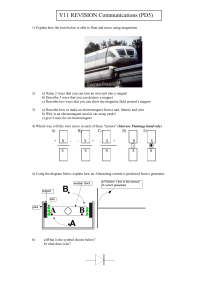
Comms Revision Questions
... b) Why is an electromagnet used in car scrap yards? c) give 6 uses for an electromagnet ...
... b) Why is an electromagnet used in car scrap yards? c) give 6 uses for an electromagnet ...
Chapter 36 Summary – Magnetism
... 19. When (resistance, current) is passed through a coil of wire with a piece of iron inside, an electromagnet is formed. 20. An electromagnet is a (permanent, temporary) magnet. 21. Adding more loops of wire to the coil (increases, decreases) the strength of an electromagnet. 22. More current flowin ...
... 19. When (resistance, current) is passed through a coil of wire with a piece of iron inside, an electromagnet is formed. 20. An electromagnet is a (permanent, temporary) magnet. 21. Adding more loops of wire to the coil (increases, decreases) the strength of an electromagnet. 22. More current flowin ...
em induction
... and currents where they originated. Previously, the fields had been envisioned as tethered to the charges and currents giving rise to them. Maxwell’s new term (he called it the displacement current) freed them to move through space in a self-sustaining fashion, and even predicted their velocity it w ...
... and currents where they originated. Previously, the fields had been envisioned as tethered to the charges and currents giving rise to them. Maxwell’s new term (he called it the displacement current) freed them to move through space in a self-sustaining fashion, and even predicted their velocity it w ...
Cleaning Up - UCF Physics
... The current through the circuit is the same throughout the circuit! IL=IR=Icircuit=I The current will not be in phase with the applied voltage so we need to include a phase shift in our calculations. ...
... The current through the circuit is the same throughout the circuit! IL=IR=Icircuit=I The current will not be in phase with the applied voltage so we need to include a phase shift in our calculations. ...
EET 104 Quiz #1 January 31, 2005
... energy: I. Find the potential drop across the wire. II. Find the resistance of the wire. III. Find the power absorbed by the wire. ...
... energy: I. Find the potential drop across the wire. II. Find the resistance of the wire. III. Find the power absorbed by the wire. ...
Chapter 30 Inductance, Electromagnetic Oscillations, and AC Circuits
... 29-6 Transformers and Transmission of Power A transformer is a device for increasing or decreasing an ac voltage A transformer consists of two coils, either interwoven or linked by an iron core. A changing emf in one induces an emf in the other. The ratio of the emfs is equal to the ratio of the nu ...
... 29-6 Transformers and Transmission of Power A transformer is a device for increasing or decreasing an ac voltage A transformer consists of two coils, either interwoven or linked by an iron core. A changing emf in one induces an emf in the other. The ratio of the emfs is equal to the ratio of the nu ...
College Physics, PHYS 104, Behavioral Objectives, Unit III (b)
... galvanometer readings show when the current in the first coil is increasing, decreasing, or remaining steady? ...
... galvanometer readings show when the current in the first coil is increasing, decreasing, or remaining steady? ...
Review Topics for Final Exam
... CMOS they use fewer transistors than AND and OR gates o conversion from SOP form to POS form, and vice versa simplification of Boolean functions using Karnaugh maps o order of column and row headers (e.g., for two digits, use 00, 01, 11, 10 so that only one variable changes value per row/column) o o ...
... CMOS they use fewer transistors than AND and OR gates o conversion from SOP form to POS form, and vice versa simplification of Boolean functions using Karnaugh maps o order of column and row headers (e.g., for two digits, use 00, 01, 11, 10 so that only one variable changes value per row/column) o o ...
Inductor

An inductor, also called a coil or reactor, is a passive two-terminal electrical component which resists changes in electric current passing through it. It consists of a conductor such as a wire, usually wound into a coil. When a current flows through it, energy is stored temporarily in a magnetic field in the coil. When the current flowing through an inductor changes, the time-varying magnetic field induces a voltage in the conductor, according to Faraday’s law of electromagnetic induction, According to Lenz's law the direction of induced e.m.f is always such that it opposes the change in current that created it. As a result, inductors always oppose a change in current, in the same way that a flywheel oppose a change in rotational velocity. Care should be taken not to confuse this with the resistance provided by a resistor.An inductor is characterized by its inductance, the ratio of the voltage to the rate of change of current, which has units of henries (H). Inductors have values that typically range from 1 µH (10−6H) to 1 H. Many inductors have a magnetic core made of iron or ferrite inside the coil, which serves to increase the magnetic field and thus the inductance. Along with capacitors and resistors, inductors are one of the three passive linear circuit elements that make up electric circuits. Inductors are widely used in alternating current (AC) electronic equipment, particularly in radio equipment. They are used to block AC while allowing DC to pass; inductors designed for this purpose are called chokes. They are also used in electronic filters to separate signals of different frequencies, and in combination with capacitors to make tuned circuits, used to tune radio and TV receivers.