Mevalonate kinase from etiolated cotyledons of French beans
... 3000 times that of the mevalonate kinase. This phosphatase activity also hydrolysed ADP and mevalonate 5-phosphate. Cotyledon mevalonate kinase was therefore purified, with a view to removing the phosphatase activity. The properties of the cotyledon enzyme were investigated preliminary to a study of ...
... 3000 times that of the mevalonate kinase. This phosphatase activity also hydrolysed ADP and mevalonate 5-phosphate. Cotyledon mevalonate kinase was therefore purified, with a view to removing the phosphatase activity. The properties of the cotyledon enzyme were investigated preliminary to a study of ...
growth regulators
... higher plant was published by A.J. Haagen-Smit and coworkers in 1946. The discovery of 2,4-D, and related chemicals, occurred independently by four research groups in Britain and the U.S. during World War II. This discovery revolutionized modern agriculture. Since the synthesis of 2,4-D, a number of ...
... higher plant was published by A.J. Haagen-Smit and coworkers in 1946. The discovery of 2,4-D, and related chemicals, occurred independently by four research groups in Britain and the U.S. during World War II. This discovery revolutionized modern agriculture. Since the synthesis of 2,4-D, a number of ...
Exam 1 Review Sheet Chapter 15 Chemistry 110b
... Synthesis of ketones: Review those from last semester and chapter 15. Ketones from the reaction of nitriles with RMgX or RLi, know the mechanism of this reaction and identify the unstable imine intermediate. [10e, 738-739; 11e, 729731] ...
... Synthesis of ketones: Review those from last semester and chapter 15. Ketones from the reaction of nitriles with RMgX or RLi, know the mechanism of this reaction and identify the unstable imine intermediate. [10e, 738-739; 11e, 729731] ...
The binding of 3´-N-piperidine-4-carboxyl-3´-deoxy-ara
... The majority of small molecule RNase A inhibitors studied thus far, have acidic groups such as phosphate, carboxylate, or sulfate [6, [7]. Aminonucleosides like 3´-N-piperidine-4-carboxyl-3´deoxy-ara-uridine (3e) have been selected for inhibition studies with the view that uridine derivatives with a ...
... The majority of small molecule RNase A inhibitors studied thus far, have acidic groups such as phosphate, carboxylate, or sulfate [6, [7]. Aminonucleosides like 3´-N-piperidine-4-carboxyl-3´deoxy-ara-uridine (3e) have been selected for inhibition studies with the view that uridine derivatives with a ...
Lec 16 - RNA and IT`s Structure
... 2. Noncoding region 1 (NC1). The cap is followed by a region of 10 to 100 nucleotides. This region is rich in A and U residues, and does not translate protein. 3. The initiation codon is AUG in both prokaryotes and eukaryotes 4. The coding region consists of about 1,500 nucleotides on the average an ...
... 2. Noncoding region 1 (NC1). The cap is followed by a region of 10 to 100 nucleotides. This region is rich in A and U residues, and does not translate protein. 3. The initiation codon is AUG in both prokaryotes and eukaryotes 4. The coding region consists of about 1,500 nucleotides on the average an ...
Full Text
... finding these and other correlations, and an inference program for searching databases with Bayesian networks. Thus, we have made a first step in bringing critical structural information in the form of correlations into the realm of sequence analysis. In this paper we demonstrate the discovery and r ...
... finding these and other correlations, and an inference program for searching databases with Bayesian networks. Thus, we have made a first step in bringing critical structural information in the form of correlations into the realm of sequence analysis. In this paper we demonstrate the discovery and r ...
Amines: The Basic Group
... CH3CH2C NH CH3 CH3CH2CH2 NH CH3 Aromatic amines are prepared via reduction of nitro compounds. E. g. ...
... CH3CH2C NH CH3 CH3CH2CH2 NH CH3 Aromatic amines are prepared via reduction of nitro compounds. E. g. ...
ab110043 – Fumarase Specific Activity Microplate Assay Kit
... that catalyzes the reversible hydration/dehydration of fumarate to Smalate (EC 4.2.1.2) in the mitochondrial Krebs cycle, see below. A second fumarase isoform exists without the mitochondrial import sequence. This cytoplasmic form of the enzyme metabolizes cytoplasmic fumarate, a byproduct of the ur ...
... that catalyzes the reversible hydration/dehydration of fumarate to Smalate (EC 4.2.1.2) in the mitochondrial Krebs cycle, see below. A second fumarase isoform exists without the mitochondrial import sequence. This cytoplasmic form of the enzyme metabolizes cytoplasmic fumarate, a byproduct of the ur ...
AP Lab #10: Preparation of Ester
... In this general reaction, Rand R' represent hydrocarbon chains, which may be the same or different. Unlike many organic chemical compounds, esters often have very pleasant, fruitlike odors. Many of the odors and flavorings of fruits and flowers are due to the presence of esters in the essential oils ...
... In this general reaction, Rand R' represent hydrocarbon chains, which may be the same or different. Unlike many organic chemical compounds, esters often have very pleasant, fruitlike odors. Many of the odors and flavorings of fruits and flowers are due to the presence of esters in the essential oils ...
Carboxylic Acid Derivatives and Nucleophilic Acyl Substitution
... Hydrolysis: Conversion of Acid Halides into Acids Acid chlorides react with water to yield carboxylic acids HCl is generated during the hydrolysis: a base is added to ...
... Hydrolysis: Conversion of Acid Halides into Acids Acid chlorides react with water to yield carboxylic acids HCl is generated during the hydrolysis: a base is added to ...
Judge, P.J. and Watts, A.
... shifts may then be used for the basis of structure calculations. The first successful demonstration of this technique has been the partial assignment of resonances from the b-barrel protein OmpX from E. coli [43]. It should be noted that most other membrane proteins have a significant a-helical cont ...
... shifts may then be used for the basis of structure calculations. The first successful demonstration of this technique has been the partial assignment of resonances from the b-barrel protein OmpX from E. coli [43]. It should be noted that most other membrane proteins have a significant a-helical cont ...
Chapter 15 ΠCarboxylic Acids and Esters
... where [H3O+] ≡ [H+]. (Recall that the water does not change concentration and therefore is incorporated into the Ka constant.) Most simple carboxylic acids have acid dissociation constants equal to about 10-5. Such a small Ka means that very little of the acid is ionized in water. Nonetheless, carbo ...
... where [H3O+] ≡ [H+]. (Recall that the water does not change concentration and therefore is incorporated into the Ka constant.) Most simple carboxylic acids have acid dissociation constants equal to about 10-5. Such a small Ka means that very little of the acid is ionized in water. Nonetheless, carbo ...
Şenol, O.İ., Viljava, T.-R., Krause, AOI
... the deesterification reaction yields carboxylic acids and methanol. The water required for the reaction may be supplied by the dehydration of the alcohols in path I. The formed carboxylic acids are either reduced to alcohol releasing a mole of water or decarboxylated to alkenes followed by hydrogena ...
... the deesterification reaction yields carboxylic acids and methanol. The water required for the reaction may be supplied by the dehydration of the alcohols in path I. The formed carboxylic acids are either reduced to alcohol releasing a mole of water or decarboxylated to alkenes followed by hydrogena ...
Chapter 18: Carboxylic Acids 18.1: Carboxylic Acid Nomenclature
... 18.4: Acidity of Carboxylic Acids. The pKa of carboxylic acids typically ~ 5. They are significantly more acidic than water or alcohols. Bronsted Acidity (Ch. 1.13): Carboxylic acids transfer a proton to water to give H3O+ and carboxylate anions, RCO2O R ...
... 18.4: Acidity of Carboxylic Acids. The pKa of carboxylic acids typically ~ 5. They are significantly more acidic than water or alcohols. Bronsted Acidity (Ch. 1.13): Carboxylic acids transfer a proton to water to give H3O+ and carboxylate anions, RCO2O R ...
Problems - TigerWeb
... All answers should be written on the exam in the spaces provided. Clearly indicate your answers in the spaces provided; if I have to guess as to what or where your answer is, it is wrong. Where applicable, outline the logic or mystical principle you used to arrive at your answer, as partial credit m ...
... All answers should be written on the exam in the spaces provided. Clearly indicate your answers in the spaces provided; if I have to guess as to what or where your answer is, it is wrong. Where applicable, outline the logic or mystical principle you used to arrive at your answer, as partial credit m ...
Visualization of RNA molecules using VMD
... Nucleotide consists of base (adenine, urasil, cytosine, guanine), phosphate and sugar parts. There are two different groups of bases: purines and pyrimidines. Adenine and guanine are purines and cytosine and urasil pyrimidines. Sugar is pentose and phosphate is bonded to its 5'-carbon. Base is bonde ...
... Nucleotide consists of base (adenine, urasil, cytosine, guanine), phosphate and sugar parts. There are two different groups of bases: purines and pyrimidines. Adenine and guanine are purines and cytosine and urasil pyrimidines. Sugar is pentose and phosphate is bonded to its 5'-carbon. Base is bonde ...
Selective Oxidation Reactions of Natural Compounds with
... commercial products (Aldrich, Milan, Italy). 3.2. General Oxidation Procedure Pyridine (0.02 mmol, 12%) and 35% hydrogen peroxide (22 µL, 0.25 mmol, 1.5 equiv) were added to a solution of the MTO (0.008 mmol, 5%) in CH2Cl2 (2.5 mL) at 25 °C and this yellow mixture was stirred for 1 min. A solution o ...
... commercial products (Aldrich, Milan, Italy). 3.2. General Oxidation Procedure Pyridine (0.02 mmol, 12%) and 35% hydrogen peroxide (22 µL, 0.25 mmol, 1.5 equiv) were added to a solution of the MTO (0.008 mmol, 5%) in CH2Cl2 (2.5 mL) at 25 °C and this yellow mixture was stirred for 1 min. A solution o ...
Holbert, Daniel: Detecting motifs with EMOTIF-MAKER and MASIA: A critical comparison of two tools for finding protein motifs
... Of course, MASIA isn't perfect at modeling amino acid conservation. In particular, it is susceptible to biases in the training sequences. It assigns the same weight to all sequences when it computes averages to construct a profile, and this could lead to undesirable results for training data that co ...
... Of course, MASIA isn't perfect at modeling amino acid conservation. In particular, it is susceptible to biases in the training sequences. It assigns the same weight to all sequences when it computes averages to construct a profile, and this could lead to undesirable results for training data that co ...
NMR spectroscopy brings invisible protein states into
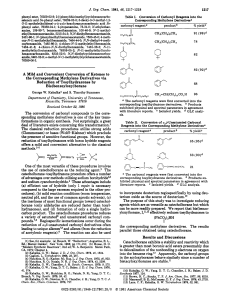
... different frequencies (the chemical shift) Figure 1 A simple schematic of a CPMG relaxation dispersion experiment. (a) A molecule interconverts when in states A and B, denoted by ωA stochastically between two conformational states, A and B, as a function of time, with states A and B and ωB, respecti ...
... different frequencies (the chemical shift) Figure 1 A simple schematic of a CPMG relaxation dispersion experiment. (a) A molecule interconverts when in states A and B, denoted by ωA stochastically between two conformational states, A and B, as a function of time, with states A and B and ωB, respecti ...
Learning Guide for Chapter 24
... Esters can be formed from carboxylic acids and alcohols by Fischer esterification, by reaction with diazomethane, or by deprotonation followed by a reactive alkyl halide. They can also be formed from acid chlorides and anhydrides, as we shall see. O OH ...
... Esters can be formed from carboxylic acids and alcohols by Fischer esterification, by reaction with diazomethane, or by deprotonation followed by a reactive alkyl halide. They can also be formed from acid chlorides and anhydrides, as we shall see. O OH ...
A Mild and Convenient Conversion of Ketones to the Corresponding
... All carbonyl reagents were obtained commercially and distilled prior to use. The only exception was 6-oxo-15-hexadecenoic acid which was prepared according to a published procedure.16 Melting points are uncorrected. Tosylhydrazone Preparation. The tosylhydrazones were prepared by reacting the approp ...
... All carbonyl reagents were obtained commercially and distilled prior to use. The only exception was 6-oxo-15-hexadecenoic acid which was prepared according to a published procedure.16 Melting points are uncorrected. Tosylhydrazone Preparation. The tosylhydrazones were prepared by reacting the approp ...
Bottromycin

Bottromycin is a macrocyclic peptide with antibiotic activity. It was first discovered in 1957 as a natural product isolated from Streptomyces bottropensis. It has been shown to inhibit methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) and vancomycin-resistant Enterococci (VRE) among other Gram-positive bacteria and mycoplasma. Bottromycin is structurally distinct from both vancomycin, a glycopeptide antibiotic, and methicillin, a beta-lactam antibiotic.Bottromycin binds to the A site of the ribosome and blocks the binding of aminoacyl-tRNA, therefore inhibiting bacterial protein synthesis. Although bottromycin exhibits antibacterial activity in vitro, it has not yet been developed as a clinical antibiotic, potentially due to its poor stability in blood plasma. To increase its stability in vivo, some bottromycin derivatives have been explored.The structure of bottromycin contains a macrocyclic amidine as well as a thiazole ring. The absolute stereochemistry at several chiral centers has been determined as of 2009. In 2012, a three-dimensional solution structure of bottromycin was published. The solution structure revealed that several methyl groups are on the same face of the structure.Bottromycin falls within the ribosomally synthesized and post-translationally modified peptide class of natural product.