Activity Overview
... By performing the lab, students will show how natural selection can alter the gene frequencies in a population. ...
... By performing the lab, students will show how natural selection can alter the gene frequencies in a population. ...
Blood
... Anti-Rh antibodies are not spontaneously formed in Rh– individuals However, if an Rh– individual receives Rh+ blood, anti-Rh antibodies form A second exposure to Rh+ blood will result in a typical transfusion reaction ...
... Anti-Rh antibodies are not spontaneously formed in Rh– individuals However, if an Rh– individual receives Rh+ blood, anti-Rh antibodies form A second exposure to Rh+ blood will result in a typical transfusion reaction ...
29 - IWS2.collin.edu
... Anti-Rh antibodies are not spontaneously formed in Rh– individuals However, if an Rh– individual receives Rh+ blood, anti-Rh antibodies form A second exposure to Rh+ blood will result in a typical transfusion reaction ...
... Anti-Rh antibodies are not spontaneously formed in Rh– individuals However, if an Rh– individual receives Rh+ blood, anti-Rh antibodies form A second exposure to Rh+ blood will result in a typical transfusion reaction ...
Human Body Fact Sheet - Scottish Wider Access Programme
... Blood that is rich in oxygen appears __________________ ...
... Blood that is rich in oxygen appears __________________ ...
Human Body Fact Sheet - Scottish Wider Access Programme
... Blood that is rich in oxygen appears __________________ ...
... Blood that is rich in oxygen appears __________________ ...
Take it Home Tuesday #8 Name
... Responsible for the elimination of most waste products. _____nervous system Breaks down food into nutrients small enough to be absorbed by cells. _____respiratory system E. Carries oxygen and nutrients to most body cells; picks up waste carbon dioxide to deliver back to the lungs. 2) Describe one wa ...
... Responsible for the elimination of most waste products. _____nervous system Breaks down food into nutrients small enough to be absorbed by cells. _____respiratory system E. Carries oxygen and nutrients to most body cells; picks up waste carbon dioxide to deliver back to the lungs. 2) Describe one wa ...
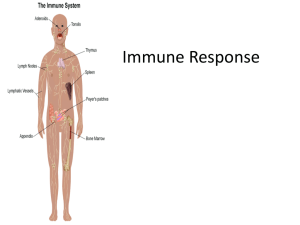
Immune Response
... • Antigen (Ag)- is a foreign substance that can elicit specific immune response (IR) when is immunogenic • Antibody (Ab)- protein produced by the body’s immune system when it detects harmful substances called antigens • White blood cells (leukocytes)- chief function is to protect the body against mi ...
... • Antigen (Ag)- is a foreign substance that can elicit specific immune response (IR) when is immunogenic • Antibody (Ab)- protein produced by the body’s immune system when it detects harmful substances called antigens • White blood cells (leukocytes)- chief function is to protect the body against mi ...
Blood type Antigen Antibody
... May block circulation, leading to tissue death Embolus: a thrombus freely floating in the blood stream Pulmonary emboli impair the ability of the body to obtain oxygen Cerebral emboli can cause strokes ...
... May block circulation, leading to tissue death Embolus: a thrombus freely floating in the blood stream Pulmonary emboli impair the ability of the body to obtain oxygen Cerebral emboli can cause strokes ...
Circulatory and Respiratory Systems
... Circulatory System • 2 functions 1. Blood delivers nutrients (food) and oxygen to cells so they can function. ...
... Circulatory System • 2 functions 1. Blood delivers nutrients (food) and oxygen to cells so they can function. ...
this handout - Physics Teacher
... 2. What is the lifespan of red blood cells? 3. Is the number of white blood cells in a human body constant throughout our life? 4. List all functions of the blood 5. How many red blood cells are there in the human body, if an average person has about 5 litres of blood? 6. How do we call red blood ce ...
... 2. What is the lifespan of red blood cells? 3. Is the number of white blood cells in a human body constant throughout our life? 4. List all functions of the blood 5. How many red blood cells are there in the human body, if an average person has about 5 litres of blood? 6. How do we call red blood ce ...
View poster - West Research Group
... and the Median Fluorescence Intensity (MFI) of CD22 in the CD27+IgM+ B cell subset. ...
... and the Median Fluorescence Intensity (MFI) of CD22 in the CD27+IgM+ B cell subset. ...
Blood, Blood, and more Blood
... • Antibodies: Proteins found free-floating in the bloodstream, will attack antigens on the RBC • There are 3 antibodies: Anti-A Anti-B Anti-Rh ...
... • Antibodies: Proteins found free-floating in the bloodstream, will attack antigens on the RBC • There are 3 antibodies: Anti-A Anti-B Anti-Rh ...
Blood Types
... i: does not produce antigens (recessive) Type AB shows codominance, both the A and B antigens are present on the cell Type O blood is homozygous recessive ...
... i: does not produce antigens (recessive) Type AB shows codominance, both the A and B antigens are present on the cell Type O blood is homozygous recessive ...
Oncoimmunology
... Irregular Antibodies There are many other red cell antigens Exposure by pregnancy, transfusion or transplant can result in an alloantibody if the person does not possess that antigen Usually IgG E.g. anti-D formation in a D negative woman who gives birth to a D-positive infant….. ...
... Irregular Antibodies There are many other red cell antigens Exposure by pregnancy, transfusion or transplant can result in an alloantibody if the person does not possess that antigen Usually IgG E.g. anti-D formation in a D negative woman who gives birth to a D-positive infant….. ...
blood type edit
... 3. Write down 3 questions & 3 facts you know about blood. Read pgs. 324 beginning with Multiple Alleles Govern Blood Types and finish at the end of 325 If possible answer any of your 3 questions or add to your 3 facts if possible. ...
... 3. Write down 3 questions & 3 facts you know about blood. Read pgs. 324 beginning with Multiple Alleles Govern Blood Types and finish at the end of 325 If possible answer any of your 3 questions or add to your 3 facts if possible. ...
CH 37-com - college of ayurved and research centre
... the P. G. degree M.D. (KayaChikitsa) in the year 1998. Her guide was Dr. B. M. Kulkarni & Research center was Tilak Ayurved Mahavidyalaya, Pune, (M.S.) India. ...
... the P. G. degree M.D. (KayaChikitsa) in the year 1998. Her guide was Dr. B. M. Kulkarni & Research center was Tilak Ayurved Mahavidyalaya, Pune, (M.S.) India. ...
Animal Structure and Function
... Cells have large surface areas with which they can have exchange with the environment. ► Gills ...
... Cells have large surface areas with which they can have exchange with the environment. ► Gills ...
RDCR – Blood Products Module
... The major principle of blood transfusion ¡ The donor red cells must survive in the recipient! ...
... The major principle of blood transfusion ¡ The donor red cells must survive in the recipient! ...
Chapter 9
... Alex Baptist died due to a peanut allergy in Kindergarten. Two attempts were made with an epipen but where administered improperly. One women actually stuck herself instead of him. ...
... Alex Baptist died due to a peanut allergy in Kindergarten. Two attempts were made with an epipen but where administered improperly. One women actually stuck herself instead of him. ...
File
... 4.WBCs, also called leukocytes, are less numerous than RBCs (4,000 – 11,000/mm3.) They contain nuclei and organelles, are formed by the same stem cell as RBCs. WBCs are involved with the immune system which defends the body against “foreign” invaders. WBCs can move into and out of the blood vessels ...
... 4.WBCs, also called leukocytes, are less numerous than RBCs (4,000 – 11,000/mm3.) They contain nuclei and organelles, are formed by the same stem cell as RBCs. WBCs are involved with the immune system which defends the body against “foreign” invaders. WBCs can move into and out of the blood vessels ...
Blood, Blood, and more Blood
... • Antibodies: Proteins found freefloating in the bloodstream, will attack antigens on the RBC • There are 3 antibodies: Anti-A Anti-B Anti-Rh ...
... • Antibodies: Proteins found freefloating in the bloodstream, will attack antigens on the RBC • There are 3 antibodies: Anti-A Anti-B Anti-Rh ...
Blood type
A blood type (also called a blood group) is a classification of blood based on the presence or absence of inherited antigenic substances on the surface of red blood cells (RBCs). These antigens may be proteins, carbohydrates, glycoproteins, or glycolipids, depending on the blood group system. Some of these antigens are also present on the surface of other types of cells of various tissues. Several of these red blood cell surface antigens can stem from one allele (or an alternative version of a gene) and collectively form a blood group system.Blood types are inherited and represent contributions from both parents. A total of 35 human blood group systems are now recognized by the International Society of Blood Transfusion (ISBT). The two most important ones are ABO and the RhD antigen; they determine someone's blood type (A, B, AB and O, with +, − or Null denoting RhD status).Many pregnant women carry a fetus with a blood type which is different from their own, which is not a problem. What can matter is whether the baby is RhD positive or negative. Mothers who are RhD- and carry a RhD+ baby can form antibodies against fetal RBCs. Sometimes these maternal antibodies are IgG, a small immunoglobulin, which can cross the placenta and cause hemolysis of fetal RBCs, which in turn can lead to hemolytic disease of the newborn called erythroblastosis fetalis, an illness of low fetal blood counts that ranges from mild to severe. Sometimes this is lethal for the fetus; in these cases it is called hydrops fetalis.