Physics Tutorial: Inductance and Transformers
... inductance occurs when two coils are so close together that the magnetic field of one coil links with the magnetic field of the other coil. Current is induced in the second coil when the magnet field produced by the first coil changes. A transformer only works with alternating current. Direct curren ...
... inductance occurs when two coils are so close together that the magnetic field of one coil links with the magnetic field of the other coil. Current is induced in the second coil when the magnet field produced by the first coil changes. A transformer only works with alternating current. Direct curren ...
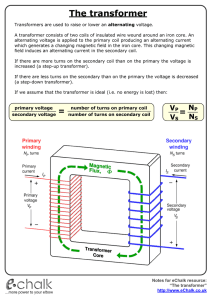
The transformer
... The national grid is the system of pylons and cables that supply electricity to houses and factories around the country. Since: power = current x voltage , the same amount of electrical power can be transported using either of the following: (A) a high voltage and a low current (B) a low voltage and ...
... The national grid is the system of pylons and cables that supply electricity to houses and factories around the country. Since: power = current x voltage , the same amount of electrical power can be transported using either of the following: (A) a high voltage and a low current (B) a low voltage and ...
notes
... mutual inductance) will use Faraday’s law and magnetic circuit theory to derive the relationship between mutual inductance and self inductance for two coupled coils, resulting in the definition of the coefficient of coupling k: ...
... mutual inductance) will use Faraday’s law and magnetic circuit theory to derive the relationship between mutual inductance and self inductance for two coupled coils, resulting in the definition of the coefficient of coupling k: ...
Transformers AM326 KB
... the rate of heating generated in the wire will be I2 R; this energy is wasted. How is this energy loss minimised for a given delivered power IV? ...
... the rate of heating generated in the wire will be I2 R; this energy is wasted. How is this energy loss minimised for a given delivered power IV? ...
Electromagnetic induction
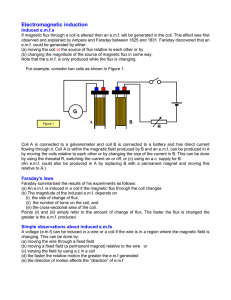
... If magnetic flux through a coil is altered then an e.m.f. will be generated in the coil. This effect was first observed and explained by Ampere and Faraday between 1825 and 1831. Faraday discovered that an e.m.f. could be generated by either: (a) moving the coil or the source of flux relative to eac ...
... If magnetic flux through a coil is altered then an e.m.f. will be generated in the coil. This effect was first observed and explained by Ampere and Faraday between 1825 and 1831. Faraday discovered that an e.m.f. could be generated by either: (a) moving the coil or the source of flux relative to eac ...
DN-63 The Current-Doubler Rectifier: An Alternative Rectification
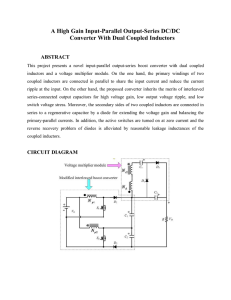
... the secondary winding of the transformer, VT is positive. Current flows in positive direction in both filter inductors, L1 and L2. During this period D1 is forward biased while D2 is kept off by VT. It means that the current path for L1 runs through D1 and the output capacitor, basically kept away f ...
... the secondary winding of the transformer, VT is positive. Current flows in positive direction in both filter inductors, L1 and L2. During this period D1 is forward biased while D2 is kept off by VT. It means that the current path for L1 runs through D1 and the output capacitor, basically kept away f ...
The Basics of Series Circuits
... of the remaining bulbs considerably. Airport runway lighting circuits avoid this problem by using constant current power supplies to supply the series circuit. Impedance and capacitance. What if a series circuit consists of elements other than resistances? Ohm’s Law still applies, but mathematically ...
... of the remaining bulbs considerably. Airport runway lighting circuits avoid this problem by using constant current power supplies to supply the series circuit. Impedance and capacitance. What if a series circuit consists of elements other than resistances? Ohm’s Law still applies, but mathematically ...
Lenzs` Law - PhysicsAPB
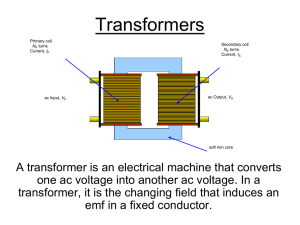
... turns in the two windings. So if the primary and secondary windings have the same number of turns, the primary and secondary voltage will be the same. If the secondary winding has half as many turns as the primary then the voltage in the secondary will be half that of the voltage in the primary. ...
... turns in the two windings. So if the primary and secondary windings have the same number of turns, the primary and secondary voltage will be the same. If the secondary winding has half as many turns as the primary then the voltage in the secondary will be half that of the voltage in the primary. ...
Electricity and Electromagnetism Study Guide
... A solenoid is a coil of wire without an iron core. A solenoid does produce a magnetic field ...
... A solenoid is a coil of wire without an iron core. A solenoid does produce a magnetic field ...
Inductor

An inductor, also called a coil or reactor, is a passive two-terminal electrical component which resists changes in electric current passing through it. It consists of a conductor such as a wire, usually wound into a coil. When a current flows through it, energy is stored temporarily in a magnetic field in the coil. When the current flowing through an inductor changes, the time-varying magnetic field induces a voltage in the conductor, according to Faraday’s law of electromagnetic induction, According to Lenz's law the direction of induced e.m.f is always such that it opposes the change in current that created it. As a result, inductors always oppose a change in current, in the same way that a flywheel oppose a change in rotational velocity. Care should be taken not to confuse this with the resistance provided by a resistor.An inductor is characterized by its inductance, the ratio of the voltage to the rate of change of current, which has units of henries (H). Inductors have values that typically range from 1 µH (10−6H) to 1 H. Many inductors have a magnetic core made of iron or ferrite inside the coil, which serves to increase the magnetic field and thus the inductance. Along with capacitors and resistors, inductors are one of the three passive linear circuit elements that make up electric circuits. Inductors are widely used in alternating current (AC) electronic equipment, particularly in radio equipment. They are used to block AC while allowing DC to pass; inductors designed for this purpose are called chokes. They are also used in electronic filters to separate signals of different frequencies, and in combination with capacitors to make tuned circuits, used to tune radio and TV receivers.