The biomolecules of terrestrial life
... Cytosine e Thymine Thymine replaces Uracyl, which is instead used in the RNA ...
... Cytosine e Thymine Thymine replaces Uracyl, which is instead used in the RNA ...
Macromolecules Notes File
... RNA carries the genetic code from the nucleus to the ribosomes where proteins are constructed ______________________________ (ATP) supplies energy to the cell. Other nucleotides and dinucleotides act as electron carriers and energy transfer molecules ...
... RNA carries the genetic code from the nucleus to the ribosomes where proteins are constructed ______________________________ (ATP) supplies energy to the cell. Other nucleotides and dinucleotides act as electron carriers and energy transfer molecules ...
G19S Amino Acid code
... these DNA instructions into proteins requires a series of coordinated steps in transcription and translation. 1. Complete column B by writing the correct mRNA codon for each sequence of DNA bases listed in the column marked DNA Base Sequence. Use the letters A, U, C, or G 2. Identify the process res ...
... these DNA instructions into proteins requires a series of coordinated steps in transcription and translation. 1. Complete column B by writing the correct mRNA codon for each sequence of DNA bases listed in the column marked DNA Base Sequence. Use the letters A, U, C, or G 2. Identify the process res ...
MGB_LNA_Substitutes
... Interested in replacing your MGBTM or LNATM probes? The (minor groove binding) and (locked nucleic acid) technologies are used to enhance the affinity of a standard oligonucleotide sequence to its complementary nucleotide strand. Since both technologies are patent protected, its use, distribution as ...
... Interested in replacing your MGBTM or LNATM probes? The (minor groove binding) and (locked nucleic acid) technologies are used to enhance the affinity of a standard oligonucleotide sequence to its complementary nucleotide strand. Since both technologies are patent protected, its use, distribution as ...
File - Ms. Poole`s Biology
... Frameshift Mutations the Effect on Proteins Frameshift mutations result from either an insertion or a deletion of a nucleotide. Missense mutation- Change in one amino acid sequence for the rest of the chain. Three insertions or deletions will put the polypeptide chain back on track. Nonsense mutati ...
... Frameshift Mutations the Effect on Proteins Frameshift mutations result from either an insertion or a deletion of a nucleotide. Missense mutation- Change in one amino acid sequence for the rest of the chain. Three insertions or deletions will put the polypeptide chain back on track. Nonsense mutati ...
dehydration synthesis
... RNA leaves the nucleus, transferring this information to a ribosome where proteins are manufactured. ...
... RNA leaves the nucleus, transferring this information to a ribosome where proteins are manufactured. ...
FARM ANIMAL NUTRITION
... meals, molasses and dried milk products • They are high in energy, low in fiber and highly digestible (80% to 90%) ...
... meals, molasses and dried milk products • They are high in energy, low in fiber and highly digestible (80% to 90%) ...
Tryptophan regulation by the formation of
... Tryptophan is one of the 20 amino acids that are essential for life. Regulation of the gene that is responsible for the synthesis of Tryptophan is key for living organisms. Over, under, or absence of this amino acid could cause the death of the organism. Bacteria have an interesting way of regulatin ...
... Tryptophan is one of the 20 amino acids that are essential for life. Regulation of the gene that is responsible for the synthesis of Tryptophan is key for living organisms. Over, under, or absence of this amino acid could cause the death of the organism. Bacteria have an interesting way of regulatin ...
Microbial warfare in the rhizosphere
... compelling evidence that nonribosomal peptide synthetase (NRPS) genes are highly dispersed and show distinct biogeographic distribution where detailed analysis has shown that bacteroidetes are an important group driving this diversity (Fig. 1)2. This means that peptides produced by bacteroidetes in ...
... compelling evidence that nonribosomal peptide synthetase (NRPS) genes are highly dispersed and show distinct biogeographic distribution where detailed analysis has shown that bacteroidetes are an important group driving this diversity (Fig. 1)2. This means that peptides produced by bacteroidetes in ...
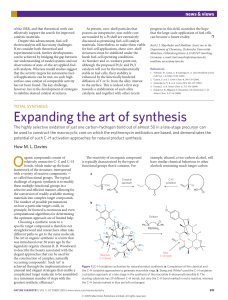
expanding the art of synthesis - Chemistry at Illinois
... closure late in the synthesis, condensing an alcohol with a carboxylic acid functional group (Fig. 1a). Because the stereochemistry of the alcohol is set, the cyclization can produce only a single three-dimensional form of the cyclized product. In contrast, the new route developed by Stang and White ...
... closure late in the synthesis, condensing an alcohol with a carboxylic acid functional group (Fig. 1a). Because the stereochemistry of the alcohol is set, the cyclization can produce only a single three-dimensional form of the cyclized product. In contrast, the new route developed by Stang and White ...
First Exam Study Guide
... 5. What is the relationship between H concentration and pH? What's the difference between an acid and a base? Can you recognize an example of each? What is a buffer? How does the carbonic acid / bicarbonate buffer respond to added acid or base? 6. Can you recognize straight chains, branched chains a ...
... 5. What is the relationship between H concentration and pH? What's the difference between an acid and a base? Can you recognize an example of each? What is a buffer? How does the carbonic acid / bicarbonate buffer respond to added acid or base? 6. Can you recognize straight chains, branched chains a ...
DNA and PROTEIN SYNTHESIS DNA, functioning as the hereditary
... There are 64 possible codons, but only 20 different amino acids. The code is therefore redundant in that several amino acids are coded for in more than one way. In addition, thre are three termination codons which stop the production of a protein. Possible codons are the amino acids for which they c ...
... There are 64 possible codons, but only 20 different amino acids. The code is therefore redundant in that several amino acids are coded for in more than one way. In addition, thre are three termination codons which stop the production of a protein. Possible codons are the amino acids for which they c ...
What happens to proteins key 14
... When abnormalities occur during protein synthesis, serious medical conditions may result. ...
... When abnormalities occur during protein synthesis, serious medical conditions may result. ...
Protein Synthesis: A Real Adventure
... 3. The tRNA student will search out the correct anti-codon sequence card and flip the card over revealing the word. Write the word down. 4. The tRNA student will bring the word back to the ribosome. 5. The rRNA student will write down each word as delivered by the tRNA 6. After completing the senten ...
... 3. The tRNA student will search out the correct anti-codon sequence card and flip the card over revealing the word. Write the word down. 4. The tRNA student will bring the word back to the ribosome. 5. The rRNA student will write down each word as delivered by the tRNA 6. After completing the senten ...
Cytochrome P450 Proteins
... therapeutic into small peptides and monitor one or more peptides as a surrogate – Trypsin is the enzyme of choice for several reasons: – Tryptic peptides are a good size for MRM assays (not too large) – Tryptic peptides tend to fragment well leading to good MRM assays – Trypsin digest quality can be ...
... therapeutic into small peptides and monitor one or more peptides as a surrogate – Trypsin is the enzyme of choice for several reasons: – Tryptic peptides are a good size for MRM assays (not too large) – Tryptic peptides tend to fragment well leading to good MRM assays – Trypsin digest quality can be ...
anti-codon
... Protein Synthesis Building protein from DNA in cells Takes code on basepai Converts it to rs ...
... Protein Synthesis Building protein from DNA in cells Takes code on basepai Converts it to rs ...
Bottromycin

Bottromycin is a macrocyclic peptide with antibiotic activity. It was first discovered in 1957 as a natural product isolated from Streptomyces bottropensis. It has been shown to inhibit methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) and vancomycin-resistant Enterococci (VRE) among other Gram-positive bacteria and mycoplasma. Bottromycin is structurally distinct from both vancomycin, a glycopeptide antibiotic, and methicillin, a beta-lactam antibiotic.Bottromycin binds to the A site of the ribosome and blocks the binding of aminoacyl-tRNA, therefore inhibiting bacterial protein synthesis. Although bottromycin exhibits antibacterial activity in vitro, it has not yet been developed as a clinical antibiotic, potentially due to its poor stability in blood plasma. To increase its stability in vivo, some bottromycin derivatives have been explored.The structure of bottromycin contains a macrocyclic amidine as well as a thiazole ring. The absolute stereochemistry at several chiral centers has been determined as of 2009. In 2012, a three-dimensional solution structure of bottromycin was published. The solution structure revealed that several methyl groups are on the same face of the structure.Bottromycin falls within the ribosomally synthesized and post-translationally modified peptide class of natural product.