EE101 - Wayne County Community College District
... Upon successful completion of this course, the student will: 1) Understand algebra to solve DC circuit. a) Determine the systems units. i) Become familiar with basic physics definitions such as mass, force, speed, acceleration, atom, and charges. ii) Be able to solve first degree, second degree equa ...
... Upon successful completion of this course, the student will: 1) Understand algebra to solve DC circuit. a) Determine the systems units. i) Become familiar with basic physics definitions such as mass, force, speed, acceleration, atom, and charges. ii) Be able to solve first degree, second degree equa ...
Electromagnetic Induction Study Guide
... 20 coils with a cross-sectional area of .0004 m2 as shown. The magnetic field inside the coils changes from 0.05 T to 0.18 T in 1.9 s. (Assume that the magnetic field is perpendicular to the coils and has the same strength at all coils) a) How big is the electromotive force between the two ends of t ...
... 20 coils with a cross-sectional area of .0004 m2 as shown. The magnetic field inside the coils changes from 0.05 T to 0.18 T in 1.9 s. (Assume that the magnetic field is perpendicular to the coils and has the same strength at all coils) a) How big is the electromotive force between the two ends of t ...
Ferrites and accessories – toroids – R 12.5 x 7.50 x 5.00
... Ferrite cores have to meet mechanical requirements during assembling and for a growing number of applications. Since ferrites are ceramic materials one has to be aware of the special behavior under mechanical load. As valid for any ceramic material, ferrite cores are brittle and sensitive to any sho ...
... Ferrite cores have to meet mechanical requirements during assembling and for a growing number of applications. Since ferrites are ceramic materials one has to be aware of the special behavior under mechanical load. As valid for any ceramic material, ferrite cores are brittle and sensitive to any sho ...
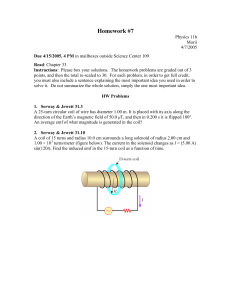
Homework #7
... A semicircular conductor of radius R = 0.250 m is rotated about the axis AC at a constant rate of 120 rev/min (figure below). A uniform magnetic field in all of the lower half of the figure is directed out of the plane of rotation and has a magnitude of 1.30 T. (a) Calculate the maximum value of the ...
... A semicircular conductor of radius R = 0.250 m is rotated about the axis AC at a constant rate of 120 rev/min (figure below). A uniform magnetic field in all of the lower half of the figure is directed out of the plane of rotation and has a magnitude of 1.30 T. (a) Calculate the maximum value of the ...
- Boston University Physics
... 2. A small planar current loop is placed in a uniform magnetic field. The magnitude of the torque on the loop in a maximum when: a) the plane of the loop is parallel to the direction of the field. b) the plane of the loop is perpendicular to the direction of the field. c) the angle between the plane ...
... 2. A small planar current loop is placed in a uniform magnetic field. The magnitude of the torque on the loop in a maximum when: a) the plane of the loop is parallel to the direction of the field. b) the plane of the loop is perpendicular to the direction of the field. c) the angle between the plane ...
Teacher`s notes 19 How does the strength of an
... A wire with a current passing through it has a magnetic field around it. Unless the current is very big, the magnetic field will be very weak. If you take a long wire and coil it up you add together the fields of each coil, and the strength of the magnetic field starts to become noticeable. When a c ...
... A wire with a current passing through it has a magnetic field around it. Unless the current is very big, the magnetic field will be very weak. If you take a long wire and coil it up you add together the fields of each coil, and the strength of the magnetic field starts to become noticeable. When a c ...
Electricity and Magnetism 3
... Electrostatics: Coulomb’s law; electric fields; Gauss’s law and pplications; Electrostatic potential, electrostatic energy, dielectrics, capacitance. Steady currents: Conduction in metals; Ohm’s law; Kirchhoff’s laws. Magnetic fields: Moving charges and magnetic fields, magnetic flux density, Hall e ...
... Electrostatics: Coulomb’s law; electric fields; Gauss’s law and pplications; Electrostatic potential, electrostatic energy, dielectrics, capacitance. Steady currents: Conduction in metals; Ohm’s law; Kirchhoff’s laws. Magnetic fields: Moving charges and magnetic fields, magnetic flux density, Hall e ...
Ch. 32
... 1) What is Ohm’s Law. Give the equation. 2) How does current flow in AC circuit. Does current flow in a closed or open circuit. 3) What are series and parallel circuit. 4) Is current constant in a series circuit. How do you measure total resistance in a series circuit. If you increase the number of ...
... 1) What is Ohm’s Law. Give the equation. 2) How does current flow in AC circuit. Does current flow in a closed or open circuit. 3) What are series and parallel circuit. 4) Is current constant in a series circuit. How do you measure total resistance in a series circuit. If you increase the number of ...
80 DC Drive An electronic device used to control the speed and
... A type of sensing switch that uses an electromagnetic coil to detect the presence of a metal object without coming into physical contact with it. Inductive proximity sensors ignore nonmetallic objects. ...
... A type of sensing switch that uses an electromagnetic coil to detect the presence of a metal object without coming into physical contact with it. Inductive proximity sensors ignore nonmetallic objects. ...
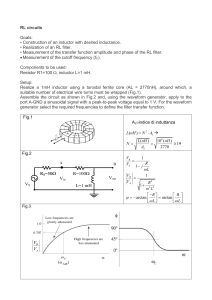
RL circuits Goals: • Construction of an inductor with desired
... Goals: • Construction of an inductor with desired inductance. • Realization of an RL filter. • Measurement of the transfer function amplitude and phase of the RL filter. Measurement of the cutoff frequency (fC). Components to be used: Resistor R1=100 inductor L=1 mH. Setup: Realize a 1mH induct ...
... Goals: • Construction of an inductor with desired inductance. • Realization of an RL filter. • Measurement of the transfer function amplitude and phase of the RL filter. Measurement of the cutoff frequency (fC). Components to be used: Resistor R1=100 inductor L=1 mH. Setup: Realize a 1mH induct ...
Inductor

An inductor, also called a coil or reactor, is a passive two-terminal electrical component which resists changes in electric current passing through it. It consists of a conductor such as a wire, usually wound into a coil. When a current flows through it, energy is stored temporarily in a magnetic field in the coil. When the current flowing through an inductor changes, the time-varying magnetic field induces a voltage in the conductor, according to Faraday’s law of electromagnetic induction, According to Lenz's law the direction of induced e.m.f is always such that it opposes the change in current that created it. As a result, inductors always oppose a change in current, in the same way that a flywheel oppose a change in rotational velocity. Care should be taken not to confuse this with the resistance provided by a resistor.An inductor is characterized by its inductance, the ratio of the voltage to the rate of change of current, which has units of henries (H). Inductors have values that typically range from 1 µH (10−6H) to 1 H. Many inductors have a magnetic core made of iron or ferrite inside the coil, which serves to increase the magnetic field and thus the inductance. Along with capacitors and resistors, inductors are one of the three passive linear circuit elements that make up electric circuits. Inductors are widely used in alternating current (AC) electronic equipment, particularly in radio equipment. They are used to block AC while allowing DC to pass; inductors designed for this purpose are called chokes. They are also used in electronic filters to separate signals of different frequencies, and in combination with capacitors to make tuned circuits, used to tune radio and TV receivers.