Chapter 1- Circulation and Immunity
... ________________ – acids and protein digesting enzymes destroy microbes Tears, saliva, mucous secretions – ____________ (enzyme) destroys bacterial cell walls b) 2nd line: specific Immunity • Lymphocytes: produced in bone marrow and seed in _________________. • When a foreign antigen (protein) i ...
... ________________ – acids and protein digesting enzymes destroy microbes Tears, saliva, mucous secretions – ____________ (enzyme) destroys bacterial cell walls b) 2nd line: specific Immunity • Lymphocytes: produced in bone marrow and seed in _________________. • When a foreign antigen (protein) i ...
Understanding the CBC
... collected by a finger stick, a lab draw from a central vein access and/or a straight draw from a peripheral vein, (usually from an arm, hand or foot). The CBC is commonly performed on an automated analyzer. However when abnormalities are noted in the blood, parts of the test can be completed manuall ...
... collected by a finger stick, a lab draw from a central vein access and/or a straight draw from a peripheral vein, (usually from an arm, hand or foot). The CBC is commonly performed on an automated analyzer. However when abnormalities are noted in the blood, parts of the test can be completed manuall ...
Human Body – Unit 2
... •when detects a foreign substance, count will increase •life span from a few days to months •attach and absorb the foreign body ...
... •when detects a foreign substance, count will increase •life span from a few days to months •attach and absorb the foreign body ...
distribution of abo blood groups in healthy young adults in
... Blood groups of people are determined genetically by the presence of specific antigens on the red blood cells. Finding out blood groups is important for blood transfusion, prevalence of different diseases, genetic studies etc. Different blood group systems are available for classification. ABO blood ...
... Blood groups of people are determined genetically by the presence of specific antigens on the red blood cells. Finding out blood groups is important for blood transfusion, prevalence of different diseases, genetic studies etc. Different blood group systems are available for classification. ABO blood ...
Pentose Phosphate Pathway
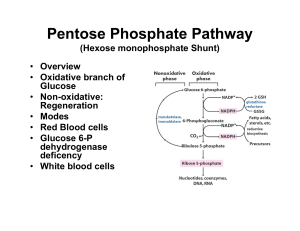
... Modes of Pentose Pathway Dependent on cytoplasmic concentration of NADP+ ...
... Modes of Pentose Pathway Dependent on cytoplasmic concentration of NADP+ ...
Gas Exchange - Crestwood Local Schools
... TIFF (Uncompressed) decompressor are needed to see this picture. ...
... TIFF (Uncompressed) decompressor are needed to see this picture. ...
Consulta: creatorFacets:"Bernardo
... Head and neck cancer is one of the 10 most frequent cancers worldwide, with an estimated 500000 new cases diagnosed annually. Treatment of head and neck cancers require a multidisciplinary approach due their complexity and the functional and esthetic alterations that cancer can cause. The interest o ...
... Head and neck cancer is one of the 10 most frequent cancers worldwide, with an estimated 500000 new cases diagnosed annually. Treatment of head and neck cancers require a multidisciplinary approach due their complexity and the functional and esthetic alterations that cancer can cause. The interest o ...
Chapter 37 circulation and respiration hya
... b. It is not affected by atherosclerosis. c. It drops a great deal when traveling through arteries. d. It is lower in veins than in arteries. Which of the following are the smallest of the blood vessels? a. veins c. capillaries b. lymphatic cells d. arteries ...
... b. It is not affected by atherosclerosis. c. It drops a great deal when traveling through arteries. d. It is lower in veins than in arteries. Which of the following are the smallest of the blood vessels? a. veins c. capillaries b. lymphatic cells d. arteries ...
Hypersensitivity
... memory B-cells (anti-Rh antibodies) The IgM antibody clears the Rh+ cells from the mother In subsequent pregnancies with an Rh+ fetus, the Rh+ RBC cross the placenta activating the memory B-cells These in turn cross the placenta and damage the fetal RBC because they are seen as “foreign” ...
... memory B-cells (anti-Rh antibodies) The IgM antibody clears the Rh+ cells from the mother In subsequent pregnancies with an Rh+ fetus, the Rh+ RBC cross the placenta activating the memory B-cells These in turn cross the placenta and damage the fetal RBC because they are seen as “foreign” ...
Case Study 3 Anemia - Brandy Schnacker MSN Portfolio
... to create red blood cells (Causes of Renal Failure & Anemia). The kidneys are the primary site for the production of the hormone erythropoietin, which controls red blood cell production (Porth & Matfin, 2009)(page 864). With his renal failure, Henry’s erythropoietin production is insufficient to sti ...
... to create red blood cells (Causes of Renal Failure & Anemia). The kidneys are the primary site for the production of the hormone erythropoietin, which controls red blood cell production (Porth & Matfin, 2009)(page 864). With his renal failure, Henry’s erythropoietin production is insufficient to sti ...
Blood
... The hematocrit is defined as the percentage of erythrocytes per unit level of blood If whole blood is centrifuged, the cells and the plasma will separate The erythrocytes, which are heavy, will pack into the bottom of the tube The plasma will be at the top of the tube The leukocytes and platelets wi ...
... The hematocrit is defined as the percentage of erythrocytes per unit level of blood If whole blood is centrifuged, the cells and the plasma will separate The erythrocytes, which are heavy, will pack into the bottom of the tube The plasma will be at the top of the tube The leukocytes and platelets wi ...
Blood+&+Clot+Formation+Blood+Groups
... unborn child The first pregnancy usually proceeds without problems The immune system is sensitized after the first pregnancy In a second pregnancy, the mother’s immune system produces antibodies to attack the Rh+ blood (hemolytic disease of the newborn) ...
... unborn child The first pregnancy usually proceeds without problems The immune system is sensitized after the first pregnancy In a second pregnancy, the mother’s immune system produces antibodies to attack the Rh+ blood (hemolytic disease of the newborn) ...
Postmortem Hemorrhage Feb. 24, 2017
... acid-base balance. In death, the body buffering system is not maintained and thus, blood pH changes can occur. In one study involving the death of 11 individuals, the pH change in the first 20 hours following death was 7.0 to 5.5. The lower pH is a reflection of the accumulation of acidic metabolite ...
... acid-base balance. In death, the body buffering system is not maintained and thus, blood pH changes can occur. In one study involving the death of 11 individuals, the pH change in the first 20 hours following death was 7.0 to 5.5. The lower pH is a reflection of the accumulation of acidic metabolite ...
Work sheet for assignment 13
... Study plants A. control, B. Mist and C. Wind, the write an essay that indicates which of these plants you think would lose the most water by transpiration. Justify your answer based on what you know about leaf structure and movement of water through the plant vascular system. 7. Essay (4 points) Wr ...
... Study plants A. control, B. Mist and C. Wind, the write an essay that indicates which of these plants you think would lose the most water by transpiration. Justify your answer based on what you know about leaf structure and movement of water through the plant vascular system. 7. Essay (4 points) Wr ...
Pathology – Lecture 17: Immunohemolytic Anemia 2/25/13
... Binds to the P blood group antigen on the red cell surface in cool, peripheral regions of the body o Glycophospholipid P antigen = main target Is a biphasic, usu. polyclonal, IgG known to bind to various antigens such as I, i-, p-, Pr-, on the RBC surface o Reaction occurs… Upon completion of ...
... Binds to the P blood group antigen on the red cell surface in cool, peripheral regions of the body o Glycophospholipid P antigen = main target Is a biphasic, usu. polyclonal, IgG known to bind to various antigens such as I, i-, p-, Pr-, on the RBC surface o Reaction occurs… Upon completion of ...
Name
... 8. The _________ side of your heart pushes the blood to your __________. 9. There are 2 kinds of cells in your blood: ________ blood cells and _______ blood cells. 10. There are _____ Trillion RBC in your body, and for every 1000 RBC there are ____ WBC. 11. Each day you make about _____ Billion RBC ...
... 8. The _________ side of your heart pushes the blood to your __________. 9. There are 2 kinds of cells in your blood: ________ blood cells and _______ blood cells. 10. There are _____ Trillion RBC in your body, and for every 1000 RBC there are ____ WBC. 11. Each day you make about _____ Billion RBC ...
Endocrine system Endocrine system
... cells detect glucagon cells release glucose to blood raising of blood glucose inhibit release of glucagon, release of insulin into blood ...
... cells detect glucagon cells release glucose to blood raising of blood glucose inhibit release of glucagon, release of insulin into blood ...
BOŞALTIM SİSTEMLERİ
... walls into the coelom. Each segment of the earthworm contains a pair of metanephridia. Each metanephridium begins in one segment as a ciliated, funnellike opening in the coelom As the fluid passes through the tubules, their cells actively resorb certain molecules from it. ...
... walls into the coelom. Each segment of the earthworm contains a pair of metanephridia. Each metanephridium begins in one segment as a ciliated, funnellike opening in the coelom As the fluid passes through the tubules, their cells actively resorb certain molecules from it. ...
Circulatory System
... Invertebrates that do not have a circulatory system but gastrovascular cavity Flatworms (i.e. planarian) Trilobed gastrovascular cavity Cells are close to the diges
... Invertebrates that do not have a circulatory system but gastrovascular cavity Flatworms (i.e. planarian) Trilobed gastrovascular cavity Cells are close to the diges
Blood type
A blood type (also called a blood group) is a classification of blood based on the presence or absence of inherited antigenic substances on the surface of red blood cells (RBCs). These antigens may be proteins, carbohydrates, glycoproteins, or glycolipids, depending on the blood group system. Some of these antigens are also present on the surface of other types of cells of various tissues. Several of these red blood cell surface antigens can stem from one allele (or an alternative version of a gene) and collectively form a blood group system.Blood types are inherited and represent contributions from both parents. A total of 35 human blood group systems are now recognized by the International Society of Blood Transfusion (ISBT). The two most important ones are ABO and the RhD antigen; they determine someone's blood type (A, B, AB and O, with +, − or Null denoting RhD status).Many pregnant women carry a fetus with a blood type which is different from their own, which is not a problem. What can matter is whether the baby is RhD positive or negative. Mothers who are RhD- and carry a RhD+ baby can form antibodies against fetal RBCs. Sometimes these maternal antibodies are IgG, a small immunoglobulin, which can cross the placenta and cause hemolysis of fetal RBCs, which in turn can lead to hemolytic disease of the newborn called erythroblastosis fetalis, an illness of low fetal blood counts that ranges from mild to severe. Sometimes this is lethal for the fetus; in these cases it is called hydrops fetalis.