Genetic Information DNA - Barnegat Township School District
... Only one chain of nucleotides – one strand Made of nucleotides that have A, C, G and U as nitrogenous bases • U replaces T • C pairs with G, A with U • Carries the coded message of DNA from the nucleus to the ribosomes (cytoplasm) – where this message is used to make proteins ...
... Only one chain of nucleotides – one strand Made of nucleotides that have A, C, G and U as nitrogenous bases • U replaces T • C pairs with G, A with U • Carries the coded message of DNA from the nucleus to the ribosomes (cytoplasm) – where this message is used to make proteins ...
Week Of: 8/22-8/26
... objective should be essential an agreed upon functions of a topic, skill, or concept from the cell involve guaranteed ACPSD chemical curriculum. reactions that take place between many different types of molecules (including carbohydrate s, lipids, proteins and nucleic acids) and are catalyzed by enz ...
... objective should be essential an agreed upon functions of a topic, skill, or concept from the cell involve guaranteed ACPSD chemical curriculum. reactions that take place between many different types of molecules (including carbohydrate s, lipids, proteins and nucleic acids) and are catalyzed by enz ...
Biochemistry Notes
... a) Saturated fat- each carbon is bonded with two hydrogens in the fatty acid chain 1) Animal fats 2) Solid at room temperature 3) Bad for you. (Cause arteriosclerosis) ...
... a) Saturated fat- each carbon is bonded with two hydrogens in the fatty acid chain 1) Animal fats 2) Solid at room temperature 3) Bad for you. (Cause arteriosclerosis) ...
Why cooking of dog food can cause allergies and
... Proteins are huge molecules - thousands of atoms combined. They are so big that they cannot penetrate the intestine's semi-permeable walls and enter into the blood stream. They must first be broken down to smaller molecules, sometimes the very building stones of proteins - amino acids (typically som ...
... Proteins are huge molecules - thousands of atoms combined. They are so big that they cannot penetrate the intestine's semi-permeable walls and enter into the blood stream. They must first be broken down to smaller molecules, sometimes the very building stones of proteins - amino acids (typically som ...
Representation and Manipulation of 3D Molecular Structures
... • Data mining for conformational properties and intermolecular interactions (CSD & PDB) • Data mining for information about intermolecular interactions (CSD & PDB) • Further understanding of the nature of protein structure and its relationship to amino acid sequence (PDB) • Homology modeling (compar ...
... • Data mining for conformational properties and intermolecular interactions (CSD & PDB) • Data mining for information about intermolecular interactions (CSD & PDB) • Further understanding of the nature of protein structure and its relationship to amino acid sequence (PDB) • Homology modeling (compar ...
Psi-blast
... Strategy for predicting new DNA-binding proteins 1. Build a database of DNA-binding and non DNA-binding proteins 2. Extract the positive electrostatic patch in all proteins in Data Set. 3. Find features that could be used to discriminate the DNA-binding proteins from other proteins. 3. Use the feat ...
... Strategy for predicting new DNA-binding proteins 1. Build a database of DNA-binding and non DNA-binding proteins 2. Extract the positive electrostatic patch in all proteins in Data Set. 3. Find features that could be used to discriminate the DNA-binding proteins from other proteins. 3. Use the feat ...
Supplementary Information (doc 34K)
... showed good discrimination between the predicted correct and incorrect peptide-spectrum assignments, and only peptides with charge states of +1, +2, and +3 were retained as confident identifications because the Peptide Prophet models were not a good fit to the data for charge states ≥ 4. Protein ide ...
... showed good discrimination between the predicted correct and incorrect peptide-spectrum assignments, and only peptides with charge states of +1, +2, and +3 were retained as confident identifications because the Peptide Prophet models were not a good fit to the data for charge states ≥ 4. Protein ide ...
Protein Separation and Purification
... IEC resins are made by covalently attaching Negatively or Positively charged functional groups to a solid support matrix to yield Cation or Anion exchangers, respectively Negatively charged exchangers bind positively charged ions – cations Positively charged exchangers bind negatively charged ion ...
... IEC resins are made by covalently attaching Negatively or Positively charged functional groups to a solid support matrix to yield Cation or Anion exchangers, respectively Negatively charged exchangers bind positively charged ions – cations Positively charged exchangers bind negatively charged ion ...
Examination in Gene Technology, TFKE38 2011-10-18
... instead you use the socalled TA cloning technique.. How does the TA cloning work? What are the requirements for the DNA polymerase used in this technique, how is the vector treated? (6p) c) For the transformation, you use two different controls, transformation and ligation control. What are the purp ...
... instead you use the socalled TA cloning technique.. How does the TA cloning work? What are the requirements for the DNA polymerase used in this technique, how is the vector treated? (6p) c) For the transformation, you use two different controls, transformation and ligation control. What are the purp ...
Biochemistry Objective Sheet Test Objectives Bio.1.2.1 • Explain
... Explain how buffers are used by living cells to maintain pH balance Explain the relationship between an atom, element, molecule, and compound. Differentiate between inorganic and organic compounds Identify THREE organic molecules and THREE inorganic molecules Identify the four major organic compound ...
... Explain how buffers are used by living cells to maintain pH balance Explain the relationship between an atom, element, molecule, and compound. Differentiate between inorganic and organic compounds Identify THREE organic molecules and THREE inorganic molecules Identify the four major organic compound ...
Protein Synthesis Bead Activity
... __________________________________ and it occurs in the ______________________ of cells. mRNA leaves the nucleus to find a _______________. Next, we start the second part of protein synthesis called _____________________________ and it happens in the _____________________ of cells. During this proce ...
... __________________________________ and it occurs in the ______________________ of cells. mRNA leaves the nucleus to find a _______________. Next, we start the second part of protein synthesis called _____________________________ and it happens in the _____________________ of cells. During this proce ...
The Genetic Code and Translation
... • Genetic Code – chart used to determine which amino acid goes with a certain codon – Universal – all organisms use the same code – There are 64 different codons, but only 20 amino acids. (So, there may be more than one codon for an amino acid.) – AUG codes for methionine (the “start” codon) • Sign ...
... • Genetic Code – chart used to determine which amino acid goes with a certain codon – Universal – all organisms use the same code – There are 64 different codons, but only 20 amino acids. (So, there may be more than one codon for an amino acid.) – AUG codes for methionine (the “start” codon) • Sign ...
Macromolecule: Carbohydrates Polarity: Polar Functions: Store
... Amino acids (20) – monomers of proteins (C with amino group, carboxyl group, and R group/side chain) Essential amino acids (8) – not produced by the body and must be consumed in food Polypeptide – polymer composed of amino acid monomers joined by covalent bonds Denaturation – unfolding of a protein, ...
... Amino acids (20) – monomers of proteins (C with amino group, carboxyl group, and R group/side chain) Essential amino acids (8) – not produced by the body and must be consumed in food Polypeptide – polymer composed of amino acid monomers joined by covalent bonds Denaturation – unfolding of a protein, ...
Experience Canola Protein in Great-Tasting Products
... curbing hunger, supplying more energy, and supporting a healthy weight. ...
... curbing hunger, supplying more energy, and supporting a healthy weight. ...
PROTEIN APPLICATIONS IN BIOTECHNOLOGY
... Describe the roles of proteins in cells and organisms Recognize and describe the properties of individual amino acids and the steps of protein synthesis (i.e. transcription and translation) Name and describe the levels of protein structure and how they are stabilized Understand the basic methodology ...
... Describe the roles of proteins in cells and organisms Recognize and describe the properties of individual amino acids and the steps of protein synthesis (i.e. transcription and translation) Name and describe the levels of protein structure and how they are stabilized Understand the basic methodology ...
Page 1
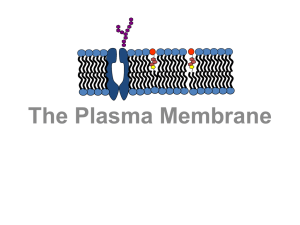
... Ser/Thr protein kinases Pdk1 and Akt/PKB close together at the plasma membrane may allow the former to phosphorylate and partially activate the latter. Akt is also phosphorylated (at a second site) by the Ser/Thr protein kinase mTOR, residing in a complex (mTORC-2) with the proteins Rictor and mLST- ...
... Ser/Thr protein kinases Pdk1 and Akt/PKB close together at the plasma membrane may allow the former to phosphorylate and partially activate the latter. Akt is also phosphorylated (at a second site) by the Ser/Thr protein kinase mTOR, residing in a complex (mTORC-2) with the proteins Rictor and mLST- ...
Additional file 6
... All the identified proteins of the non-redundant, high-confidence dataset of glomerulus proteome consisting of 1,817 unique proteins representing 1,478 unique genes were analyzed based onGene Ontology (GO) Cellular Component (Panel A) and GO Molecular Function (Panel B) vocabularies using PANTHER ve ...
... All the identified proteins of the non-redundant, high-confidence dataset of glomerulus proteome consisting of 1,817 unique proteins representing 1,478 unique genes were analyzed based onGene Ontology (GO) Cellular Component (Panel A) and GO Molecular Function (Panel B) vocabularies using PANTHER ve ...
Chapter 4 BSCS Green Sections 4.7
... 35. In decomposition (or digestion) reactions the enzyme reacts with the ____________ molecules and splits it into ______ or more smaller molecules. 36. Lactose is the double sugar (disaccharide) present in milk. If a person inherits the DNA instructions to make the enzyme lactase they are able to d ...
... 35. In decomposition (or digestion) reactions the enzyme reacts with the ____________ molecules and splits it into ______ or more smaller molecules. 36. Lactose is the double sugar (disaccharide) present in milk. If a person inherits the DNA instructions to make the enzyme lactase they are able to d ...
Chapter 3 Exam
... NaCl. With respect to this system, which of the following statements would be true? A) water would move from solution A to solution B B) water would move from solution B to solution A C) Na+ would move from solution A to solution B D) Na+ would move from solution B to solution A E) no net movement o ...
... NaCl. With respect to this system, which of the following statements would be true? A) water would move from solution A to solution B B) water would move from solution B to solution A C) Na+ would move from solution A to solution B D) Na+ would move from solution B to solution A E) no net movement o ...
Chapter 14 Proteins
... ◦ Peptide: A short polymer of amino acids joined by peptide bonds; they are classified by the number of amino acids in the chain. ◦ Dipeptide: A molecule containing two amino acids joined by a peptide bond. ◦ Tripeptide: A molecule containing three amino acids joined by peptide bonds. ◦ Polypeptide: ...
... ◦ Peptide: A short polymer of amino acids joined by peptide bonds; they are classified by the number of amino acids in the chain. ◦ Dipeptide: A molecule containing two amino acids joined by a peptide bond. ◦ Tripeptide: A molecule containing three amino acids joined by peptide bonds. ◦ Polypeptide: ...
Protein

Proteins (/ˈproʊˌtiːnz/ or /ˈproʊti.ɨnz/) are large biomolecules, or macromolecules, consisting of one or more long chains of amino acid residues. Proteins perform a vast array of functions within living organisms, including catalyzing metabolic reactions, DNA replication, responding to stimuli, and transporting molecules from one location to another. Proteins differ from one another primarily in their sequence of amino acids, which is dictated by the nucleotide sequence of their genes, and which usually results in protein folding into a specific three-dimensional structure that determines its activity.A linear chain of amino acid residues is called a polypeptide. A protein contains at least one long polypeptide. Short polypeptides, containing less than about 20-30 residues, are rarely considered to be proteins and are commonly called peptides, or sometimes oligopeptides. The individual amino acid residues are bonded together by peptide bonds and adjacent amino acid residues. The sequence of amino acid residues in a protein is defined by the sequence of a gene, which is encoded in the genetic code. In general, the genetic code specifies 20 standard amino acids; however, in certain organisms the genetic code can include selenocysteine and—in certain archaea—pyrrolysine. Shortly after or even during synthesis, the residues in a protein are often chemically modified by posttranslational modification, which alters the physical and chemical properties, folding, stability, activity, and ultimately, the function of the proteins. Sometimes proteins have non-peptide groups attached, which can be called prosthetic groups or cofactors. Proteins can also work together to achieve a particular function, and they often associate to form stable protein complexes.Once formed, proteins only exist for a certain period of time and are then degraded and recycled by the cell's machinery through the process of protein turnover. A protein's lifespan is measured in terms of its half-life and covers a wide range. They can exist for minutes or years with an average lifespan of 1–2 days in mammalian cells. Abnormal and or misfolded proteins are degraded more rapidly either due to being targeted for destruction or due to being unstable.Like other biological macromolecules such as polysaccharides and nucleic acids, proteins are essential parts of organisms and participate in virtually every process within cells. Many proteins are enzymes that catalyze biochemical reactions and are vital to metabolism. Proteins also have structural or mechanical functions, such as actin and myosin in muscle and the proteins in the cytoskeleton, which form a system of scaffolding that maintains cell shape. Other proteins are important in cell signaling, immune responses, cell adhesion, and the cell cycle. Proteins are also necessary in animals' diets, since animals cannot synthesize all the amino acids they need and must obtain essential amino acids from food. Through the process of digestion, animals break down ingested protein into free amino acids that are then used in metabolism.Proteins may be purified from other cellular components using a variety of techniques such as ultracentrifugation, precipitation, electrophoresis, and chromatography; the advent of genetic engineering has made possible a number of methods to facilitate purification. Methods commonly used to study protein structure and function include immunohistochemistry, site-directed mutagenesis, X-ray crystallography, nuclear magnetic resonance and mass spectrometry.