Convergent evolution of complex regulatory
... sequences active either in GT only (GT1 and GT2), in digits only (Island II-1) (11), or in both (Prox) (17) were thus narrowed down and assayed in vivo using a LacZ reporter system (18) (Fig. 3). Accordingly, embryo transgenics for the GT2 sequence displayed strong activity in GT cells exclusively, ...
... sequences active either in GT only (GT1 and GT2), in digits only (Island II-1) (11), or in both (Prox) (17) were thus narrowed down and assayed in vivo using a LacZ reporter system (18) (Fig. 3). Accordingly, embryo transgenics for the GT2 sequence displayed strong activity in GT cells exclusively, ...
Mechanism of Translation
... 4. How are the termination codons different from other codons? A) They contain thymines. B) The termination codon always codes for methionine. C) They are not recognized by any tRNA molecules. D) Their conformations do not allow them to fit properly in the A site of the ribosome. ...
... 4. How are the termination codons different from other codons? A) They contain thymines. B) The termination codon always codes for methionine. C) They are not recognized by any tRNA molecules. D) Their conformations do not allow them to fit properly in the A site of the ribosome. ...
Sickle Cell Disease SS – No Sickle Cell
... What is sickle cell? • Sickle cell is a genetic condition that causes the red protein in blood (hemoglobin) to make the blood cells rigid and pointy. • The gene for sickle trait is spread throughout the world. • It was most common in the areas where there was a lot of malaria because sickle trait a ...
... What is sickle cell? • Sickle cell is a genetic condition that causes the red protein in blood (hemoglobin) to make the blood cells rigid and pointy. • The gene for sickle trait is spread throughout the world. • It was most common in the areas where there was a lot of malaria because sickle trait a ...
Having it both ways: transcription factors that bind DNA and RNA
... for legitimate partners. It is in the context of this rich network of potential interactions that biomolecules must function. Thus, we might expect that individual molecules could participate in multiple, perhaps super®cially unrelated regulatory pathways. These multiple functions may be dif®cult to ...
... for legitimate partners. It is in the context of this rich network of potential interactions that biomolecules must function. Thus, we might expect that individual molecules could participate in multiple, perhaps super®cially unrelated regulatory pathways. These multiple functions may be dif®cult to ...
Chapter 10 PowerPoint
... called the polymerase chain reaction (PCR). The polymerase enzyme most often used with PCR comes from a strain of bacteria that lives in (b) the hot springs of Yellowstone National Park. (Credit a: modification of work by Magnus Manske; credit b: modification of work by Jon Sullivan) ...
... called the polymerase chain reaction (PCR). The polymerase enzyme most often used with PCR comes from a strain of bacteria that lives in (b) the hot springs of Yellowstone National Park. (Credit a: modification of work by Magnus Manske; credit b: modification of work by Jon Sullivan) ...
EMBL-EBI Powerpoint Presentation
... Filter for all genes that are annotated with the GO term ‘pentosephosphate shunt’, the official GO term for the pentose-phosphate pathway (http://amigo.geneontology.org/cgibin/amigo/term_details?term=GO:0006098 ) Select the following attributes: Ensembl Gene ID, Associated Gene Name and Descript ...
... Filter for all genes that are annotated with the GO term ‘pentosephosphate shunt’, the official GO term for the pentose-phosphate pathway (http://amigo.geneontology.org/cgibin/amigo/term_details?term=GO:0006098 ) Select the following attributes: Ensembl Gene ID, Associated Gene Name and Descript ...
Genetics
... 3) Match each scenario with one of Mendel’s laws (select the law that matches the scenario the best). ...
... 3) Match each scenario with one of Mendel’s laws (select the law that matches the scenario the best). ...
Phenotypic overlap in the contribution of individual genes to CNV
... advent of the Human Phenotype Ontology (HPO) (Robinson et al., 2008; Robinson and Mundlos, 2010) addresses these problems with human data and is increasingly being used by clinical geneticists and systems biologists; we are now in a position to address the crossmining of phenotype data from humans a ...
... advent of the Human Phenotype Ontology (HPO) (Robinson et al., 2008; Robinson and Mundlos, 2010) addresses these problems with human data and is increasingly being used by clinical geneticists and systems biologists; we are now in a position to address the crossmining of phenotype data from humans a ...
Calcitonin
... Carr 5). It is important to note that in this signal transduction pathway CAMP act as a second messenger to amplify and carry the bioregulators signal into the cell. The Phospholipase C signal transduction pathway is completed through the use of a G protein named GQ. During this signal transduct ...
... Carr 5). It is important to note that in this signal transduction pathway CAMP act as a second messenger to amplify and carry the bioregulators signal into the cell. The Phospholipase C signal transduction pathway is completed through the use of a G protein named GQ. During this signal transduct ...
Autism-lessons from the X chromosome
... mind’. This has been measured by the ability to infer a person’s emotional state from looking at photographs of their eye regions and from the ability to attribute mental states to animated shapes (Frith, 2003). Comparatively, the deficit in ‘reading the mind from the eyes’ is more severe in women w ...
... mind’. This has been measured by the ability to infer a person’s emotional state from looking at photographs of their eye regions and from the ability to attribute mental states to animated shapes (Frith, 2003). Comparatively, the deficit in ‘reading the mind from the eyes’ is more severe in women w ...
GATA factor function in heart development
... y w67c23 served as our wild-type stock. The Gal4 strain used to direct gene expression in the mesoderm and mesectoderm was twi-Gal4 (Baylies and Bate, 1996). The UAS lines included UAS-pnr (Haenlin et al., 1997), UAS-tin (Yin and Frasch, 1998) and UAS-GATA4 generated in this study. The latter was ob ...
... y w67c23 served as our wild-type stock. The Gal4 strain used to direct gene expression in the mesoderm and mesectoderm was twi-Gal4 (Baylies and Bate, 1996). The UAS lines included UAS-pnr (Haenlin et al., 1997), UAS-tin (Yin and Frasch, 1998) and UAS-GATA4 generated in this study. The latter was ob ...
Retina-Specific Expression of 5A11/Basigin-2, a
... primer and a gene-specific primer, Bsgex2RV (5⬘-GCAGGTAAACTGTGTTTTGGAGTTGAC), that anneals within exon 2 of the Basigin gene in the antisense direction. PCR conditions were as follows: 96°C for 5 minutes, followed by 30 cycles of 96°C for 1 minute, 55°C for 1 minute, and 72°C for 3 minutes. All spec ...
... primer and a gene-specific primer, Bsgex2RV (5⬘-GCAGGTAAACTGTGTTTTGGAGTTGAC), that anneals within exon 2 of the Basigin gene in the antisense direction. PCR conditions were as follows: 96°C for 5 minutes, followed by 30 cycles of 96°C for 1 minute, 55°C for 1 minute, and 72°C for 3 minutes. All spec ...
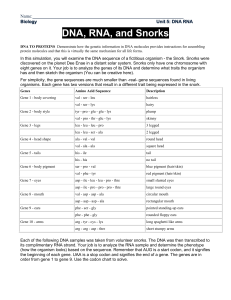
Snorks Lab File
... protein molecules and that this is virtually the same mechanism for all life forms. ...
... protein molecules and that this is virtually the same mechanism for all life forms. ...
Review Non-ribosomal peptide synthetases: Identifying the cryptic
... development of gene identification algorithms. Further on, the biggest challenge remains the prediction of the encoded natural product from the identified putative biosynthetic cluster, especially those of PKSs and NRPSs, as the sequence and selection of the carboxyl/amino acid dictates the final pr ...
... development of gene identification algorithms. Further on, the biggest challenge remains the prediction of the encoded natural product from the identified putative biosynthetic cluster, especially those of PKSs and NRPSs, as the sequence and selection of the carboxyl/amino acid dictates the final pr ...
Divinyl Chlorophyll(ide) a Can Be Converted to Monovinyl
... The 824ys mutant was a spontaneous mutant isolated from indica rice cv 824B, which exhibited a yellow-green leaf phenotype throughout development. The mutant and wild type were planted under natural conditions, in which average air temperature per day was 18.6°C to 28.4°C, average sunlight intensity ...
... The 824ys mutant was a spontaneous mutant isolated from indica rice cv 824B, which exhibited a yellow-green leaf phenotype throughout development. The mutant and wild type were planted under natural conditions, in which average air temperature per day was 18.6°C to 28.4°C, average sunlight intensity ...
Characterization of sparfloxacin-resistant mutants of Staphylococcus aureus Original article
... It has been shown that the most important mechanism in the acquisition of quinolone resistance is the development of mutations in the quinolone-target molecules [7,8,15– 17,21–24]. The primary quinolonetarget in Gram-positive microorganisms seems to be Topoisomerase IV [15–17]. Although, it has been ...
... It has been shown that the most important mechanism in the acquisition of quinolone resistance is the development of mutations in the quinolone-target molecules [7,8,15– 17,21–24]. The primary quinolonetarget in Gram-positive microorganisms seems to be Topoisomerase IV [15–17]. Although, it has been ...
The Synthesis and Degradation of Nucleotides
... Ribonucleotide Reductase has a unique control mechanism to assure that the deoxyribonucleotides are synthesized in adequate and balanced amounts. This enzyme contains an Activity Site, a Specificity Site, and the catalytic site. The Activity Site turns the enzyme “ON” or “OFF”; the Specificity Site ...
... Ribonucleotide Reductase has a unique control mechanism to assure that the deoxyribonucleotides are synthesized in adequate and balanced amounts. This enzyme contains an Activity Site, a Specificity Site, and the catalytic site. The Activity Site turns the enzyme “ON” or “OFF”; the Specificity Site ...
Population Genetics1
... discuss the effect of selection one immediately comes up against the problem that selective values are not properties of genes; they are rather properties of individuals (i.e. of the whole interacting collection of genes which an individual has), and then refer properly only to a given environment. ...
... discuss the effect of selection one immediately comes up against the problem that selective values are not properties of genes; they are rather properties of individuals (i.e. of the whole interacting collection of genes which an individual has), and then refer properly only to a given environment. ...
Supplemental Tables
... probes for genes on the fourth chromosome of D. melanogaster and found that they hybridized to the most basal section of the third chromosome. Thus, the dot chromosome or Muller element F has apparently fused to the E element in D. willistoni. D. virilis Chromosome Map Preparation. The sequenced st ...
... probes for genes on the fourth chromosome of D. melanogaster and found that they hybridized to the most basal section of the third chromosome. Thus, the dot chromosome or Muller element F has apparently fused to the E element in D. willistoni. D. virilis Chromosome Map Preparation. The sequenced st ...
DNA Replication/Transcription/RNA Splicing
... Sites of Ongoing Transcription The intranuclear position of many genes has been correlated with their activity state, suggesting that migration to functional subcompartments may influence gene expression. Indeed, nascent RNA production and RNA polymerase II seem to be localized into discrete foci or ...
... Sites of Ongoing Transcription The intranuclear position of many genes has been correlated with their activity state, suggesting that migration to functional subcompartments may influence gene expression. Indeed, nascent RNA production and RNA polymerase II seem to be localized into discrete foci or ...
PDF
... shown that Npc2 has three disulfide bonds and forms a hydrophobic core implicated in cholesterol binding (Friedland et al., 2003; Ko et al., 2003). All six disulfide bond-forming cysteine residues are absolutely conserved in Drosophila Npc2a-h proteins. At other positions shown to be functional in m ...
... shown that Npc2 has three disulfide bonds and forms a hydrophobic core implicated in cholesterol binding (Friedland et al., 2003; Ko et al., 2003). All six disulfide bond-forming cysteine residues are absolutely conserved in Drosophila Npc2a-h proteins. At other positions shown to be functional in m ...
Cytochrome P450 3A4: The Impossible Protein
... this situation the drugs will not be oxidized in the same way that they would be if there were only one bound to the protein. This makes it difficult to administer more than one drug at once because of the possible effects that occur due to 3A4. In addition to having this binding property, 3A4 is t ...
... this situation the drugs will not be oxidized in the same way that they would be if there were only one bound to the protein. This makes it difficult to administer more than one drug at once because of the possible effects that occur due to 3A4. In addition to having this binding property, 3A4 is t ...
Document
... Finding SNPs: HapMap Browser 1. HapMap data sets are useful because individual genotype data in deeply sampled populations can be used to determine optimal genotyping strategies (tagSNPs) or perform population genetic analyses (linkage disequilbrium) ...
... Finding SNPs: HapMap Browser 1. HapMap data sets are useful because individual genotype data in deeply sampled populations can be used to determine optimal genotyping strategies (tagSNPs) or perform population genetic analyses (linkage disequilbrium) ...