biochemistry - apbiostafford
... Draw a lipid molecule (triglyceride). Point out the carboxyl, or acid, group and the hydrocarbon chains. Explain the difference between a saturated fatty acid and an unsaturated fatty acid. For butter and corn oil, indicate whether each is considered a saturated or an unsaturated fat. Using a diagra ...
... Draw a lipid molecule (triglyceride). Point out the carboxyl, or acid, group and the hydrocarbon chains. Explain the difference between a saturated fatty acid and an unsaturated fatty acid. For butter and corn oil, indicate whether each is considered a saturated or an unsaturated fat. Using a diagra ...
Mechanism of peptide bond formation on ribosomes
... Mechanism of peptide bond formation on ribosomes D. P. Burma In spite of extensive studies carried out on structure and function of ribosomes during the last four decades or so, the crucial information on the mechanism of peptide bond formation was missing. However, with the very recent elucidation ...
... Mechanism of peptide bond formation on ribosomes D. P. Burma In spite of extensive studies carried out on structure and function of ribosomes during the last four decades or so, the crucial information on the mechanism of peptide bond formation was missing. However, with the very recent elucidation ...
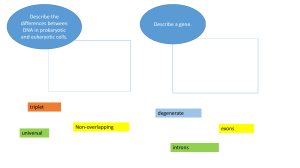
Gene Expression
... (Exons) are spliced back together. This way, more than one protein can be made from a single gene! • Now it is mature mRNA ...
... (Exons) are spliced back together. This way, more than one protein can be made from a single gene! • Now it is mature mRNA ...
Biocatalysis in Organic Synthesis
... "cleaner" and laborious purification of product(s) from impurities emerging through side-reactions can largely be omitted. Regioselectivity and Diastereoselectivity: Due to their complex three-dimensional structure, enzymes may distinguish between functional groups which are chemically situated in d ...
... "cleaner" and laborious purification of product(s) from impurities emerging through side-reactions can largely be omitted. Regioselectivity and Diastereoselectivity: Due to their complex three-dimensional structure, enzymes may distinguish between functional groups which are chemically situated in d ...
FMOC The solid phase peptide synthesis (SPPS) was first
... peptides can be synthesized routinely. These modified peptides can be catagorized as biotinylated, branched, chromogenic, Cterminal modified, fatty acid containing, fluorescent, glycosylated, isoprenated, cyclic lactam , multiple disulfide, peptide mimetics, phosphorated and sulfation peptides Pepti ...
... peptides can be synthesized routinely. These modified peptides can be catagorized as biotinylated, branched, chromogenic, Cterminal modified, fatty acid containing, fluorescent, glycosylated, isoprenated, cyclic lactam , multiple disulfide, peptide mimetics, phosphorated and sulfation peptides Pepti ...
Nuclease Digestion
... to form the primary structure of a protein • H-bonding and folding lead to secondary and tertiary structure ...
... to form the primary structure of a protein • H-bonding and folding lead to secondary and tertiary structure ...
Slide () - Anesthesiology - American Society of Anesthesiologists
... catabolized, releasing amino acids into circulation (including glutamine, alanine, and the branched chain amino acids [BCAAs]), while hepatic amino acid uptake is enhanced. This allows for reprioritization of protein synthesis to acute phase reactants and the production of glucose via gluconeogenesi ...
... catabolized, releasing amino acids into circulation (including glutamine, alanine, and the branched chain amino acids [BCAAs]), while hepatic amino acid uptake is enhanced. This allows for reprioritization of protein synthesis to acute phase reactants and the production of glucose via gluconeogenesi ...
Amino acids - Boardworks
... 4.2.1 Amino acids and chirality: amino acids; peptide formation and hydrolysis of proteins. 4.2.2 Polyesters and polyamides: condensation polymers; hydrolysis and degradable polymers. ...
... 4.2.1 Amino acids and chirality: amino acids; peptide formation and hydrolysis of proteins. 4.2.2 Polyesters and polyamides: condensation polymers; hydrolysis and degradable polymers. ...
Association Triangles: Supplemental Examples mRNA rRNA tRNA
... SUPPLEMENTAL RESOURCE | Tools for Thoughtful Assessment > Page 83 > Association Triangles > How is this tool used in the classroom? © 2012 Silver Strong & Associates | Visit www.ThoughtfulClassroom.com/Tools to download this page. ...
... SUPPLEMENTAL RESOURCE | Tools for Thoughtful Assessment > Page 83 > Association Triangles > How is this tool used in the classroom? © 2012 Silver Strong & Associates | Visit www.ThoughtfulClassroom.com/Tools to download this page. ...
PowerPoint 簡報
... if the the haemagglutinine of the current H5N1 virus has one amino acid changed, its conformation would be changed. The conformation may become much easier to combine with the receptor protein on the surface of the human cells. Then, human would become susceptible to the infection of the virus. ...
... if the the haemagglutinine of the current H5N1 virus has one amino acid changed, its conformation would be changed. The conformation may become much easier to combine with the receptor protein on the surface of the human cells. Then, human would become susceptible to the infection of the virus. ...
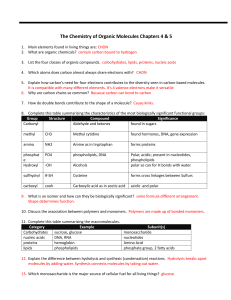
04-05 Biochem review sheet answers ws
... 3. List the four classes of organic compounds. carbohydrates, lipids, proteins, nucleic acids 4. Which atoms does carbon almost always share electrons with? CHON 5. Explain how carbon’s need for four electrons contributes to the diversity seen in carbon-based molecules. It is compatible with many di ...
... 3. List the four classes of organic compounds. carbohydrates, lipids, proteins, nucleic acids 4. Which atoms does carbon almost always share electrons with? CHON 5. Explain how carbon’s need for four electrons contributes to the diversity seen in carbon-based molecules. It is compatible with many di ...
charged
... The information encoded in DNA is transcribed into RNA and finally translated into the sequence of proteins. The genetic unit coding for one single amino acid is a codon. One gene codes for one proteins, one cistron for one polypeptide chain. As many proteins consist of only one polypeptide chain, m ...
... The information encoded in DNA is transcribed into RNA and finally translated into the sequence of proteins. The genetic unit coding for one single amino acid is a codon. One gene codes for one proteins, one cistron for one polypeptide chain. As many proteins consist of only one polypeptide chain, m ...
Cardiff International School Dhaka (CISD) Lost Class Make Up
... specific sequence of amino acids. When two amino acids are in such a position that the carboxyl groups of each amino acid are adjacent to each other, they can be combined by undergoing a dehydration reaction which results in the formation of a peptide bond. Amino acids in a polypeptide (protein) are ...
... specific sequence of amino acids. When two amino acids are in such a position that the carboxyl groups of each amino acid are adjacent to each other, they can be combined by undergoing a dehydration reaction which results in the formation of a peptide bond. Amino acids in a polypeptide (protein) are ...
File - Siegel Science
... in living cells, with glycine as the most abundant. Sugars, lipids, and some of the building blocks for nucleic acids were also formed. Since this experiment, other scientists have repeated and extended the research. As a result, all 20 amino acids, sugars, lipids, nucleotides, and ATP have been ...
... in living cells, with glycine as the most abundant. Sugars, lipids, and some of the building blocks for nucleic acids were also formed. Since this experiment, other scientists have repeated and extended the research. As a result, all 20 amino acids, sugars, lipids, nucleotides, and ATP have been ...
max 6
... Transcription and translation Describe the synthesis of a protein from DNA. HINT: Use an image to build up a list of key words for the structure, then use that as a framework for your answer ...
... Transcription and translation Describe the synthesis of a protein from DNA. HINT: Use an image to build up a list of key words for the structure, then use that as a framework for your answer ...
Supplementary Information (doc 68K)
... (TCM) AIM-V (Life Technologies) supplemented with 5 % human AB serum, 2 mM Lglutamine and 50 µg / ml gentamycine to a concentration of 1 x 106 / ml. For every peptide concentration to be tested T2 cells were pulsed with a serial dilution of 0.1 – 100 µM peptide and then incubated for 16 hours at 37 ...
... (TCM) AIM-V (Life Technologies) supplemented with 5 % human AB serum, 2 mM Lglutamine and 50 µg / ml gentamycine to a concentration of 1 x 106 / ml. For every peptide concentration to be tested T2 cells were pulsed with a serial dilution of 0.1 – 100 µM peptide and then incubated for 16 hours at 37 ...
n-formyl methionine
... synthesis taking place in the cytosol of eukaryotes, where eukaryotic nuclear genes are translated. fMet is a starting residue in the synthesis of proteins in prokaryotes and, consequently, is located at the N-terminus of the growing polypeptide. N-Formylmethionine is coded by the same codon as meth ...
... synthesis taking place in the cytosol of eukaryotes, where eukaryotic nuclear genes are translated. fMet is a starting residue in the synthesis of proteins in prokaryotes and, consequently, is located at the N-terminus of the growing polypeptide. N-Formylmethionine is coded by the same codon as meth ...
How do we get proteins? - Sebastian Charter Junior High
... complementary to the DNA base pairs. The enzyme used is RNA polymerase ...
... complementary to the DNA base pairs. The enzyme used is RNA polymerase ...
Document
... 4. Olestra F. Proteins 5.4 1. Uses 2. Amino Acid structure 3. Different R groups 4. Peptide bond 5. Protein structure (primary, secondary, tertiary, quaternary) 6. Simple vs. compound proteins 7. primary structure determines 3D shape of protein. How? G. Chemical Reactions ...
... 4. Olestra F. Proteins 5.4 1. Uses 2. Amino Acid structure 3. Different R groups 4. Peptide bond 5. Protein structure (primary, secondary, tertiary, quaternary) 6. Simple vs. compound proteins 7. primary structure determines 3D shape of protein. How? G. Chemical Reactions ...
Bottromycin

Bottromycin is a macrocyclic peptide with antibiotic activity. It was first discovered in 1957 as a natural product isolated from Streptomyces bottropensis. It has been shown to inhibit methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) and vancomycin-resistant Enterococci (VRE) among other Gram-positive bacteria and mycoplasma. Bottromycin is structurally distinct from both vancomycin, a glycopeptide antibiotic, and methicillin, a beta-lactam antibiotic.Bottromycin binds to the A site of the ribosome and blocks the binding of aminoacyl-tRNA, therefore inhibiting bacterial protein synthesis. Although bottromycin exhibits antibacterial activity in vitro, it has not yet been developed as a clinical antibiotic, potentially due to its poor stability in blood plasma. To increase its stability in vivo, some bottromycin derivatives have been explored.The structure of bottromycin contains a macrocyclic amidine as well as a thiazole ring. The absolute stereochemistry at several chiral centers has been determined as of 2009. In 2012, a three-dimensional solution structure of bottromycin was published. The solution structure revealed that several methyl groups are on the same face of the structure.Bottromycin falls within the ribosomally synthesized and post-translationally modified peptide class of natural product.