polymerisation
... Process • during polymerisation, an alkene undergoes an addition reaction with itself • all the atoms in the original alkenes are used to form the polymer • long hydrocarbon chains are formed ...
... Process • during polymerisation, an alkene undergoes an addition reaction with itself • all the atoms in the original alkenes are used to form the polymer • long hydrocarbon chains are formed ...
No Slide Title
... Process • during polymerisation, an alkene undergoes an addition reaction with itself • all the atoms in the original alkenes are used to form the polymer • long hydrocarbon chains are formed ...
... Process • during polymerisation, an alkene undergoes an addition reaction with itself • all the atoms in the original alkenes are used to form the polymer • long hydrocarbon chains are formed ...
essential fatty acid
... Building blocks of proteins. An amino acid is an organic acid that has an amine (-NH2) group attached to a chain containing an acid group. Amphoteric compounds, i.e. can react with an acid or base, account for their ability to act as buffers in the blood. At a certain pH, amino acids will not migrat ...
... Building blocks of proteins. An amino acid is an organic acid that has an amine (-NH2) group attached to a chain containing an acid group. Amphoteric compounds, i.e. can react with an acid or base, account for their ability to act as buffers in the blood. At a certain pH, amino acids will not migrat ...
Section 8: Genetic Mutations, Ribosome Structure
... 2. Which of the following mutations would be MOST likely to have a harmful effect on an organism? A. A base-pair substitution in the middle of the coding sequence. B. A deletion of three nucleotides in the middle of the coding sequence. C. A single nucleotide deletion in the middle of an intron. D. ...
... 2. Which of the following mutations would be MOST likely to have a harmful effect on an organism? A. A base-pair substitution in the middle of the coding sequence. B. A deletion of three nucleotides in the middle of the coding sequence. C. A single nucleotide deletion in the middle of an intron. D. ...
M-MuLV Reverse Transcriptase, RNase H minus
... M-MuLV Reverse transcriptase is purified from an E.coli strain harbouring a plasmid that directs the synthesis of a modified form of Moloney Murine Leukemia virus (M-MuLV) reverse transcriptase. M-MuLV reverse transcriptase is a RNA or DNA directed DNA polymerase. The enzyme can synthesize a complem ...
... M-MuLV Reverse transcriptase is purified from an E.coli strain harbouring a plasmid that directs the synthesis of a modified form of Moloney Murine Leukemia virus (M-MuLV) reverse transcriptase. M-MuLV reverse transcriptase is a RNA or DNA directed DNA polymerase. The enzyme can synthesize a complem ...
Amino Acids
... • Proteins are linear heteropolymers of -amino acids • Amino acids have properties that are well-suited to carry out a variety of biological functions ...
... • Proteins are linear heteropolymers of -amino acids • Amino acids have properties that are well-suited to carry out a variety of biological functions ...
Introduction to Organic Synthesis
... simpler molecules by means of DISCONNECTIONS and/or FUNCTIONAL GROUP INTERCONVERSIONS that correspond to known reactions. When you've got to a simple enough starting material (like something you can buy [and usually is cheap]) then the synthetic plan is simply the reverse of the analysis. The design ...
... simpler molecules by means of DISCONNECTIONS and/or FUNCTIONAL GROUP INTERCONVERSIONS that correspond to known reactions. When you've got to a simple enough starting material (like something you can buy [and usually is cheap]) then the synthetic plan is simply the reverse of the analysis. The design ...
Homework set 1: Biological Molecules
... Prostaglandins are a group of about 20 lipids that are modified fatty acids, with two nonpolar "tails" attached to a five-carbon ring. Prostaglandins occur in many vertebrate tissues, where they appear to act as local chemical messengers. The name is derived from the fact that the original members o ...
... Prostaglandins are a group of about 20 lipids that are modified fatty acids, with two nonpolar "tails" attached to a five-carbon ring. Prostaglandins occur in many vertebrate tissues, where they appear to act as local chemical messengers. The name is derived from the fact that the original members o ...
C1-esterase inhibitor attenuates the inflammatory
... local anaesthesia (lidocaine HCL 20 mg/ml). This catheter was connected to an arterial pressure monitoring set (Edwards Lifesciences LLC, Irvine, CA) and a Philips IntelliVue MP70 monitor (Philips Medical Systems, Eindhoven, The Netherlands). The mean arterial pressure (MAP) was determined using the ...
... local anaesthesia (lidocaine HCL 20 mg/ml). This catheter was connected to an arterial pressure monitoring set (Edwards Lifesciences LLC, Irvine, CA) and a Philips IntelliVue MP70 monitor (Philips Medical Systems, Eindhoven, The Netherlands). The mean arterial pressure (MAP) was determined using the ...
From RNA to protein
... e.g. wheat endosperm storage proteins. The same proteins can cause intense suffering in certain individuals - e.g. celiac disease ...
... e.g. wheat endosperm storage proteins. The same proteins can cause intense suffering in certain individuals - e.g. celiac disease ...
Microsoft Word
... efficient synthetic routes is of considerable interest. Although, there are several routes to synthesis of Clopidogrel, most of the routes utilize either the 2chloromandalate or 2-chlorophenylglycine derivatives as the starting materials. Initially, the final product was made in the racemic form and ...
... efficient synthetic routes is of considerable interest. Although, there are several routes to synthesis of Clopidogrel, most of the routes utilize either the 2chloromandalate or 2-chlorophenylglycine derivatives as the starting materials. Initially, the final product was made in the racemic form and ...
From RNA to protein
... e.g. wheat endosperm storage proteins. The same proteins can cause intense suffering in certain individuals - e.g. celiac disease ...
... e.g. wheat endosperm storage proteins. The same proteins can cause intense suffering in certain individuals - e.g. celiac disease ...
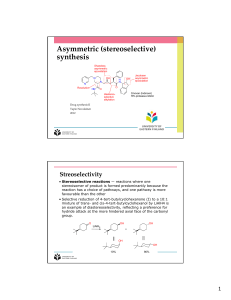
Asymmetric (stereoselective) synthesis
... products as starting materials • Enalapril is prepared by a diastereoselective reductive amination between ethyl-2-oxo-4-phenylbutyrate and alanyl-proline favoring the desired (S,S,S)-enantiomer (17:1) ...
... products as starting materials • Enalapril is prepared by a diastereoselective reductive amination between ethyl-2-oxo-4-phenylbutyrate and alanyl-proline favoring the desired (S,S,S)-enantiomer (17:1) ...
synthase is regulated by mRNA splicing
... synthesis and cell division, and it is now well established that many mitogens induce PGHS activity (4-11). Significantly, it has also been shown that some nonsteroidal antiinflammatory drugs exert antiproliferative and antitumor activities in vitro and in vivo, suggesting that PGHS plays an importa ...
... synthesis and cell division, and it is now well established that many mitogens induce PGHS activity (4-11). Significantly, it has also been shown that some nonsteroidal antiinflammatory drugs exert antiproliferative and antitumor activities in vitro and in vivo, suggesting that PGHS plays an importa ...
DNA Lecture 2
... Note that when the phosphate group forms a diester linkage there is only one ionizable oxygen that is usually represented in the ionized (charged) form. Consider why the phosphodiester is in the ionized form. Recall that phosphoric acid itself has three acidionization equilibria- ...
... Note that when the phosphate group forms a diester linkage there is only one ionizable oxygen that is usually represented in the ionized (charged) form. Consider why the phosphodiester is in the ionized form. Recall that phosphoric acid itself has three acidionization equilibria- ...
Derivatization reagents
... ● Purified, dried and packaged under nitrogen in convenient 50mL Hypo-Vial Sample Storage Vials ● Supplied with elastomer septa, allowing immediate access to the sample without exposure to moisture and oxygen ● Use polar solvents (acetonitrile, dimethylformamide, dimethylsulfoxide, pyridine, tetrahy ...
... ● Purified, dried and packaged under nitrogen in convenient 50mL Hypo-Vial Sample Storage Vials ● Supplied with elastomer septa, allowing immediate access to the sample without exposure to moisture and oxygen ● Use polar solvents (acetonitrile, dimethylformamide, dimethylsulfoxide, pyridine, tetrahy ...
RIBONUCLEIC ACID (RNA)
... • These so-called non-coding RNAs ("ncRNA") can be encoded by their own genes (RNA genes), but can also derive from mRNA introns • The most prominent examples of non-coding RNAs are transfer RNA (tRNA) and ribosomal RNA (rRNA), both of which are involved in the process of translation ...
... • These so-called non-coding RNAs ("ncRNA") can be encoded by their own genes (RNA genes), but can also derive from mRNA introns • The most prominent examples of non-coding RNAs are transfer RNA (tRNA) and ribosomal RNA (rRNA), both of which are involved in the process of translation ...
Computational Biochemistry - Structural Bioinformatics and
... Competitors may use Homology Modelling, Fold recognition or Ab Initio structural prediction methods to propose the structure of the protein. ...
... Competitors may use Homology Modelling, Fold recognition or Ab Initio structural prediction methods to propose the structure of the protein. ...
chapter 19 antibiotics
... Naturally produced antibiotics are products of secondary metabolic pathways. These pathways are not turned on all the time. Continuous production could adversely affect the organism. Some bacteria restrict antibiotic production to the stationary ...
... Naturally produced antibiotics are products of secondary metabolic pathways. These pathways are not turned on all the time. Continuous production could adversely affect the organism. Some bacteria restrict antibiotic production to the stationary ...
AE-December-2016-04-BS-12
... beverages. Explain why drug screenings are able to detect the presence of THC but not ethanol weeks after these substances have been introduced into the body ...
... beverages. Explain why drug screenings are able to detect the presence of THC but not ethanol weeks after these substances have been introduced into the body ...
Bottromycin

Bottromycin is a macrocyclic peptide with antibiotic activity. It was first discovered in 1957 as a natural product isolated from Streptomyces bottropensis. It has been shown to inhibit methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) and vancomycin-resistant Enterococci (VRE) among other Gram-positive bacteria and mycoplasma. Bottromycin is structurally distinct from both vancomycin, a glycopeptide antibiotic, and methicillin, a beta-lactam antibiotic.Bottromycin binds to the A site of the ribosome and blocks the binding of aminoacyl-tRNA, therefore inhibiting bacterial protein synthesis. Although bottromycin exhibits antibacterial activity in vitro, it has not yet been developed as a clinical antibiotic, potentially due to its poor stability in blood plasma. To increase its stability in vivo, some bottromycin derivatives have been explored.The structure of bottromycin contains a macrocyclic amidine as well as a thiazole ring. The absolute stereochemistry at several chiral centers has been determined as of 2009. In 2012, a three-dimensional solution structure of bottromycin was published. The solution structure revealed that several methyl groups are on the same face of the structure.Bottromycin falls within the ribosomally synthesized and post-translationally modified peptide class of natural product.