Purification of GST::TaABF1 Fusion Protein in Order to Assess its
... We are able to successfully purify GST::TaABF1 fusion protein from bacteria cultures GST::TaABF1 fusion protein was successfully recovered after endosperm phosphorylation assay Phosphorylation was not detected on the GST::TaABF1 protein using mass spectrometry ...
... We are able to successfully purify GST::TaABF1 fusion protein from bacteria cultures GST::TaABF1 fusion protein was successfully recovered after endosperm phosphorylation assay Phosphorylation was not detected on the GST::TaABF1 protein using mass spectrometry ...
What more do we need to know to optimize the
... (ingredients) and with what characteristics will have the greatest potential for a protease to work on – Diet Ca concentrations and solubility – Refractory proteins in ingredients are potential feed proteins that can be digested by exogenous proteases ...
... (ingredients) and with what characteristics will have the greatest potential for a protease to work on – Diet Ca concentrations and solubility – Refractory proteins in ingredients are potential feed proteins that can be digested by exogenous proteases ...
Scholarly Interest Report
... Morozova, N., Aller, J.A., Myers, J., and Shamoo, Y. "Protein-RNA interactions: Exploring binding patterns with a three-dimensional superposition analysis of high resolution structures." Bioinformatics, 22 (2006) : 2746-2752. Sun, S., Geng, L., and Shamoo, Y. "Fusion of bacteriophage RB69 DNA polym ...
... Morozova, N., Aller, J.A., Myers, J., and Shamoo, Y. "Protein-RNA interactions: Exploring binding patterns with a three-dimensional superposition analysis of high resolution structures." Bioinformatics, 22 (2006) : 2746-2752. Sun, S., Geng, L., and Shamoo, Y. "Fusion of bacteriophage RB69 DNA polym ...
Problem Set 1 Solution
... When this transmembrane protein is embedded in the lipid bilayer, what is the highest order of structure (choose from primary, secondary, tertiary and quaternary) of this protein? Explain why you selected this option. This protein is comprised of a single polypeptide chain. Therefore it should have ...
... When this transmembrane protein is embedded in the lipid bilayer, what is the highest order of structure (choose from primary, secondary, tertiary and quaternary) of this protein? Explain why you selected this option. This protein is comprised of a single polypeptide chain. Therefore it should have ...
lecture 5
... In a metabolically active cell, approximately 3% to 5% of the cellular RNA is mRNA, 90% is rRNA, and about 4% is tRNA. - Hundreds of different mRNAs can be in one cell. - By contrast, there are four types of rRNA. Three of the rRNAs combine with a set of proteins to form a ribonucleoprotein complex ...
... In a metabolically active cell, approximately 3% to 5% of the cellular RNA is mRNA, 90% is rRNA, and about 4% is tRNA. - Hundreds of different mRNAs can be in one cell. - By contrast, there are four types of rRNA. Three of the rRNAs combine with a set of proteins to form a ribonucleoprotein complex ...
물리화학 소개
... his students started with two types of particles: 1-micrometer plastic spheres with magnetic iron cores, and much smaller nonmagnetic gold nanoparticles. The researchers linked the iron particles to genetically engineered proteins called monoclonal antibodies, designed to bind to PSA using the same ...
... his students started with two types of particles: 1-micrometer plastic spheres with magnetic iron cores, and much smaller nonmagnetic gold nanoparticles. The researchers linked the iron particles to genetically engineered proteins called monoclonal antibodies, designed to bind to PSA using the same ...
4.2 How to get other molecules across membranes
... family of transporters. There are 7 different, but related, proteins. But, only four (GLUT1-4) are known to be involved in glucose transport. All GLUT proteins share a set of similar structural features and are all about 500 amino acids in length (giving them a predicted molecular weight of about 55 ...
... family of transporters. There are 7 different, but related, proteins. But, only four (GLUT1-4) are known to be involved in glucose transport. All GLUT proteins share a set of similar structural features and are all about 500 amino acids in length (giving them a predicted molecular weight of about 55 ...
Chapter 7 Membrane Structure and Function
... Receptor-mediated endocytosis enables the cell to acquire bulk quantities of specific substances, even though those substances may not be very concentrated in the extracellular fluid. Embedded in the membrane are proteins with specific receptor sites exposed to the extracellular fluid. The receptor ...
... Receptor-mediated endocytosis enables the cell to acquire bulk quantities of specific substances, even though those substances may not be very concentrated in the extracellular fluid. Embedded in the membrane are proteins with specific receptor sites exposed to the extracellular fluid. The receptor ...
Cell Structure and Function
... The cytoplasmic/plasma/cell membrane Contains glycolipids as well as complex lipids called sterols Cholesterol molecules found in animal cell membranes not found in prokaryotic membranes(except for some mycoplasmas Sterols make the membrane less permeable to most biological molecules Help to ...
... The cytoplasmic/plasma/cell membrane Contains glycolipids as well as complex lipids called sterols Cholesterol molecules found in animal cell membranes not found in prokaryotic membranes(except for some mycoplasmas Sterols make the membrane less permeable to most biological molecules Help to ...
Poly-acrylamide Gel Electrophoresis (PAGE) PAGE is based upon
... • a rarely used technique, although it can be informative. • proteins are not denatured as in SDSPAGE. • one can perform enzymatic assays on bands in gel as we shall do in this class. • “primarily” separates based on mass of proteins, assuming low pI. • is possible to get some idea of subunit compos ...
... • a rarely used technique, although it can be informative. • proteins are not denatured as in SDSPAGE. • one can perform enzymatic assays on bands in gel as we shall do in this class. • “primarily” separates based on mass of proteins, assuming low pI. • is possible to get some idea of subunit compos ...
Cell Structure and Function
... The cytoplasmic/plasma/cell membrane Contains glycolipids as well as complex lipids called sterols Cholesterol molecules found in animal cell membranes not found in prokaryotic membranes(except for some mycoplasmas Sterols make the membrane less permeable to most biological molecules Help to ...
... The cytoplasmic/plasma/cell membrane Contains glycolipids as well as complex lipids called sterols Cholesterol molecules found in animal cell membranes not found in prokaryotic membranes(except for some mycoplasmas Sterols make the membrane less permeable to most biological molecules Help to ...
Domain structure and sequence similarities in cartilage proteoglycan
... points for bearing chondroitin sulphate chains. This region is less well conserved than the globular G 3 domain and suggests that the precise pattern and number of Ser-Gly dipeptides is not critical to its function in bearing large numbers of chondroitin sulphate chains. A general feature of the Ser ...
... points for bearing chondroitin sulphate chains. This region is less well conserved than the globular G 3 domain and suggests that the precise pattern and number of Ser-Gly dipeptides is not critical to its function in bearing large numbers of chondroitin sulphate chains. A general feature of the Ser ...
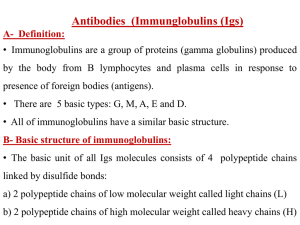
1. Inter-chain disulfide bonds
... immunologic protection until the endogeenous Ig G is produced. The half life of Ig G is about 30 days and with prolonged breast feeding the ...
... immunologic protection until the endogeenous Ig G is produced. The half life of Ig G is about 30 days and with prolonged breast feeding the ...
Conserved BK Channel-Protein Interactions Reveal Signals
... functions, we undertook a systems analysis of BK and BK-Associated Proteins (BKAPS) in the chicken cochlea and compared these results to other species. We identified 110 putative partners from cytoplasmic and membrane/cytoskeletal fractions, using a combination of coimmunoprecipitation, 2-D gel, and ...
... functions, we undertook a systems analysis of BK and BK-Associated Proteins (BKAPS) in the chicken cochlea and compared these results to other species. We identified 110 putative partners from cytoplasmic and membrane/cytoskeletal fractions, using a combination of coimmunoprecipitation, 2-D gel, and ...
1. PROTEIN MODIFICATION 1.1 What are posttranslational
... catabolism of all 20 amino acids is the same: deamination that is catalyzed by an aminotransferase, which is dependent upon the cofactor pyridoxalphosphate (PLP). In the first part of the deamination reaction, pyridoxamine (PMP) and an α-ketoacid are formed from the PLP-Ezyme imine and an amino acid ...
... catabolism of all 20 amino acids is the same: deamination that is catalyzed by an aminotransferase, which is dependent upon the cofactor pyridoxalphosphate (PLP). In the first part of the deamination reaction, pyridoxamine (PMP) and an α-ketoacid are formed from the PLP-Ezyme imine and an amino acid ...
Sequencing genomes
... A new species of frog has been introduced into an area where it has too few natural predators. In an attempt to restore the ecological balance, a team of scientists is considering introducing a species of bird which feeds on this frog. Experimental data suggests that the population of frogs and bird ...
... A new species of frog has been introduced into an area where it has too few natural predators. In an attempt to restore the ecological balance, a team of scientists is considering introducing a species of bird which feeds on this frog. Experimental data suggests that the population of frogs and bird ...
Structural and functional analyses of a yeast mitochondrial
... devoid of acidic residues, consistent with a role for these sequences in targeting MRPS28p to the mitochondria] matrix (34). Further analysis of these sequences revealed the MRPS28p precursor may belong to a subset of mitochondrial proteins that are processed in two steps (35). Comparison of the seq ...
... devoid of acidic residues, consistent with a role for these sequences in targeting MRPS28p to the mitochondria] matrix (34). Further analysis of these sequences revealed the MRPS28p precursor may belong to a subset of mitochondrial proteins that are processed in two steps (35). Comparison of the seq ...
Max ARM PDS pg1
... • Post-workout scientific innovation to provide complete nutrition to support maximum protein synthesis (anabolism), restore fluids and electrolytes, replenish glycogen and accelerate overall muscle repair and recovery.† • Packed with 28 gm (56% DV) multi-fractional whey proteins from WPI and WPC so ...
... • Post-workout scientific innovation to provide complete nutrition to support maximum protein synthesis (anabolism), restore fluids and electrolytes, replenish glycogen and accelerate overall muscle repair and recovery.† • Packed with 28 gm (56% DV) multi-fractional whey proteins from WPI and WPC so ...
Objective
... K. Belhajjame1, R. Cote4, S.M. Embury1, H. Fan2, C. Goble1, H. Hermjakob, S.J. Hubbard1, D. Jones3, P. Jones4, N. Martin2, S. Oliver1, C. Orengo3, N.W. Paton1, M. Pentony3, A. Poulovassilis2, J. Siepen, R.D. Stevens1, C. Taylor4, L. Zamboulis2, and W. Zhu4 1University ...
... K. Belhajjame1, R. Cote4, S.M. Embury1, H. Fan2, C. Goble1, H. Hermjakob, S.J. Hubbard1, D. Jones3, P. Jones4, N. Martin2, S. Oliver1, C. Orengo3, N.W. Paton1, M. Pentony3, A. Poulovassilis2, J. Siepen, R.D. Stevens1, C. Taylor4, L. Zamboulis2, and W. Zhu4 1University ...
How Enzymes Are Named - Our biological products and solutions
... protein, they are catalysts. This means that by their mere presence, and without being consumed in the process, enzymes can speed up chemical processes that would otherwise run very slowly, if at all.; Enzymes are specific Contrary to inorganic catalysts such as acids, bases, metals and metal oxides ...
... protein, they are catalysts. This means that by their mere presence, and without being consumed in the process, enzymes can speed up chemical processes that would otherwise run very slowly, if at all.; Enzymes are specific Contrary to inorganic catalysts such as acids, bases, metals and metal oxides ...
Bionano
... We are investigating the mechanical properties of nucleic acids by focusing in particular on hairpins. These structures consist of single strands of DNA or RNA whose ends are self-complementary, such that they loop back on themselves to form a duplex "stem" connected to a single-stranded loop (inset ...
... We are investigating the mechanical properties of nucleic acids by focusing in particular on hairpins. These structures consist of single strands of DNA or RNA whose ends are self-complementary, such that they loop back on themselves to form a duplex "stem" connected to a single-stranded loop (inset ...
Lecture 2
... centre of the strip and current is passed through it. The colorless amino acid solution can be detected by spraying the strip with ninhydrin, which gives it a purple color. Migration of the spot towards the negatively charged cathode confirms the net positive charge of the amino acid. All amino acid ...
... centre of the strip and current is passed through it. The colorless amino acid solution can be detected by spraying the strip with ninhydrin, which gives it a purple color. Migration of the spot towards the negatively charged cathode confirms the net positive charge of the amino acid. All amino acid ...
Over Expression of IPTG inducible GST protein in E.coli BL21
... these enzyme involves in nucleophilic attack by glutathione on an electrophilic substrate [2]. The resulting glutathione S conjugate are more soluble than the original substrate and thus more easily transported from the cell, mediated by ATP dependent MAPEG family membrane glycoprotein belonging to ...
... these enzyme involves in nucleophilic attack by glutathione on an electrophilic substrate [2]. The resulting glutathione S conjugate are more soluble than the original substrate and thus more easily transported from the cell, mediated by ATP dependent MAPEG family membrane glycoprotein belonging to ...
Identification of Pseudomonas proteins coordinately
... presence of root exudates (van Overbeek & van Elsas, 1995; Bayliss et al., 1997). Although a number of such genes have been identified, the precise roles of most of them have remained elusive. The main organic components of root exudates are sugars, various organic acids and a number of amino acids ...
... presence of root exudates (van Overbeek & van Elsas, 1995; Bayliss et al., 1997). Although a number of such genes have been identified, the precise roles of most of them have remained elusive. The main organic components of root exudates are sugars, various organic acids and a number of amino acids ...
Document
... Myosin is anchored into the inner membrane complex membrane Short actin filaments form and are moved towards the posterior end of the parasite by the myosin power The short actin filaments are linked to microneme proteins by an adaptor -- movement of actin filaments results in movement of microne ...
... Myosin is anchored into the inner membrane complex membrane Short actin filaments form and are moved towards the posterior end of the parasite by the myosin power The short actin filaments are linked to microneme proteins by an adaptor -- movement of actin filaments results in movement of microne ...
Protein

Proteins (/ˈproʊˌtiːnz/ or /ˈproʊti.ɨnz/) are large biomolecules, or macromolecules, consisting of one or more long chains of amino acid residues. Proteins perform a vast array of functions within living organisms, including catalyzing metabolic reactions, DNA replication, responding to stimuli, and transporting molecules from one location to another. Proteins differ from one another primarily in their sequence of amino acids, which is dictated by the nucleotide sequence of their genes, and which usually results in protein folding into a specific three-dimensional structure that determines its activity.A linear chain of amino acid residues is called a polypeptide. A protein contains at least one long polypeptide. Short polypeptides, containing less than about 20-30 residues, are rarely considered to be proteins and are commonly called peptides, or sometimes oligopeptides. The individual amino acid residues are bonded together by peptide bonds and adjacent amino acid residues. The sequence of amino acid residues in a protein is defined by the sequence of a gene, which is encoded in the genetic code. In general, the genetic code specifies 20 standard amino acids; however, in certain organisms the genetic code can include selenocysteine and—in certain archaea—pyrrolysine. Shortly after or even during synthesis, the residues in a protein are often chemically modified by posttranslational modification, which alters the physical and chemical properties, folding, stability, activity, and ultimately, the function of the proteins. Sometimes proteins have non-peptide groups attached, which can be called prosthetic groups or cofactors. Proteins can also work together to achieve a particular function, and they often associate to form stable protein complexes.Once formed, proteins only exist for a certain period of time and are then degraded and recycled by the cell's machinery through the process of protein turnover. A protein's lifespan is measured in terms of its half-life and covers a wide range. They can exist for minutes or years with an average lifespan of 1–2 days in mammalian cells. Abnormal and or misfolded proteins are degraded more rapidly either due to being targeted for destruction or due to being unstable.Like other biological macromolecules such as polysaccharides and nucleic acids, proteins are essential parts of organisms and participate in virtually every process within cells. Many proteins are enzymes that catalyze biochemical reactions and are vital to metabolism. Proteins also have structural or mechanical functions, such as actin and myosin in muscle and the proteins in the cytoskeleton, which form a system of scaffolding that maintains cell shape. Other proteins are important in cell signaling, immune responses, cell adhesion, and the cell cycle. Proteins are also necessary in animals' diets, since animals cannot synthesize all the amino acids they need and must obtain essential amino acids from food. Through the process of digestion, animals break down ingested protein into free amino acids that are then used in metabolism.Proteins may be purified from other cellular components using a variety of techniques such as ultracentrifugation, precipitation, electrophoresis, and chromatography; the advent of genetic engineering has made possible a number of methods to facilitate purification. Methods commonly used to study protein structure and function include immunohistochemistry, site-directed mutagenesis, X-ray crystallography, nuclear magnetic resonance and mass spectrometry.