5 circulatorysystem - Teacher Geeks
... all the cells of your body alive. There are four components to the blood: plasma, red blood cells, white blood cells and platelets. The plasma is mostly water and its function is to carry all the other components through the body. It is pale yellow and contains some sugar, protein, minerals and wast ...
... all the cells of your body alive. There are four components to the blood: plasma, red blood cells, white blood cells and platelets. The plasma is mostly water and its function is to carry all the other components through the body. It is pale yellow and contains some sugar, protein, minerals and wast ...
Blood Notes
... transporting carbon dioxide to the lungs (for removal) transporting nitrogenous wastes to the kidneys (for removal) carrying hormones from the endocrine glands to the target tissues. The regulation functions include: removing heat from active areas, such as skeletal muscles, and transporting ...
... transporting carbon dioxide to the lungs (for removal) transporting nitrogenous wastes to the kidneys (for removal) carrying hormones from the endocrine glands to the target tissues. The regulation functions include: removing heat from active areas, such as skeletal muscles, and transporting ...
blood - apbiostafford
... body and the environment (by way of organs). Capillaries are the major vessel where material is exchanged. Overall, there is an evolution in complexity to supply organisms with more efficient circulation, as required by increasing metabolic needs. ...
... body and the environment (by way of organs). Capillaries are the major vessel where material is exchanged. Overall, there is an evolution in complexity to supply organisms with more efficient circulation, as required by increasing metabolic needs. ...
Blood Disorders
... thereby hypoxia. • This can give the blood a bluish or chocolate-brown color. ...
... thereby hypoxia. • This can give the blood a bluish or chocolate-brown color. ...
Antigens(NoTP)
... What will happen when concentration of Anti-HCG-Ab is about equal to Haptencarrier conjugate? ...
... What will happen when concentration of Anti-HCG-Ab is about equal to Haptencarrier conjugate? ...
We Get Around - BirdBrain Science
... would flow back into the water gun, just like blood from veins flows back into your heart. If you look at your hands or feet, you might be able to see blue or purple lines beneath your skin. These lines are veins. Both arteries and veins have thick walls because they are mostly used to carry the blo ...
... would flow back into the water gun, just like blood from veins flows back into your heart. If you look at your hands or feet, you might be able to see blue or purple lines beneath your skin. These lines are veins. Both arteries and veins have thick walls because they are mostly used to carry the blo ...
Cardiovascular Physiology
... • Pluripotent because it is already partially differentiated… won’t produce anything else but blood cell types ...
... • Pluripotent because it is already partially differentiated… won’t produce anything else but blood cell types ...
Preventing Needlestick Injury and Occupational Exposure to
... and treatment of exposures to bloodborne pathogens Comprehensive training programs for HCWs - general information about bloodborne pathogens - mechanisms of transmission, - methods to prevent exposure to blood and other potentially contaminated fluids and ways to implement those methods during var ...
... and treatment of exposures to bloodborne pathogens Comprehensive training programs for HCWs - general information about bloodborne pathogens - mechanisms of transmission, - methods to prevent exposure to blood and other potentially contaminated fluids and ways to implement those methods during var ...
BOSY_DEFENCE__ARISTO_
... more blood flows to the area – the permeability of skin capillaries increases so that more phagocytes & fluid come into the infected tissues – the skin becomes red & swell up with pain (because of high pressure) ...
... more blood flows to the area – the permeability of skin capillaries increases so that more phagocytes & fluid come into the infected tissues – the skin becomes red & swell up with pain (because of high pressure) ...
3.4 Circulatroy System
... A. The heart is a strong muscular organ that constantly pumps blood throughout the body. a. It is a the size of a fist b. It is located in the corner of the chest behind the sternum bone. c. It has a protective sac of tissue called the pericardium surrounding it. B. The heart has two sides separated ...
... A. The heart is a strong muscular organ that constantly pumps blood throughout the body. a. It is a the size of a fist b. It is located in the corner of the chest behind the sternum bone. c. It has a protective sac of tissue called the pericardium surrounding it. B. The heart has two sides separated ...
Quick Reference
... per MILD guidelines • Follow with a snack of carbohydrate and protein (e.g., cheese and crackers). ...
... per MILD guidelines • Follow with a snack of carbohydrate and protein (e.g., cheese and crackers). ...
The Excretory System - ESC-2
... • 2. the needed material is returned to the blood • 3. the waste is eliminated in the urine ...
... • 2. the needed material is returned to the blood • 3. the waste is eliminated in the urine ...
The Circulatory System - missmayerhealthscience20
... arterioles into the small tissues of the body and back again to the arterioles and then to the veins. Their walls consist of only a single layer of endothelial cells (the inner most layer of most arteries) and permit only a single file line of red blood cells to pass through them. They are an essent ...
... arterioles into the small tissues of the body and back again to the arterioles and then to the veins. Their walls consist of only a single layer of endothelial cells (the inner most layer of most arteries) and permit only a single file line of red blood cells to pass through them. They are an essent ...
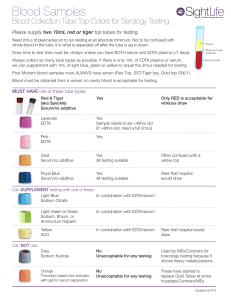
Blood Samples
... Blood Collection Tube Top Colors for Serology Testing Please supply two 10mL red or tiger top tubes for testing. Need 2mLs of plasma/serum to run testing at an absolute minimum. Not to be confused with whole blood in the tube. It is what is separated off after the tube is spun down. ...
... Blood Collection Tube Top Colors for Serology Testing Please supply two 10mL red or tiger top tubes for testing. Need 2mLs of plasma/serum to run testing at an absolute minimum. Not to be confused with whole blood in the tube. It is what is separated off after the tube is spun down. ...
Final Exam 2016 Medical Terminology
... A) The palatine tonsils are located in the nasal cavity. B) The tonsils are composed of lymphatic tissue. C) Sometimes the tonsils have to be removed if they become chronically infected. D) The tonsils remove pathogens for the digestive and respiratory systems. 15) Which of the following is NOT part ...
... A) The palatine tonsils are located in the nasal cavity. B) The tonsils are composed of lymphatic tissue. C) Sometimes the tonsils have to be removed if they become chronically infected. D) The tonsils remove pathogens for the digestive and respiratory systems. 15) Which of the following is NOT part ...
biology 20 unit d review answers
... 16. Which organ system transports materials to all parts of the body? a. skeletal system c. digestive system b. respiratory system @circulatory system 17. The largest blood vessel in the body is the ...
... 16. Which organ system transports materials to all parts of the body? a. skeletal system c. digestive system b. respiratory system @circulatory system 17. The largest blood vessel in the body is the ...
Blood Type
... of Caucasians, 94 percent of African Americans, and 99 percent of all Asians Americans are Rh positive. ...
... of Caucasians, 94 percent of African Americans, and 99 percent of all Asians Americans are Rh positive. ...
• Diagram the blood flow • Name some of the gill functions?
... Gill filaments, A: scanning electron micrograph (left) and a corresponding confocal laser scanning micrograph (right) of a filament from a tilapia. MRCs are stained red; note their increased abundance between the lamellae, which are stained green, and on the Afferent A, compared with the Efferent A ...
... Gill filaments, A: scanning electron micrograph (left) and a corresponding confocal laser scanning micrograph (right) of a filament from a tilapia. MRCs are stained red; note their increased abundance between the lamellae, which are stained green, and on the Afferent A, compared with the Efferent A ...
Blood - My CCSD
... Blood Types • Rh factor antigen present – positive Rh factor = Rh+ antigen absent – negative Rh factor = Rh no anti-Rh antibodies are present in Rh- individuals unless due to previous exposure to Rh+ blood “Rh” omitted in blood type terminology Ex: O+ or A- ...
... Blood Types • Rh factor antigen present – positive Rh factor = Rh+ antigen absent – negative Rh factor = Rh no anti-Rh antibodies are present in Rh- individuals unless due to previous exposure to Rh+ blood “Rh” omitted in blood type terminology Ex: O+ or A- ...
b5losh - Macmillan Academy
... Relate the structure of blood components to their functions (to include haemoglobin in red blood cells). Discuss whether the carrying of donor cards should be made compulsory. Describe the process of blood donation and blood transfusion. Haemophilia is an inherited condition in which the blood does ...
... Relate the structure of blood components to their functions (to include haemoglobin in red blood cells). Discuss whether the carrying of donor cards should be made compulsory. Describe the process of blood donation and blood transfusion. Haemophilia is an inherited condition in which the blood does ...
Genetics Human inheritance
... • Can a couple of blood groups A and B have a child with blood group O? P AO X BO Gametes (½A +½O) , (½B +½O) F1 genotypes ¼AB + ¼AO + ¼BO + ¼OO F1 phenotypes ¼AB + ¼A + ¼B + ¼O ...
... • Can a couple of blood groups A and B have a child with blood group O? P AO X BO Gametes (½A +½O) , (½B +½O) F1 genotypes ¼AB + ¼AO + ¼BO + ¼OO F1 phenotypes ¼AB + ¼A + ¼B + ¼O ...
Blood & the Cardiovascular System
... “foreign”; stimulates immune system to release a defense (antibodies) against “foreigners” ...
... “foreign”; stimulates immune system to release a defense (antibodies) against “foreigners” ...
Blood type
A blood type (also called a blood group) is a classification of blood based on the presence or absence of inherited antigenic substances on the surface of red blood cells (RBCs). These antigens may be proteins, carbohydrates, glycoproteins, or glycolipids, depending on the blood group system. Some of these antigens are also present on the surface of other types of cells of various tissues. Several of these red blood cell surface antigens can stem from one allele (or an alternative version of a gene) and collectively form a blood group system.Blood types are inherited and represent contributions from both parents. A total of 35 human blood group systems are now recognized by the International Society of Blood Transfusion (ISBT). The two most important ones are ABO and the RhD antigen; they determine someone's blood type (A, B, AB and O, with +, − or Null denoting RhD status).Many pregnant women carry a fetus with a blood type which is different from their own, which is not a problem. What can matter is whether the baby is RhD positive or negative. Mothers who are RhD- and carry a RhD+ baby can form antibodies against fetal RBCs. Sometimes these maternal antibodies are IgG, a small immunoglobulin, which can cross the placenta and cause hemolysis of fetal RBCs, which in turn can lead to hemolytic disease of the newborn called erythroblastosis fetalis, an illness of low fetal blood counts that ranges from mild to severe. Sometimes this is lethal for the fetus; in these cases it is called hydrops fetalis.