Ch. 5 Biochemistry
... Hydrophobic; H bonds in water exclude fats Carboxyl group = fatty acid Non-polar C-H bonds in fatty acid ‘tails’ Ester linkage: 3 fatty acids to 1 glycerol (dehydration formation) ...
... Hydrophobic; H bonds in water exclude fats Carboxyl group = fatty acid Non-polar C-H bonds in fatty acid ‘tails’ Ester linkage: 3 fatty acids to 1 glycerol (dehydration formation) ...
Macromolecules of the Cell
... Glycosidic bonds These are of two types according to the location of the hydroxyl group on C atom 1. a(1-4) glycosidic bond and B(1-4) glycosidic bond. The polymers are storage and structural polysaccharides. Starch and glycogen are storage polysaccharides. The type of bond found in each is the a(1 ...
... Glycosidic bonds These are of two types according to the location of the hydroxyl group on C atom 1. a(1-4) glycosidic bond and B(1-4) glycosidic bond. The polymers are storage and structural polysaccharides. Starch and glycogen are storage polysaccharides. The type of bond found in each is the a(1 ...
Chapter 12 Power point 2
... (transfer RNA) - transports specific amino acids to ribosome during protein synthesis (translation). Anticodon - specific sequence of 3 ...
... (transfer RNA) - transports specific amino acids to ribosome during protein synthesis (translation). Anticodon - specific sequence of 3 ...
242140_Fx_DNA-RNA
... Go back to Mr. Mason’s website and click on the link labeled “Genetics – Translation” 5. Much of the process of making an amino acid chain will be explained more fully in the next link, so we’ll leave the details of where and how an amino acid chain is built for later. How many amino acids are there ...
... Go back to Mr. Mason’s website and click on the link labeled “Genetics – Translation” 5. Much of the process of making an amino acid chain will be explained more fully in the next link, so we’ll leave the details of where and how an amino acid chain is built for later. How many amino acids are there ...
Gibbs sampler
... weighting clustering (Hobohm) techniques Peptide MHC binding predictions using artificial neural networks with different sequence encoding schemes Gibbs sampler approach to the prediction of MHC class II binding motifs Improved protein template identification using hidden Markov models (HMMER) Imple ...
... weighting clustering (Hobohm) techniques Peptide MHC binding predictions using artificial neural networks with different sequence encoding schemes Gibbs sampler approach to the prediction of MHC class II binding motifs Improved protein template identification using hidden Markov models (HMMER) Imple ...
Nucleic Acids (DNA and RNA) are not boring long polymers
... well as of genetic materials against virus aggression. ...
... well as of genetic materials against virus aggression. ...
PROTEIN SYNTHESIS
... Because the DNA is inside the nucleus and the ____________________ (organelle that makes proteins) is in the cytoplasm, the directions for making the protein must be sent from the nucleus to the cytoplasm. This is done with a molecule called mRNA (messenger RNA). ...
... Because the DNA is inside the nucleus and the ____________________ (organelle that makes proteins) is in the cytoplasm, the directions for making the protein must be sent from the nucleus to the cytoplasm. This is done with a molecule called mRNA (messenger RNA). ...
Proteins Protein Structure Proteins are the major components of
... the polypeptide chain ,amino acids with a polar ( water soluble) side chain are often found on the surface of the molecule while amino acids with non-polar (water insoluble) side chain are buried in the interior .This means that the folded protein is soluble in water or aqueous solutions. Covalent ...
... the polypeptide chain ,amino acids with a polar ( water soluble) side chain are often found on the surface of the molecule while amino acids with non-polar (water insoluble) side chain are buried in the interior .This means that the folded protein is soluble in water or aqueous solutions. Covalent ...
AP BIOLOGY STUDY GUIDE: CH 17, FROM GENE TO PROTEIN
... AP BIOLOGY STUDY GUIDE: CH 17, FROM GENE TO PROTEIN The Gene—Protein Connection ...
... AP BIOLOGY STUDY GUIDE: CH 17, FROM GENE TO PROTEIN The Gene—Protein Connection ...
paper 14 organic synthesis: disconnection approach - e
... ORGANIC SYNTHESIS: DISCONNECTION APPROACH I. Disconnection Approach An introduction to synthons and synthetic equivalents, disconnection approach, functional group inter- conversions, the importance of the order of events in organic synthesis, one group C-X and two group C-X disconnections, chemosel ...
... ORGANIC SYNTHESIS: DISCONNECTION APPROACH I. Disconnection Approach An introduction to synthons and synthetic equivalents, disconnection approach, functional group inter- conversions, the importance of the order of events in organic synthesis, one group C-X and two group C-X disconnections, chemosel ...
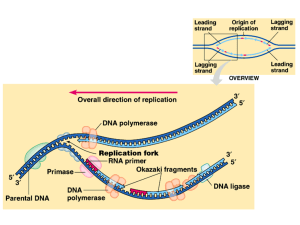
Biology 212 General Genetics
... Can lead to mental retardation if not treated from birth Treat by placing babies on diet low in phenylalanine Screening with routine blood test just after birth 1/8000 among Caucasians in U.S., therefore relatively common Defects in other enzymes of this pathway lead to other diseases. 3. DN ...
... Can lead to mental retardation if not treated from birth Treat by placing babies on diet low in phenylalanine Screening with routine blood test just after birth 1/8000 among Caucasians in U.S., therefore relatively common Defects in other enzymes of this pathway lead to other diseases. 3. DN ...
Dave Ousterout – Jin Lab – Project Proposal 08/14/08 Adeno
... in the long term, to use a genetically modified vector as a therapeutic delivery system to specific tissue The aa 453 site has shown promise in previous research, but has not been fully evaluated to date (Lochrie, et. al. 2005 and Wu, et. al. 2000). I have looked at the site using the solved cryst ...
... in the long term, to use a genetically modified vector as a therapeutic delivery system to specific tissue The aa 453 site has shown promise in previous research, but has not been fully evaluated to date (Lochrie, et. al. 2005 and Wu, et. al. 2000). I have looked at the site using the solved cryst ...
Lecture 14
... The R-groups can be alkyl, aromatic, alcoholic or phenolic, thiol or thioether, basic groups like amine or guanidine and carboxylic acids. In proteins these individual groups act together to perform various functions. functions The linear chain of amino acids (primary structure), folds itself throug ...
... The R-groups can be alkyl, aromatic, alcoholic or phenolic, thiol or thioether, basic groups like amine or guanidine and carboxylic acids. In proteins these individual groups act together to perform various functions. functions The linear chain of amino acids (primary structure), folds itself throug ...
Transcription & Translation PowerPoint
... A certain gene codes for a polypeptide that is 120 amino acids long. Approximately how many nucleotides long is the mRNA that codes for this polypeptide likely to be? A. ...
... A certain gene codes for a polypeptide that is 120 amino acids long. Approximately how many nucleotides long is the mRNA that codes for this polypeptide likely to be? A. ...
Ch 17 Protein Synthesis
... 1. small ribosomal subunit binds to mRNA upstream from the start codon 2. ribosome scans mRNA until it put start codon (AUG) at the P-site 3. tRNA with Met hydrogen bonds to start codon 4. large subunit attaches ...
... 1. small ribosomal subunit binds to mRNA upstream from the start codon 2. ribosome scans mRNA until it put start codon (AUG) at the P-site 3. tRNA with Met hydrogen bonds to start codon 4. large subunit attaches ...
BIOMG 3310: Principles of Biochemistry
... For example, Val, Ile, and Thr have a second methyl group branching out of the beta carbon, creating steric hindrance. ...
... For example, Val, Ile, and Thr have a second methyl group branching out of the beta carbon, creating steric hindrance. ...
Nucleic Acids
... Other lipid polymers = phospholipids and steroids; both components of cell membranes ...
... Other lipid polymers = phospholipids and steroids; both components of cell membranes ...
Studies on some essential amino acids: Synthesis of methyl esters
... The antifungal activity was determined by the radial growth method [13]. The fungal cultures were incubated at 37°C for 4 days.Finally, the zones of inhibition were carefully measured. In this technique, sterilized hot PDA nutrient medium (composition: potato (200 g), dextrose (20g), agar (15g) and ...
... The antifungal activity was determined by the radial growth method [13]. The fungal cultures were incubated at 37°C for 4 days.Finally, the zones of inhibition were carefully measured. In this technique, sterilized hot PDA nutrient medium (composition: potato (200 g), dextrose (20g), agar (15g) and ...
No Slide Title
... Transfer RNA (tRNA) leaves the nucleus, binds to the amino acid specified by it’s anticodon and transfers it to the ribisome where it meets up with mRNA to assemble a protein. ...
... Transfer RNA (tRNA) leaves the nucleus, binds to the amino acid specified by it’s anticodon and transfers it to the ribisome where it meets up with mRNA to assemble a protein. ...
Chapter 5: Biological Molecules Molecules of Life • All life made up
... Account for over 50% of cell’s dry mass Functions – enzyme, storage, structural support, transport, movement, cellular communications, & defense against foreign substances Polypeptide o Polymer built from set of 20 amino acids o Linked by peptide bonds via dehydration reaction o Each has uniqu ...
... Account for over 50% of cell’s dry mass Functions – enzyme, storage, structural support, transport, movement, cellular communications, & defense against foreign substances Polypeptide o Polymer built from set of 20 amino acids o Linked by peptide bonds via dehydration reaction o Each has uniqu ...
Comparison of Trypsin Immobilization Techniques With or Without a
... The first stage in peptide mapping consists of chemical or enzymatic cleavage of a protein into specific peptides in order to obtain its fingerprint. To address the need for higher throughput in proteomics, fast enzymatic digestions and efficient analysis techniques like capillary electrophoresis (C ...
... The first stage in peptide mapping consists of chemical or enzymatic cleavage of a protein into specific peptides in order to obtain its fingerprint. To address the need for higher throughput in proteomics, fast enzymatic digestions and efficient analysis techniques like capillary electrophoresis (C ...
Spectroscopy
... IR of Secondary Structure •Amide I mode (1600--1700 cm ) of the peptide group is the most widely used band in studies of protein secondary structure. •Strong IR absorption of water between 1640--1650 cm , use D2O solution •Concerns?? •Amide II region is relatively strong, it is not very sensitive t ...
... IR of Secondary Structure •Amide I mode (1600--1700 cm ) of the peptide group is the most widely used band in studies of protein secondary structure. •Strong IR absorption of water between 1640--1650 cm , use D2O solution •Concerns?? •Amide II region is relatively strong, it is not very sensitive t ...
Bottromycin

Bottromycin is a macrocyclic peptide with antibiotic activity. It was first discovered in 1957 as a natural product isolated from Streptomyces bottropensis. It has been shown to inhibit methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) and vancomycin-resistant Enterococci (VRE) among other Gram-positive bacteria and mycoplasma. Bottromycin is structurally distinct from both vancomycin, a glycopeptide antibiotic, and methicillin, a beta-lactam antibiotic.Bottromycin binds to the A site of the ribosome and blocks the binding of aminoacyl-tRNA, therefore inhibiting bacterial protein synthesis. Although bottromycin exhibits antibacterial activity in vitro, it has not yet been developed as a clinical antibiotic, potentially due to its poor stability in blood plasma. To increase its stability in vivo, some bottromycin derivatives have been explored.The structure of bottromycin contains a macrocyclic amidine as well as a thiazole ring. The absolute stereochemistry at several chiral centers has been determined as of 2009. In 2012, a three-dimensional solution structure of bottromycin was published. The solution structure revealed that several methyl groups are on the same face of the structure.Bottromycin falls within the ribosomally synthesized and post-translationally modified peptide class of natural product.