30.1 Respiratory and Circulatory Functions
... • Red blood cells make up 40-45 % of all blood cells. – transport oxygen to cells and carry away carbon dioxide – have no nuclei and contain hemoglobin ...
... • Red blood cells make up 40-45 % of all blood cells. – transport oxygen to cells and carry away carbon dioxide – have no nuclei and contain hemoglobin ...
The Cardiovascular System
... removes the waste products of metabolism. • Plasma also contains blood clotting factors, sugars, lipids, vitamins, minerals, hormones, enzymes, antibodies, and other proteins. ...
... removes the waste products of metabolism. • Plasma also contains blood clotting factors, sugars, lipids, vitamins, minerals, hormones, enzymes, antibodies, and other proteins. ...
Handwriting analysis takes many years of dedicated study
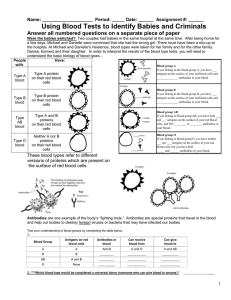
... 3. ****Which blood type would be considered a universal acceptor (someone who can accept blood from anyone)? ...
... 3. ****Which blood type would be considered a universal acceptor (someone who can accept blood from anyone)? ...
circulation and gas exchange
... water; also includes ions, proteins, gases, and nutrients • Erythrocytes (red) –lack nuclei in mammals –lack mitochondria –hemoglobin carries oxygen ...
... water; also includes ions, proteins, gases, and nutrients • Erythrocytes (red) –lack nuclei in mammals –lack mitochondria –hemoglobin carries oxygen ...
Biology Ch. 30 Note Slide Show on Circulatory and Respiratory
... • Red blood cells make up 40-45 % of all blood cells. – transport oxygen to cells and carry away carbon dioxide – have no nuclei and contain hemoglobin ...
... • Red blood cells make up 40-45 % of all blood cells. – transport oxygen to cells and carry away carbon dioxide – have no nuclei and contain hemoglobin ...
Local regulation of arterial blood flow Local (tissue) blood flow: why
... Heat increases blood flow to an area by causing localised vasodilation. Cold causes vasoconstriction and therefore decreased blood flow. Myogenic responses to stretch Nerve-independent contractile activity initiated by the muscle itself. Arteriolar smooth muscle responds to being stretched by myogen ...
... Heat increases blood flow to an area by causing localised vasodilation. Cold causes vasoconstriction and therefore decreased blood flow. Myogenic responses to stretch Nerve-independent contractile activity initiated by the muscle itself. Arteriolar smooth muscle responds to being stretched by myogen ...
Hemolytic Transfusion Reactions: Immune and Non
... Although much less frequent, transfusion of a unit contaminated by a malarial protozoan could manifest as unexplained fevers several days to weeks after transfusion, thereby mimicking a DHTR. Any suspicion that a contaminated unit is being infused should be met by immediate discontinuation of the tr ...
... Although much less frequent, transfusion of a unit contaminated by a malarial protozoan could manifest as unexplained fevers several days to weeks after transfusion, thereby mimicking a DHTR. Any suspicion that a contaminated unit is being infused should be met by immediate discontinuation of the tr ...
Blood Pressure - Sarah E. Goode STEM Academy
... cells, carries carbon dioxide and wastes away from cells, and fights disease through blood cells that fight infection. ...
... cells, carries carbon dioxide and wastes away from cells, and fights disease through blood cells that fight infection. ...
CBC Basic Interpretation - Thalassemia Center
... • Circulating blood cells, including red blood cells (RBCs), white blood cells (WBCs), and platelets, are counted and sized electronically by modern instruments. • One such instrument, the Coulter counter, generates an electrical pulse when a blood cell passes through a small aperture surrounded by ...
... • Circulating blood cells, including red blood cells (RBCs), white blood cells (WBCs), and platelets, are counted and sized electronically by modern instruments. • One such instrument, the Coulter counter, generates an electrical pulse when a blood cell passes through a small aperture surrounded by ...
insider - The Paleo Diet
... Peter’s suggestion that O is the original human blood type is incorrect. Studies in humans, chimpanzees and bonobos (a specific type of chimpanzee) show that alleles (different versions of genes) coding for the A blood type was actually the most ancient version of the ABO blood group, and was shared ...
... Peter’s suggestion that O is the original human blood type is incorrect. Studies in humans, chimpanzees and bonobos (a specific type of chimpanzee) show that alleles (different versions of genes) coding for the A blood type was actually the most ancient version of the ABO blood group, and was shared ...
Antibiotics: When They Can and Can`t Help
... (See Fig 12.2) Beneath the scab the tissue can become inflamed, which is red and painful. This time, mast cells (a type of connective tissue cell) produce a substance called histamine, which dilates blood vessels, and allows _____________ to leak out of them. The extra plasma helps dilute toxins tha ...
... (See Fig 12.2) Beneath the scab the tissue can become inflamed, which is red and painful. This time, mast cells (a type of connective tissue cell) produce a substance called histamine, which dilates blood vessels, and allows _____________ to leak out of them. The extra plasma helps dilute toxins tha ...
Blood managemenT, TransfusIons and surgerY
... personal history. Blood donated by someone who was recently exposed to HIV or other infections could pass the screening tests but still infect you. Directed donation is possible only in certain situations, provided that the donor’s blood type is compatible with the patient and that the date of possi ...
... personal history. Blood donated by someone who was recently exposed to HIV or other infections could pass the screening tests but still infect you. Directed donation is possible only in certain situations, provided that the donor’s blood type is compatible with the patient and that the date of possi ...
Capillaries - Del Mar College
... Drains right upper portion of the body Thymus Gland Site where certain white blood cells acquire means to chemically recognize specific foreign invaders Thoracic Duct Drains most of the body Spleen Major site of antibody production; disposal site for old red blood cells and foreign debris; site of r ...
... Drains right upper portion of the body Thymus Gland Site where certain white blood cells acquire means to chemically recognize specific foreign invaders Thoracic Duct Drains most of the body Spleen Major site of antibody production; disposal site for old red blood cells and foreign debris; site of r ...
Blood 1 - biologyonline.us
... B-cells develop into plasma cells in response to antigen presence plasma cells produce antibodies specific atibodies will bind to specific antigens creating antigen-antibody complexes antibodies “cover” the antigen inactivating them T-CELLS Killer T-cells (cytotoxic T-cells) destroy foreign invaders ...
... B-cells develop into plasma cells in response to antigen presence plasma cells produce antibodies specific atibodies will bind to specific antigens creating antigen-antibody complexes antibodies “cover” the antigen inactivating them T-CELLS Killer T-cells (cytotoxic T-cells) destroy foreign invaders ...
GI Bleeds
... EMERGENT TIPS. This is done by IR. Usually someone from GI is calling them while the Blakemore is being prepared. ...
... EMERGENT TIPS. This is done by IR. Usually someone from GI is calling them while the Blakemore is being prepared. ...
6c Immunity
... – Go out and directly kill bacteria or infected host cells Helper T cells – Release chemicals called “cytokines” to call in more white blood cells of all types to join in the war. They also present the macrophage’s antigen to a B cell, which causes it to produce antibodies against that particular ...
... – Go out and directly kill bacteria or infected host cells Helper T cells – Release chemicals called “cytokines” to call in more white blood cells of all types to join in the war. They also present the macrophage’s antigen to a B cell, which causes it to produce antibodies against that particular ...
INTENDED USE - Sigma
... Blood smearing instrument or Cytocentrifuge Glass tubes, 10x75 mm or 12x75 mm Laboratory droppers or Pasteur pipets Microscope slides and coverslips NOTES: It is recommended that blood smears prepared from healthy donors be processed along with patient samples as normal controls. A small amou ...
... Blood smearing instrument or Cytocentrifuge Glass tubes, 10x75 mm or 12x75 mm Laboratory droppers or Pasteur pipets Microscope slides and coverslips NOTES: It is recommended that blood smears prepared from healthy donors be processed along with patient samples as normal controls. A small amou ...
Z333 Lecture
... Erythrocyte = Red blood cell • Biconcave shape (“certs”) • Increased surface area for gas exchange ...
... Erythrocyte = Red blood cell • Biconcave shape (“certs”) • Increased surface area for gas exchange ...
Heart and Blood Vessels
... • All blood is constantly moving along the circulatory system • The most vital nutrient which is used most quickly is oxygen, so blood is usually divided into oxygenated and deoxygenated blood in graphs – Realistically even “deoxygenated” blood usually still has about 2550% oxygen load ...
... • All blood is constantly moving along the circulatory system • The most vital nutrient which is used most quickly is oxygen, so blood is usually divided into oxygenated and deoxygenated blood in graphs – Realistically even “deoxygenated” blood usually still has about 2550% oxygen load ...
B - Sewanhaka Central High School District
... could be prevented by eating oranges and lemons. This suggests that scurvy is a disease caused by (1)exposure to sea air (2) a microorganism (3) a nutritional deficiency (4) lack of exercise ...
... could be prevented by eating oranges and lemons. This suggests that scurvy is a disease caused by (1)exposure to sea air (2) a microorganism (3) a nutritional deficiency (4) lack of exercise ...
Blood type
A blood type (also called a blood group) is a classification of blood based on the presence or absence of inherited antigenic substances on the surface of red blood cells (RBCs). These antigens may be proteins, carbohydrates, glycoproteins, or glycolipids, depending on the blood group system. Some of these antigens are also present on the surface of other types of cells of various tissues. Several of these red blood cell surface antigens can stem from one allele (or an alternative version of a gene) and collectively form a blood group system.Blood types are inherited and represent contributions from both parents. A total of 35 human blood group systems are now recognized by the International Society of Blood Transfusion (ISBT). The two most important ones are ABO and the RhD antigen; they determine someone's blood type (A, B, AB and O, with +, − or Null denoting RhD status).Many pregnant women carry a fetus with a blood type which is different from their own, which is not a problem. What can matter is whether the baby is RhD positive or negative. Mothers who are RhD- and carry a RhD+ baby can form antibodies against fetal RBCs. Sometimes these maternal antibodies are IgG, a small immunoglobulin, which can cross the placenta and cause hemolysis of fetal RBCs, which in turn can lead to hemolytic disease of the newborn called erythroblastosis fetalis, an illness of low fetal blood counts that ranges from mild to severe. Sometimes this is lethal for the fetus; in these cases it is called hydrops fetalis.