The Structure and Function of Macromolecules
... The function of a protein depends on its chemical structure and unique 3-D shape ...
... The function of a protein depends on its chemical structure and unique 3-D shape ...
Primary Structure - LaurensAPBiology
... Many biological molecules are macromolecules – huge assemblies of atoms. Biological macromolecules are formed by linking together a set of building blocks (monomers) into long chains (a polymer). ...
... Many biological molecules are macromolecules – huge assemblies of atoms. Biological macromolecules are formed by linking together a set of building blocks (monomers) into long chains (a polymer). ...
Structural Biochemistry/Proteins/Synthesis
... and third step. Activating the C-terminus and then, coupling the next amino acid. The advantages of this synthesis are it works very fast, and have a good percentage yield of the product. However, it can only be used for small protein chain. The yields become smaller with larger protein. Therefore, ...
... and third step. Activating the C-terminus and then, coupling the next amino acid. The advantages of this synthesis are it works very fast, and have a good percentage yield of the product. However, it can only be used for small protein chain. The yields become smaller with larger protein. Therefore, ...
[Kliknite ovde da ukucate naslov]
... Chemoselective ligation approaches are widely used in the synthesis of cyclic peptides and peptide conjugates. Oxime bond formation is one of the most commonly used, due to its chemical stability and easy synthesis. The oxime linkage is formed between an oxo group (ketone or aldehyde) and a hydroxyl ...
... Chemoselective ligation approaches are widely used in the synthesis of cyclic peptides and peptide conjugates. Oxime bond formation is one of the most commonly used, due to its chemical stability and easy synthesis. The oxime linkage is formed between an oxo group (ketone or aldehyde) and a hydroxyl ...
Jan. 28 Bio II Answer to warm up Protein Synthesis
... codons each When a tRNA bumps into the ribosome that has the complimentary sequence to a codon, the tRNA is trapped and fit into place. The bond between the tRNA and the amino is broken and the amino acid is now held by the ...
... codons each When a tRNA bumps into the ribosome that has the complimentary sequence to a codon, the tRNA is trapped and fit into place. The bond between the tRNA and the amino is broken and the amino acid is now held by the ...
Antibiotics (Chapter 20)
... V. Inhibits synthesis of Essential Metabolites: competitively inhibited by similar substance Sulfanilamides; competes with PABA (para aminobenzoic acid) that is necessary for folic acid synthesis MIC minimum inhibitory concentration: lowest dose that will inhibit growth of bacterial MBC minimum bac ...
... V. Inhibits synthesis of Essential Metabolites: competitively inhibited by similar substance Sulfanilamides; competes with PABA (para aminobenzoic acid) that is necessary for folic acid synthesis MIC minimum inhibitory concentration: lowest dose that will inhibit growth of bacterial MBC minimum bac ...
Ch. 5 - ltcconline.net
... 9. Distinguish between a protein and a polypeptide, and list/describe 8 protein functions. 10. Explain how a peptide bond forms between two amino acids. 11. List and describe the four major components of an amino acid. Explain how amino acids may be grouped according to the physical and chemical pro ...
... 9. Distinguish between a protein and a polypeptide, and list/describe 8 protein functions. 10. Explain how a peptide bond forms between two amino acids. 11. List and describe the four major components of an amino acid. Explain how amino acids may be grouped according to the physical and chemical pro ...
Answers
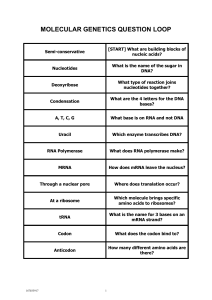
... i Histone coat protecting the DNA double helix in the region of the cistron is stripped away c Hydrogen bonds between complementary base pairs of DNA break n Double helix of DNA unwinds f RNA Polymerase binds to single stranded DNA e RNA Nucleotides are attached to the DNA strand according to the ru ...
... i Histone coat protecting the DNA double helix in the region of the cistron is stripped away c Hydrogen bonds between complementary base pairs of DNA break n Double helix of DNA unwinds f RNA Polymerase binds to single stranded DNA e RNA Nucleotides are attached to the DNA strand according to the ru ...
DNA
... • Why: DNA can’t leave the nucleus but the message must get to the ribosome • You are now using U’s no T’s. • RNA polymerase – Enzyme that brings in RNA nucleotides to match up with DNA ...
... • Why: DNA can’t leave the nucleus but the message must get to the ribosome • You are now using U’s no T’s. • RNA polymerase – Enzyme that brings in RNA nucleotides to match up with DNA ...
Nahla abd elmoaty mohamed
... The phthalazine derivative azelastine (A) is an antihistamine used in the treatment of allergic rhinitis. Cl ...
... The phthalazine derivative azelastine (A) is an antihistamine used in the treatment of allergic rhinitis. Cl ...
DNA RNA Protein Hwk KEY
... GTP (like ATP) Provides energy to charge tRNA's, catalyze peptide bonding, and move ribosomes… mRNA Its sequence of codons determines order of a.a.'s in protein ribosome Holds mRNA; takes in tRNA-a.a.'s; rbs enzymes make peptide bonds between a.a.'s tRNA Adapter molecules that carry a.a.'s to the rb ...
... GTP (like ATP) Provides energy to charge tRNA's, catalyze peptide bonding, and move ribosomes… mRNA Its sequence of codons determines order of a.a.'s in protein ribosome Holds mRNA; takes in tRNA-a.a.'s; rbs enzymes make peptide bonds between a.a.'s tRNA Adapter molecules that carry a.a.'s to the rb ...
Inverse mapping
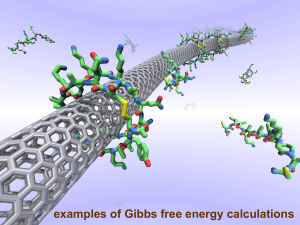
... MD simulation of C350H702 adsorbed onto a planar graphite surface at room temperature. can see, visually, the competition between enthalpy and entropy ...
... MD simulation of C350H702 adsorbed onto a planar graphite surface at room temperature. can see, visually, the competition between enthalpy and entropy ...
DNA-RNA-Protein Synthesis
... 4 blue tubes (cytosine) 4 yellow tubes (guanine) 5 green tubes (thymine) 5 orange tubes (adenine) 20 white tubes (phosphates) 9 white rods (hydrogen bonds) 18 black pentagons (deoxyribose sugar) 5 lavender tubes (uracil) 9 purple pentagons (ribose sugar) 1 large purple ribosome 3 grey tubes (peptide ...
... 4 blue tubes (cytosine) 4 yellow tubes (guanine) 5 green tubes (thymine) 5 orange tubes (adenine) 20 white tubes (phosphates) 9 white rods (hydrogen bonds) 18 black pentagons (deoxyribose sugar) 5 lavender tubes (uracil) 9 purple pentagons (ribose sugar) 1 large purple ribosome 3 grey tubes (peptide ...
Protien Synthesis
... Decoding mRNA (codons) into an amino acid sequence (protein) Location: Cytoplasm ...
... Decoding mRNA (codons) into an amino acid sequence (protein) Location: Cytoplasm ...
Lecture 5
... transcribe Some (but not all) methylations are reversible Abnormal methylation can lead to problems - Ex: FMR1 – hypermethylation leads to Fragile X syndrome; which is the leading Mendelian (single gene) disorder that causes mental retardation RNA Splicing One gene can result in a large number ...
... transcribe Some (but not all) methylations are reversible Abnormal methylation can lead to problems - Ex: FMR1 – hypermethylation leads to Fragile X syndrome; which is the leading Mendelian (single gene) disorder that causes mental retardation RNA Splicing One gene can result in a large number ...
The role of the C-terminal tail of the ribosomal protein S13 in protein
... mRNA by transcription, and then passed onto proteins by translation. The ribosome synthesizes proteins based on the information on the mRNA sequence in the cell; like building a house using bricks according to a blueprint. Bacterial growth is determined by how fast the whole process is. The bacteria ...
... mRNA by transcription, and then passed onto proteins by translation. The ribosome synthesizes proteins based on the information on the mRNA sequence in the cell; like building a house using bricks according to a blueprint. Bacterial growth is determined by how fast the whole process is. The bacteria ...
PROTIEN SYNTHESIS
... an·ti·co·don A sequence of three adjacent nucleotides in transfer RNA that binds to a corresponding codon in messenger RNA and designates a specific amino acid during protein synthesis. co·don A sequence of three adjacent nucleotides constituting the genetic code that determines the insertion of a s ...
... an·ti·co·don A sequence of three adjacent nucleotides in transfer RNA that binds to a corresponding codon in messenger RNA and designates a specific amino acid during protein synthesis. co·don A sequence of three adjacent nucleotides constituting the genetic code that determines the insertion of a s ...
Answer keys
... 3. Rank the compounds in order of increasing reactivity in nucleophilic acyl substitution. ...
... 3. Rank the compounds in order of increasing reactivity in nucleophilic acyl substitution. ...
Translation PPT
... • GENETIC CODE - language of the mRNA instructions as determined by the N-bases • CODON- sequence of 3 nucleotides (or just the N-bases) on mRNA that code for one amino acid • POLYLPEPTIDES- proteins made by joining any combination of the 20 amino acids during Translation process of Protein Synthesi ...
... • GENETIC CODE - language of the mRNA instructions as determined by the N-bases • CODON- sequence of 3 nucleotides (or just the N-bases) on mRNA that code for one amino acid • POLYLPEPTIDES- proteins made by joining any combination of the 20 amino acids during Translation process of Protein Synthesi ...
CH 102 Practice exam This represents the new material that
... ____ 11. The animal fats are classified as esters because of the way they are chemically produced. ____ 12. Both fats and oils produce glycerol and fatty acids when hydrolized in an acid solution. ____ 13. Triglycerides are examples of simple lipids. ____ 14. Phosphotriglycerides are examples of com ...
... ____ 11. The animal fats are classified as esters because of the way they are chemically produced. ____ 12. Both fats and oils produce glycerol and fatty acids when hydrolized in an acid solution. ____ 13. Triglycerides are examples of simple lipids. ____ 14. Phosphotriglycerides are examples of com ...
Bottromycin

Bottromycin is a macrocyclic peptide with antibiotic activity. It was first discovered in 1957 as a natural product isolated from Streptomyces bottropensis. It has been shown to inhibit methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) and vancomycin-resistant Enterococci (VRE) among other Gram-positive bacteria and mycoplasma. Bottromycin is structurally distinct from both vancomycin, a glycopeptide antibiotic, and methicillin, a beta-lactam antibiotic.Bottromycin binds to the A site of the ribosome and blocks the binding of aminoacyl-tRNA, therefore inhibiting bacterial protein synthesis. Although bottromycin exhibits antibacterial activity in vitro, it has not yet been developed as a clinical antibiotic, potentially due to its poor stability in blood plasma. To increase its stability in vivo, some bottromycin derivatives have been explored.The structure of bottromycin contains a macrocyclic amidine as well as a thiazole ring. The absolute stereochemistry at several chiral centers has been determined as of 2009. In 2012, a three-dimensional solution structure of bottromycin was published. The solution structure revealed that several methyl groups are on the same face of the structure.Bottromycin falls within the ribosomally synthesized and post-translationally modified peptide class of natural product.


![[Kliknite ovde da ukucate naslov]](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/009256082_1-6a09de328714676facd0953d80fff2c0-300x300.png)