A blood type (also called a blood group) is a classification of blood based on the presence or absence of inherited antigenic substances on the surface of red blood cells (RBCs). These antigens may be proteins, carbohydrates, glycoproteins, or glycolipids, depending on the blood group system. Some of these antigens are also present on the surface of other types of cells of various tissues. Several of these red blood cell surface antigens can stem from one allele (or an alternative version of a gene) and collectively form a blood group system.Blood types are inherited and represent contributions from both parents. A total of 35 human blood group systems are now recognized by the International Society of Blood Transfusion (ISBT). The two most important ones are ABO and the RhD antigen; they determine someone's blood type (A, B, AB and O, with +, − or Null denoting RhD status).Many pregnant women carry a fetus with a blood type which is different from their own, which is not a problem. What can matter is whether the baby is RhD positive or negative. Mothers who are RhD- and carry a RhD+ baby can form antibodies against fetal RBCs. Sometimes these maternal antibodies are IgG, a small immunoglobulin, which can cross the placenta and cause hemolysis of fetal RBCs, which in turn can lead to hemolytic disease of the newborn called erythroblastosis fetalis, an illness of low fetal blood counts that ranges from mild to severe. Sometimes this is lethal for the fetus; in these cases it is called hydrops fetalis.