From Gene to Protein
... polymerase (I, II – used in RNA synthesis and III) • Bacteria have one kind – it makes not only mRNA but also other types of RNA • Bacteria have one chromosome and many plasmids. Information is constantly being sent to ribosomes for translation into proteins needed by the bacterial cell ...
... polymerase (I, II – used in RNA synthesis and III) • Bacteria have one kind – it makes not only mRNA but also other types of RNA • Bacteria have one chromosome and many plasmids. Information is constantly being sent to ribosomes for translation into proteins needed by the bacterial cell ...
Chapter Three Power Point-The molecules of life
... different amino acids along length of chain – Puts R groups in positions that allow them to interact ...
... different amino acids along length of chain – Puts R groups in positions that allow them to interact ...
Senna (Cassia angustifolia)
... Targets the liver, which becomes enlarged due to fat deposition, cell necrosis, etc. Recent dog food contamination resulted in several pet deaths Aflatoxin B1 is carcinogenic - after epoxidization by CYP450 it can intercalate DNA, ...
... Targets the liver, which becomes enlarged due to fat deposition, cell necrosis, etc. Recent dog food contamination resulted in several pet deaths Aflatoxin B1 is carcinogenic - after epoxidization by CYP450 it can intercalate DNA, ...
notes 12B
... 4. There is at least one _______________ molecule for each of the 20 amino acids found in proteins. 5. There are fewer _______________ than codons because some tRNAs pair with more than one codon; if an anticodon contains a U in the third position, it will pair with either an A or G–this is called t ...
... 4. There is at least one _______________ molecule for each of the 20 amino acids found in proteins. 5. There are fewer _______________ than codons because some tRNAs pair with more than one codon; if an anticodon contains a U in the third position, it will pair with either an A or G–this is called t ...
Principles of Life
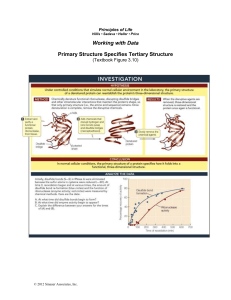
... After the tertiary structures of proteins were first shown to be highly specific, the question arose as to how the order of amino acids determined the three-dimensional structure. The second protein whose structure was determined was ribonuclease A, an enzyme from cows that was readily available fro ...
... After the tertiary structures of proteins were first shown to be highly specific, the question arose as to how the order of amino acids determined the three-dimensional structure. The second protein whose structure was determined was ribonuclease A, an enzyme from cows that was readily available fro ...
Transcription and Translation
... The instructions for protein structure are carried in the genes, which are sequences of DNA nucleotides. Three nucleotides code for an amino acid, e.g. AAA on the transcribing strand codes for phenylalanine whilst AAT codes for leucine. So, successive triplets of DNA nucleotides determine the sequen ...
... The instructions for protein structure are carried in the genes, which are sequences of DNA nucleotides. Three nucleotides code for an amino acid, e.g. AAA on the transcribing strand codes for phenylalanine whilst AAT codes for leucine. So, successive triplets of DNA nucleotides determine the sequen ...
Chapter 17 - Ellis Benjamin
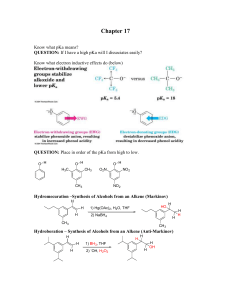
... Chapter 17 Know what pKa means? QUESTION: If I have a high pKa will I dissociates easily? Know what electron inductive effects do (below) ...
... Chapter 17 Know what pKa means? QUESTION: If I have a high pKa will I dissociates easily? Know what electron inductive effects do (below) ...
P8100Datasheet-Lot0041208
... respectively for 16 hours at 37°C in GluC Reaction Buffer. 1 µl of the above reaction (10 ng) was mixed with 1 µl of α-cyano-4-hydroxycinnamic acid matrix solution, air-dried and subjected to MALDI-TOF MS analysis. Fluorometric Assay: 1 µg (~1 µmol) of Anthranilyl-Ala-Phe-Ala-Phe-Glu-Val-Phe(NO2)-Ty ...
... respectively for 16 hours at 37°C in GluC Reaction Buffer. 1 µl of the above reaction (10 ng) was mixed with 1 µl of α-cyano-4-hydroxycinnamic acid matrix solution, air-dried and subjected to MALDI-TOF MS analysis. Fluorometric Assay: 1 µg (~1 µmol) of Anthranilyl-Ala-Phe-Ala-Phe-Glu-Val-Phe(NO2)-Ty ...
Lecture 39 - Chemistry at Winthrop University
... Progressively Oxidizing (adding Oxygen) the alcohol allows us to go from an alcohol to a carboxylic acid ...
... Progressively Oxidizing (adding Oxygen) the alcohol allows us to go from an alcohol to a carboxylic acid ...
Proteins and amino acids
... one side turned to the surface (hydrophilic) one side turned to the core (hydrophobic) ...
... one side turned to the surface (hydrophilic) one side turned to the core (hydrophobic) ...
mass
... biochemical research was replicated, and ...a U1-C protein, not detected above, was identified as a component in the system, and ...four novel proteins have been ID’d, – not necessarily components, – but excellent research leads. ...
... biochemical research was replicated, and ...a U1-C protein, not detected above, was identified as a component in the system, and ...four novel proteins have been ID’d, – not necessarily components, – but excellent research leads. ...
Protein Synthesis PP
... It is catalyzed by RNA polymerase. Bonds nucleotides together in a chain to make a new RNA molecule. ...
... It is catalyzed by RNA polymerase. Bonds nucleotides together in a chain to make a new RNA molecule. ...
gida bi̇yoteknoloji̇si̇-2
... • Poromoter is 35 bases upstream of the start of trancription sites. This is called as -35 position. promoter sequence is not transcribed. • There are two specific sequence (consensus sequences) on the promoter region which provide the recognition and binding of the enzyme to the promoter for the in ...
... • Poromoter is 35 bases upstream of the start of trancription sites. This is called as -35 position. promoter sequence is not transcribed. • There are two specific sequence (consensus sequences) on the promoter region which provide the recognition and binding of the enzyme to the promoter for the in ...
Molecules of Life
... charge, and other properties of functional groups that become neighbors in the growing chain. Stepped Art Fig. 3-16a, p. 44 ...
... charge, and other properties of functional groups that become neighbors in the growing chain. Stepped Art Fig. 3-16a, p. 44 ...
Document
... charge, and other properties of functional groups that become neighbors in the growing chain. Stepped Art Fig. 3-16a, p. 44 ...
... charge, and other properties of functional groups that become neighbors in the growing chain. Stepped Art Fig. 3-16a, p. 44 ...
Organic Molecules
... kinds of atoms are called isomers. Glucose and fructose (shown below) are both C6H12O6 but the atoms are arranged differently in each molecule. Same molecular formula: C6H12O6 Different structural formula ...
... kinds of atoms are called isomers. Glucose and fructose (shown below) are both C6H12O6 but the atoms are arranged differently in each molecule. Same molecular formula: C6H12O6 Different structural formula ...
Document
... The required signal sequence for a protein to enter the ER is 15– 30 N-terminal amino acids. As the signal sequence is produced by translation, it is bound by a signal recognition particle (SRP) composed of RNA and protein. The SRP suspends translation until the complex binds a docking protein on th ...
... The required signal sequence for a protein to enter the ER is 15– 30 N-terminal amino acids. As the signal sequence is produced by translation, it is bound by a signal recognition particle (SRP) composed of RNA and protein. The SRP suspends translation until the complex binds a docking protein on th ...
DNA RNA
... • Effects: Can be harmful, beneficial or neither – May cause of genetic disorders – May be beneficial and lead to production of proteins with new or altered activities, which has an important role in the evolutionary process of natural selection – Some mutations are “silent” and have no effect becau ...
... • Effects: Can be harmful, beneficial or neither – May cause of genetic disorders – May be beneficial and lead to production of proteins with new or altered activities, which has an important role in the evolutionary process of natural selection – Some mutations are “silent” and have no effect becau ...
Reaction of amino acids with exo-3,6-epoxy-1,2,3,6
... signal of maleimide derivatives has a strong solvent dependence. Rich et al.5 reported values of δ 6.67-6.78 in CDCl3, 6.78-6.92 in MeOH-d4 and 7.00-7.13 in DMSO-d6, while Keller and Rudinger4 reported δ 6.95 for 1 in acetone-d6. The olefinic resonance reported at 6.04 p.p.m. by Ondruš et al. for th ...
... signal of maleimide derivatives has a strong solvent dependence. Rich et al.5 reported values of δ 6.67-6.78 in CDCl3, 6.78-6.92 in MeOH-d4 and 7.00-7.13 in DMSO-d6, while Keller and Rudinger4 reported δ 6.95 for 1 in acetone-d6. The olefinic resonance reported at 6.04 p.p.m. by Ondruš et al. for th ...
Computational Prediction of Beta Structure from Amino Acid
... Because structure dictates the function of proteins - physiological or pathological - protein structure discovery is of great interest to biological science. Though experimental approaches have yielded good results, these efforts have proven ineffective for beta-rich proteins such as amyloids and au ...
... Because structure dictates the function of proteins - physiological or pathological - protein structure discovery is of great interest to biological science. Though experimental approaches have yielded good results, these efforts have proven ineffective for beta-rich proteins such as amyloids and au ...
Bottromycin

Bottromycin is a macrocyclic peptide with antibiotic activity. It was first discovered in 1957 as a natural product isolated from Streptomyces bottropensis. It has been shown to inhibit methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) and vancomycin-resistant Enterococci (VRE) among other Gram-positive bacteria and mycoplasma. Bottromycin is structurally distinct from both vancomycin, a glycopeptide antibiotic, and methicillin, a beta-lactam antibiotic.Bottromycin binds to the A site of the ribosome and blocks the binding of aminoacyl-tRNA, therefore inhibiting bacterial protein synthesis. Although bottromycin exhibits antibacterial activity in vitro, it has not yet been developed as a clinical antibiotic, potentially due to its poor stability in blood plasma. To increase its stability in vivo, some bottromycin derivatives have been explored.The structure of bottromycin contains a macrocyclic amidine as well as a thiazole ring. The absolute stereochemistry at several chiral centers has been determined as of 2009. In 2012, a three-dimensional solution structure of bottromycin was published. The solution structure revealed that several methyl groups are on the same face of the structure.Bottromycin falls within the ribosomally synthesized and post-translationally modified peptide class of natural product.