Effect of peptide chain length on amino acid and
... In earlier intestinal perfusion experiments, differences were found in the handling of four different protein hydrolysates [S, 6, 81. Although it seemed, at the time, that there could be a number of explanations for the differences (varying amino acid composition of the starter proteins, different p ...
... In earlier intestinal perfusion experiments, differences were found in the handling of four different protein hydrolysates [S, 6, 81. Although it seemed, at the time, that there could be a number of explanations for the differences (varying amino acid composition of the starter proteins, different p ...
Bioinformatics Research and Resources at the University of
... The equilibrium length of the peptide bond (C -- N) is about 2 [Ang]. The average Ca - Ca distance in a polypeptide chain is about 3.8 [Ang]. The angle of rotation around N - Ca bond is called j, and the angle around the Ca - C bond is called f. These two angles define the overall conformation of po ...
... The equilibrium length of the peptide bond (C -- N) is about 2 [Ang]. The average Ca - Ca distance in a polypeptide chain is about 3.8 [Ang]. The angle of rotation around N - Ca bond is called j, and the angle around the Ca - C bond is called f. These two angles define the overall conformation of po ...
unravelling the therapeutic potential of transmembrane peptides
... The computed helical anti‐membrane protein (CHAMP) is a cheap method to generate new TM peptide binders by in silico modeling using the target helix sequence as a starting point. The first step includes database mining and selection of a two‐helix bundle. T ...
... The computed helical anti‐membrane protein (CHAMP) is a cheap method to generate new TM peptide binders by in silico modeling using the target helix sequence as a starting point. The first step includes database mining and selection of a two‐helix bundle. T ...
Allosteric Inhibition of Aminoglycoside Phosphotransferase by a
... APH is an ideal model system for all kinases sharing this fold (Hon et al., 1997). EPKs are of great biological and medical importance because of their fundamental role in signal transduction and regulatory pathways in eukaryotic cells. Diseases, including cancer, inflammation and diabetes, are ofte ...
... APH is an ideal model system for all kinases sharing this fold (Hon et al., 1997). EPKs are of great biological and medical importance because of their fundamental role in signal transduction and regulatory pathways in eukaryotic cells. Diseases, including cancer, inflammation and diabetes, are ofte ...
Print - Circulation Research
... was maintained for an identical period in the same medium plus the experimental agent. In some experiments, the final media (both control and experimental) contained cycloheximide, 2.5 /xg/ml, to block protein synthesis and reutilization of label. For experiments involving chloroquine, initial stabi ...
... was maintained for an identical period in the same medium plus the experimental agent. In some experiments, the final media (both control and experimental) contained cycloheximide, 2.5 /xg/ml, to block protein synthesis and reutilization of label. For experiments involving chloroquine, initial stabi ...
Mitochondrial protein acetylation regulates metabolism
... group to the ε-amino group of lysine residues that occurs on a wide array of proteins. This simple modification neutralizes the positive charge of the lysine residue, potentially altering its propensity to interact with nearby amino acids or other proteins. In this way, acetylation can influence mul ...
... group to the ε-amino group of lysine residues that occurs on a wide array of proteins. This simple modification neutralizes the positive charge of the lysine residue, potentially altering its propensity to interact with nearby amino acids or other proteins. In this way, acetylation can influence mul ...
Electrophoresis
... according to molar masses of its components • However, the shape and charge will also determine the drift speed • One way to avoid this problem and to effect separation by molar mass is to denature the proteins in a controlled way • Sodium dodecyl sulfate is an anionic detergent that is very useful ...
... according to molar masses of its components • However, the shape and charge will also determine the drift speed • One way to avoid this problem and to effect separation by molar mass is to denature the proteins in a controlled way • Sodium dodecyl sulfate is an anionic detergent that is very useful ...
Serine phosphorylation of the cotton cytosolic pyruvate kinase
... cotton fiber cell is one of the longest and fastest elongating cells in the plant kingdom, making it a suitable model system for studying the mechanism of fast cell expansion [2]. In recent years, the key roles of carbohydrate metabolism in cotton fiber development have gradually been recognized. Sp ...
... cotton fiber cell is one of the longest and fastest elongating cells in the plant kingdom, making it a suitable model system for studying the mechanism of fast cell expansion [2]. In recent years, the key roles of carbohydrate metabolism in cotton fiber development have gradually been recognized. Sp ...
SARS: Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome
... to a page that contains the results of your search. At the time this tutorial was written, the search engine found 49 matches for “SARS”. If you get more then 49 results, do not panic. Inconsistencies in the number of search results can occur because new sequences are being added to the databases on ...
... to a page that contains the results of your search. At the time this tutorial was written, the search engine found 49 matches for “SARS”. If you get more then 49 results, do not panic. Inconsistencies in the number of search results can occur because new sequences are being added to the databases on ...
Co-translational Folding
... But the released polypeptide chain received the instructions for folding from the ribosome (Fedorov, A. N., Friguet, B., Djavadi-Ohaniance, L., Alakhov, Yu, B. and Goldberg, M. E., J. Mol. Biol., 1992, 228, 351–358 in http://www.ias.ac.in/currsci/aug25/articles27.htm by DasGupta ...
... But the released polypeptide chain received the instructions for folding from the ribosome (Fedorov, A. N., Friguet, B., Djavadi-Ohaniance, L., Alakhov, Yu, B. and Goldberg, M. E., J. Mol. Biol., 1992, 228, 351–358 in http://www.ias.ac.in/currsci/aug25/articles27.htm by DasGupta ...
The dark side of dioxygen biochemistry Joan Selverstone Valentine
... proteins such as hemoglobin or myoglobin that bind, transport, store, and release dioxygen have evolved to aid in its rapid delivery. Dioxygen is also used as a source of oxygen atoms in a large variety of enzyme-catalyzed biosynthetic reactions of organic substrate molecules. The same oxidizing pow ...
... proteins such as hemoglobin or myoglobin that bind, transport, store, and release dioxygen have evolved to aid in its rapid delivery. Dioxygen is also used as a source of oxygen atoms in a large variety of enzyme-catalyzed biosynthetic reactions of organic substrate molecules. The same oxidizing pow ...
Gene Section NOL3 (nucleolar protein 3 (apoptosis repressor with CARD domain))
... two splice donors separated by 10 nucleotides in exon 2 connecting to a single splice acceptor in exon 3 (Stoss et al., 1999). Because the separation between the splice donors, 10 nucleotides, is not an exact multiple of 3, alternative splicing results in two open reading frames distal to the splice ...
... two splice donors separated by 10 nucleotides in exon 2 connecting to a single splice acceptor in exon 3 (Stoss et al., 1999). Because the separation between the splice donors, 10 nucleotides, is not an exact multiple of 3, alternative splicing results in two open reading frames distal to the splice ...
Lecture 27
... excreted. This results in increase in Glu through transamination reactions. Excess Glu causes an increase in N-acetylglutamate which stimulates CPS I causing increases in urea cycle. ...
... excreted. This results in increase in Glu through transamination reactions. Excess Glu causes an increase in N-acetylglutamate which stimulates CPS I causing increases in urea cycle. ...
How do non-enyzmatic domains become enzymes
... Bio-catalysis relies on a constellation of a few amino acid residues that are embedded in a distinct globular domain of the enzyme (the catalytic domain). ...
... Bio-catalysis relies on a constellation of a few amino acid residues that are embedded in a distinct globular domain of the enzyme (the catalytic domain). ...
MIBCB Syllabus
... Chemistry of amino acids and proteins: Structure and properties of amino acids. Classification based on structure, ionic properties of amino acids, isoelectric pH, buffering action of amino acids and proteins. Structural organization of proteins – primary, secondary, teritiary and quarternary, force ...
... Chemistry of amino acids and proteins: Structure and properties of amino acids. Classification based on structure, ionic properties of amino acids, isoelectric pH, buffering action of amino acids and proteins. Structural organization of proteins – primary, secondary, teritiary and quarternary, force ...
Changes in chemical composition in male turkeys
... The viscera and feather contents generally decreased with increasing age (Table 1), resulting in an increase in carcass content from 75.2 to 90.2% of BW between 1 and 15 wk. These tendencies are also reflected in the scale parameter (b) of equation 2b, which was greater than unity for the carcass an ...
... The viscera and feather contents generally decreased with increasing age (Table 1), resulting in an increase in carcass content from 75.2 to 90.2% of BW between 1 and 15 wk. These tendencies are also reflected in the scale parameter (b) of equation 2b, which was greater than unity for the carcass an ...
Slide 1
... supply vitamins and minerals. It is suitable for consumption by special groups of people, aiming to regulate human body functions, but is not used for therapeutic purposes. ...
... supply vitamins and minerals. It is suitable for consumption by special groups of people, aiming to regulate human body functions, but is not used for therapeutic purposes. ...
BPM§1.2_Protein Struktur.key
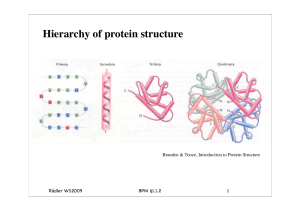
... This describes the overall shape of the domain structure as determined by the orientations of the secondary structures but ignores the connectivity between the secondary structures. ...
... This describes the overall shape of the domain structure as determined by the orientations of the secondary structures but ignores the connectivity between the secondary structures. ...
Intracellular catalysis of disulfide bond formation by the human
... In order to investigate the role of mammalian QSOX in oxidative protein folding, we created a stable cell line expressing the longer form of the human QSOX1 (hQSOX1a) enzyme as well as a model protein, human tPA (tissue plasminogen activator). We have previously shown [16] that overexpression of Ero ...
... In order to investigate the role of mammalian QSOX in oxidative protein folding, we created a stable cell line expressing the longer form of the human QSOX1 (hQSOX1a) enzyme as well as a model protein, human tPA (tissue plasminogen activator). We have previously shown [16] that overexpression of Ero ...
Selective Dimerization of a C2H2 Zinc Finger Subfamily
... et al., 2000). In addition to the cysteines and histidines that coordinate zinc, C2H2 fingers contain conserved hybrophobic residues that pack in the hydrophobic core. These conserved amino acids lead to the formation of the characteristic structure comprised of a twostranded antiparallel  sheet an ...
... et al., 2000). In addition to the cysteines and histidines that coordinate zinc, C2H2 fingers contain conserved hybrophobic residues that pack in the hydrophobic core. These conserved amino acids lead to the formation of the characteristic structure comprised of a twostranded antiparallel  sheet an ...
Molecular Components of the Bacterial Cytoskeleton
... protein polymer formation). The core structures of α- and β-tubulin are composed of two β-sheets surrounded by α-helices (Nogales et al. 1998b), making up two functional domains. The N-terminal of the two domains has a Rossmann fold similar to that of many ATPases, and it contains a GTP binding site ...
... protein polymer formation). The core structures of α- and β-tubulin are composed of two β-sheets surrounded by α-helices (Nogales et al. 1998b), making up two functional domains. The N-terminal of the two domains has a Rossmann fold similar to that of many ATPases, and it contains a GTP binding site ...
CHAPTER 26
... In each of the following multiple-choice questions, place the letter of the correct response in the blank at the left. There may be more than one correct response (choice d) or no correct response for a question (choice e). ...
... In each of the following multiple-choice questions, place the letter of the correct response in the blank at the left. There may be more than one correct response (choice d) or no correct response for a question (choice e). ...
Document
... light chains where about 200 different V regions may recombine with about 5 different J regions giving rise to 200 x 5 = 1000 possible light chains. 1. Since in any particular B-cell, any light chain combination can occur along with any heavy chain combination, the total possible immunoglobulin comb ...
... light chains where about 200 different V regions may recombine with about 5 different J regions giving rise to 200 x 5 = 1000 possible light chains. 1. Since in any particular B-cell, any light chain combination can occur along with any heavy chain combination, the total possible immunoglobulin comb ...
Protein

Proteins (/ˈproʊˌtiːnz/ or /ˈproʊti.ɨnz/) are large biomolecules, or macromolecules, consisting of one or more long chains of amino acid residues. Proteins perform a vast array of functions within living organisms, including catalyzing metabolic reactions, DNA replication, responding to stimuli, and transporting molecules from one location to another. Proteins differ from one another primarily in their sequence of amino acids, which is dictated by the nucleotide sequence of their genes, and which usually results in protein folding into a specific three-dimensional structure that determines its activity.A linear chain of amino acid residues is called a polypeptide. A protein contains at least one long polypeptide. Short polypeptides, containing less than about 20-30 residues, are rarely considered to be proteins and are commonly called peptides, or sometimes oligopeptides. The individual amino acid residues are bonded together by peptide bonds and adjacent amino acid residues. The sequence of amino acid residues in a protein is defined by the sequence of a gene, which is encoded in the genetic code. In general, the genetic code specifies 20 standard amino acids; however, in certain organisms the genetic code can include selenocysteine and—in certain archaea—pyrrolysine. Shortly after or even during synthesis, the residues in a protein are often chemically modified by posttranslational modification, which alters the physical and chemical properties, folding, stability, activity, and ultimately, the function of the proteins. Sometimes proteins have non-peptide groups attached, which can be called prosthetic groups or cofactors. Proteins can also work together to achieve a particular function, and they often associate to form stable protein complexes.Once formed, proteins only exist for a certain period of time and are then degraded and recycled by the cell's machinery through the process of protein turnover. A protein's lifespan is measured in terms of its half-life and covers a wide range. They can exist for minutes or years with an average lifespan of 1–2 days in mammalian cells. Abnormal and or misfolded proteins are degraded more rapidly either due to being targeted for destruction or due to being unstable.Like other biological macromolecules such as polysaccharides and nucleic acids, proteins are essential parts of organisms and participate in virtually every process within cells. Many proteins are enzymes that catalyze biochemical reactions and are vital to metabolism. Proteins also have structural or mechanical functions, such as actin and myosin in muscle and the proteins in the cytoskeleton, which form a system of scaffolding that maintains cell shape. Other proteins are important in cell signaling, immune responses, cell adhesion, and the cell cycle. Proteins are also necessary in animals' diets, since animals cannot synthesize all the amino acids they need and must obtain essential amino acids from food. Through the process of digestion, animals break down ingested protein into free amino acids that are then used in metabolism.Proteins may be purified from other cellular components using a variety of techniques such as ultracentrifugation, precipitation, electrophoresis, and chromatography; the advent of genetic engineering has made possible a number of methods to facilitate purification. Methods commonly used to study protein structure and function include immunohistochemistry, site-directed mutagenesis, X-ray crystallography, nuclear magnetic resonance and mass spectrometry.