COMMUNICATION
... tween the two a subunit genes. The differences demon- from but homologous to the human vitronectin receptor strate that the p150.95 a x subunit and the Mac-1 aM and the platelet IIb/IIIa protein (Fig. 3). The vitronectin subunit areencoded by distinct genes. The greater than receptor and IIb/IIIa ar ...
... tween the two a subunit genes. The differences demon- from but homologous to the human vitronectin receptor strate that the p150.95 a x subunit and the Mac-1 aM and the platelet IIb/IIIa protein (Fig. 3). The vitronectin subunit areencoded by distinct genes. The greater than receptor and IIb/IIIa ar ...
CapraZyme by Mt. Capra "First in Enzyme Function" A complete
... Alpha-Galactosidase: Aids in the digestion of complex sugars found in whole grains, beans, legumes, and cruciferous vegetables such as cabbage, broccoli, and cauliflower. The complex sugars (raffinose, stachyose, and verbascose) and fibrous nature of these foods pose digestive challenges for many pe ...
... Alpha-Galactosidase: Aids in the digestion of complex sugars found in whole grains, beans, legumes, and cruciferous vegetables such as cabbage, broccoli, and cauliflower. The complex sugars (raffinose, stachyose, and verbascose) and fibrous nature of these foods pose digestive challenges for many pe ...
Identification of a Protein with Antioxidant Activity that is Important for
... of these chemical components determines the shelf life of packaged beer. As the exportation of beer continues to grow, flavour stability has become an important issue for breweries. However, the ubiquitous nature of beer ageing has made it a vexing problem. Various flavour characters were developed ...
... of these chemical components determines the shelf life of packaged beer. As the exportation of beer continues to grow, flavour stability has become an important issue for breweries. However, the ubiquitous nature of beer ageing has made it a vexing problem. Various flavour characters were developed ...
Gene7-06
... 2. Each subunit contains a single major rRNA, 16S and 23S in prokaryotes, 18S and 28S in eukaryotic cytosol. 3. Each subunit has several active centers, concentrated in the translational domain of the ribosome where proteins are synthesized. 4. The major rRNAs contain regions that are localized at s ...
... 2. Each subunit contains a single major rRNA, 16S and 23S in prokaryotes, 18S and 28S in eukaryotic cytosol. 3. Each subunit has several active centers, concentrated in the translational domain of the ribosome where proteins are synthesized. 4. The major rRNAs contain regions that are localized at s ...
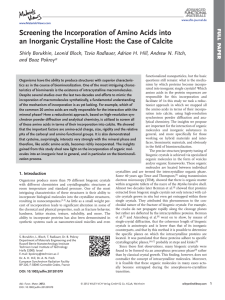
Screening the Incorporation of Amino Acids into an Inorganic
... boundaries, strongly suggesting an intercalated network-like proteinaceous organic matrix.[13] Rousseau et al. used dark-field TEM to image nacre and found that the intracrystalline organic matrix might itself possibly be crystalline.[14] Li et al.[15] used ...
... boundaries, strongly suggesting an intercalated network-like proteinaceous organic matrix.[13] Rousseau et al. used dark-field TEM to image nacre and found that the intracrystalline organic matrix might itself possibly be crystalline.[14] Li et al.[15] used ...
She2p Is a Novel RNA Binding Protein
... two pairs belonging to each opposite mating type. Only cells of opposing mating type are able to mate and form a diploid cell. To ensure that cells within a population are equally distributed between the two mating types, and, thus, capable of reproduction, the mother cell but not the daughter cell ...
... two pairs belonging to each opposite mating type. Only cells of opposing mating type are able to mate and form a diploid cell. To ensure that cells within a population are equally distributed between the two mating types, and, thus, capable of reproduction, the mother cell but not the daughter cell ...
Protein Dynamics in the Plant Extracellular Space
... contamination, such as the analysis of the growth medium of cell cultures. This method allows the study of secreted proteins but has limited biological significance. Extracellular proteins, that should have a signal peptide, are secreted by the endomembrane system formed by the endoplasmic reticulum ...
... contamination, such as the analysis of the growth medium of cell cultures. This method allows the study of secreted proteins but has limited biological significance. Extracellular proteins, that should have a signal peptide, are secreted by the endomembrane system formed by the endoplasmic reticulum ...
Chpt14_Translation.doc
... to the mRNA, they encode Met or Val, respectively. 5. tRNAf has a different structure from tRNAm, and these differences determine their use either in initiation or elongation. 6. In eukaryotes, Met-tRNAi is used for initiation. Although it is not formylated, the basic process is similar to that in p ...
... to the mRNA, they encode Met or Val, respectively. 5. tRNAf has a different structure from tRNAm, and these differences determine their use either in initiation or elongation. 6. In eukaryotes, Met-tRNAi is used for initiation. Although it is not formylated, the basic process is similar to that in p ...
amino acid, peptides, proteins, enzymes, and nucleic acids
... The structures and names of some particularly important a-amino acids are shown in Table 25-1. You will notice that the names in common use for amino acids are not descriptive of their structural formulas; but at least they have the advantage of being shorter than the systematic names. The abbreviat ...
... The structures and names of some particularly important a-amino acids are shown in Table 25-1. You will notice that the names in common use for amino acids are not descriptive of their structural formulas; but at least they have the advantage of being shorter than the systematic names. The abbreviat ...
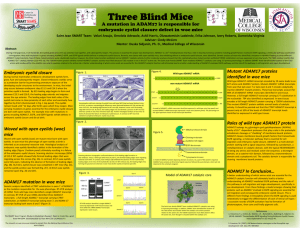
Poster
... Wild type ADAM17 mRNA transcript encoded by 19 exons leads to an 827 amino acid ADAM17 protein. Mutant ADAM17 mRNA transcripts from woe that lack exon 7 or lack exon 6 and 7 encode catalytically inactive ADAM17 mutant proteins. These two transcripts account for 90% of all ADAM17 mRNA transcripts ide ...
... Wild type ADAM17 mRNA transcript encoded by 19 exons leads to an 827 amino acid ADAM17 protein. Mutant ADAM17 mRNA transcripts from woe that lack exon 7 or lack exon 6 and 7 encode catalytically inactive ADAM17 mutant proteins. These two transcripts account for 90% of all ADAM17 mRNA transcripts ide ...
4-BCH201_Enzymes
... Enzyme specificity can be classified into the following; 1-Absolute specificity; Here the enzyme reacts with one substrate only , such as the glucokinase enzyme which acts on glucose only. 2- Group specificity; The enzyme acts upon a group of substrates (reactants) that share a common functional gro ...
... Enzyme specificity can be classified into the following; 1-Absolute specificity; Here the enzyme reacts with one substrate only , such as the glucokinase enzyme which acts on glucose only. 2- Group specificity; The enzyme acts upon a group of substrates (reactants) that share a common functional gro ...
HMB HMB for Muscle Health HMB Promotes an Anabolic State and
... pathway known as ubiquitination. In this pathway a small molecule called ubiquitin (because it is found in all cell types) is linked to protein molecules. This targets them for degradation in proteasomes. Obviously if you are a body builder or an athlete you don’t want your proteins to be degraded. ...
... pathway known as ubiquitination. In this pathway a small molecule called ubiquitin (because it is found in all cell types) is linked to protein molecules. This targets them for degradation in proteasomes. Obviously if you are a body builder or an athlete you don’t want your proteins to be degraded. ...
(PSD) November 2015 PBAC Meeting
... comparator, PKU Cooler 15®; but it does not contain choline. There is an RDI level for choline, and patients on a PKU-suitable diet are likely to have low intake of choline. The sponsor was therefore encouraged to consider adding choline to future formulations of the product. The product has a sim ...
... comparator, PKU Cooler 15®; but it does not contain choline. There is an RDI level for choline, and patients on a PKU-suitable diet are likely to have low intake of choline. The sponsor was therefore encouraged to consider adding choline to future formulations of the product. The product has a sim ...
Redistribution and differential extraction of soluble proteins in
... but it has also been used to gain novel information on the location, and hence function, of proteins whose properties are poorly understood. In the broadest sense, preparation of cells for primary antibody application involves membrane permeabilization to allow entry of the antibodies into the cell ...
... but it has also been used to gain novel information on the location, and hence function, of proteins whose properties are poorly understood. In the broadest sense, preparation of cells for primary antibody application involves membrane permeabilization to allow entry of the antibodies into the cell ...
Studies of focal adhesion assembly
... Focal adhesion complexes are formed by proteins with a wide range of functions, including adhesion receptors for the ECM, such as integrins, signalling molecules, such as Src and FAK (focal adhesion kinase), and adaptors that facilitate intracellular complex formation, such as paxillin. Focal adhesi ...
... Focal adhesion complexes are formed by proteins with a wide range of functions, including adhesion receptors for the ECM, such as integrins, signalling molecules, such as Src and FAK (focal adhesion kinase), and adaptors that facilitate intracellular complex formation, such as paxillin. Focal adhesi ...
proteins
... • In liver, most AA are utilized for synthesis of proteins, Glc, FA. • Val, Leu, Ile are not metabolized in liver due to the lack of aminotrasferases they predominate (70 %) in central circulation • High content of ammonia in portal blood is removed by liver urea ...
... • In liver, most AA are utilized for synthesis of proteins, Glc, FA. • Val, Leu, Ile are not metabolized in liver due to the lack of aminotrasferases they predominate (70 %) in central circulation • High content of ammonia in portal blood is removed by liver urea ...
Communication - Department of Molecular Physiology and Biophysics
... syntrophin triplet suggesting that all the syntrophins including α- as well as β-type may directly bind to dystrophin (Fig. 2). Previous work by Ozawa's group indicated that one of 43-DAGs was overlaid by dystrophin fusion protein containing cysteinerich and C-terminal domains (16). This interaction ...
... syntrophin triplet suggesting that all the syntrophins including α- as well as β-type may directly bind to dystrophin (Fig. 2). Previous work by Ozawa's group indicated that one of 43-DAGs was overlaid by dystrophin fusion protein containing cysteinerich and C-terminal domains (16). This interaction ...
Amino Acids, Proteins, and Enzymes
... For more information on the source of this book, or why it is available for free, please see the project's home page (http://2012books.lardbucket.org/). You can browse or download additional books there. ...
... For more information on the source of this book, or why it is available for free, please see the project's home page (http://2012books.lardbucket.org/). You can browse or download additional books there. ...
Protein Foods
... o Complete: Animal sources of protein. These proteins contain all of the protein building blocks called amino acids that your body needs to grow and maintain tissue. o Incomplete: Plant sources of protein. These proteins are missing one or more amino acids; not all of the building blocks are there. ...
... o Complete: Animal sources of protein. These proteins contain all of the protein building blocks called amino acids that your body needs to grow and maintain tissue. o Incomplete: Plant sources of protein. These proteins are missing one or more amino acids; not all of the building blocks are there. ...
Chapter 3 - GEOCITIES.ws
... 41. What type of biomolecule makes up muscle tissue, hair, and enzymes? A. Protein ...
... 41. What type of biomolecule makes up muscle tissue, hair, and enzymes? A. Protein ...
Interpretation of bafilomycin, pH neutralizing or protease inhibitor
... re-use. By now it has become widely accepted that analyzing the number of autophagy-related structures alone is an inadequate measure of autophagic degradation activity (flux), as increased autophagosome numbers can reflect both their accelerated generation or decreased clearence. Similarly, the num ...
... re-use. By now it has become widely accepted that analyzing the number of autophagy-related structures alone is an inadequate measure of autophagic degradation activity (flux), as increased autophagosome numbers can reflect both their accelerated generation or decreased clearence. Similarly, the num ...
Secreted Hepatitis B Surface Antigen Polypeptides Are Derived from
... protease-sensitive transmembrane form (labeled F ) is seen after a 40-min labeling period (Fig. 2 A, lane 8); this is generated from cleavage of chains synthesized at the end of the labeling period before sufficient time has elapsed for conversion to the protease-resistant form. These studies sugges ...
... protease-sensitive transmembrane form (labeled F ) is seen after a 40-min labeling period (Fig. 2 A, lane 8); this is generated from cleavage of chains synthesized at the end of the labeling period before sufficient time has elapsed for conversion to the protease-resistant form. These studies sugges ...
Protein

Proteins (/ˈproʊˌtiːnz/ or /ˈproʊti.ɨnz/) are large biomolecules, or macromolecules, consisting of one or more long chains of amino acid residues. Proteins perform a vast array of functions within living organisms, including catalyzing metabolic reactions, DNA replication, responding to stimuli, and transporting molecules from one location to another. Proteins differ from one another primarily in their sequence of amino acids, which is dictated by the nucleotide sequence of their genes, and which usually results in protein folding into a specific three-dimensional structure that determines its activity.A linear chain of amino acid residues is called a polypeptide. A protein contains at least one long polypeptide. Short polypeptides, containing less than about 20-30 residues, are rarely considered to be proteins and are commonly called peptides, or sometimes oligopeptides. The individual amino acid residues are bonded together by peptide bonds and adjacent amino acid residues. The sequence of amino acid residues in a protein is defined by the sequence of a gene, which is encoded in the genetic code. In general, the genetic code specifies 20 standard amino acids; however, in certain organisms the genetic code can include selenocysteine and—in certain archaea—pyrrolysine. Shortly after or even during synthesis, the residues in a protein are often chemically modified by posttranslational modification, which alters the physical and chemical properties, folding, stability, activity, and ultimately, the function of the proteins. Sometimes proteins have non-peptide groups attached, which can be called prosthetic groups or cofactors. Proteins can also work together to achieve a particular function, and they often associate to form stable protein complexes.Once formed, proteins only exist for a certain period of time and are then degraded and recycled by the cell's machinery through the process of protein turnover. A protein's lifespan is measured in terms of its half-life and covers a wide range. They can exist for minutes or years with an average lifespan of 1–2 days in mammalian cells. Abnormal and or misfolded proteins are degraded more rapidly either due to being targeted for destruction or due to being unstable.Like other biological macromolecules such as polysaccharides and nucleic acids, proteins are essential parts of organisms and participate in virtually every process within cells. Many proteins are enzymes that catalyze biochemical reactions and are vital to metabolism. Proteins also have structural or mechanical functions, such as actin and myosin in muscle and the proteins in the cytoskeleton, which form a system of scaffolding that maintains cell shape. Other proteins are important in cell signaling, immune responses, cell adhesion, and the cell cycle. Proteins are also necessary in animals' diets, since animals cannot synthesize all the amino acids they need and must obtain essential amino acids from food. Through the process of digestion, animals break down ingested protein into free amino acids that are then used in metabolism.Proteins may be purified from other cellular components using a variety of techniques such as ultracentrifugation, precipitation, electrophoresis, and chromatography; the advent of genetic engineering has made possible a number of methods to facilitate purification. Methods commonly used to study protein structure and function include immunohistochemistry, site-directed mutagenesis, X-ray crystallography, nuclear magnetic resonance and mass spectrometry.