Cloning - Cloudfront.net
... – to ensure this, a gene for antibiotic resistance is attached to donor gene and antibiotic is used to kill all unwanted bacteria that do not have the donor gene ...
... – to ensure this, a gene for antibiotic resistance is attached to donor gene and antibiotic is used to kill all unwanted bacteria that do not have the donor gene ...
Cloning - cloudfront.net
... – to ensure this, a gene for antibiotic resistance is attached to donor gene and antibiotic is used to kill all unwanted bacteria that do not have the donor gene ...
... – to ensure this, a gene for antibiotic resistance is attached to donor gene and antibiotic is used to kill all unwanted bacteria that do not have the donor gene ...
dihybrid cross: a genetic cross which examines the transmission of
... chromosome: rod/thread-like structure composed of DNA and protein, contains the genetic information (genes) which is passed from one generation of cells or organisms to the next. Occur in pairs in most plant and animal cell nuclei. ...
... chromosome: rod/thread-like structure composed of DNA and protein, contains the genetic information (genes) which is passed from one generation of cells or organisms to the next. Occur in pairs in most plant and animal cell nuclei. ...
Sažetak za I Međunarodni simpozij(PBF) Udruga Helix
... final electron transfer from ferredoxin to NADP+. So, TROL is considered necessary for anchoring FNR to the thylakoid membranes. As FNR interacts with redox sensible ferredoxin we can conclude that TROL could be the sensor which responds to redox changes in ...
... final electron transfer from ferredoxin to NADP+. So, TROL is considered necessary for anchoring FNR to the thylakoid membranes. As FNR interacts with redox sensible ferredoxin we can conclude that TROL could be the sensor which responds to redox changes in ...
Chapter 13 Chromosomes
... to construct an evolutionary tree diagram. An assumption is that mutation rate is constant. A limitation is that only one biochemical is considered, and not large scale characteristics such as behavior and anatomy. ...
... to construct an evolutionary tree diagram. An assumption is that mutation rate is constant. A limitation is that only one biochemical is considered, and not large scale characteristics such as behavior and anatomy. ...
Variation and Evolution
... 1. The sequence of DNA may be changed by radiation or mistakes in replication 2. The mutated DNA could cause a new characteristic to be seen. More often the mutation leads to genetic problems or death ...
... 1. The sequence of DNA may be changed by radiation or mistakes in replication 2. The mutated DNA could cause a new characteristic to be seen. More often the mutation leads to genetic problems or death ...
This examination paper consists of 4 pages
... 15. All eukaryotic nuclear chromosomes are circular have only one origin of replication have only one centromer end in telomeres ...
... 15. All eukaryotic nuclear chromosomes are circular have only one origin of replication have only one centromer end in telomeres ...
From Gene to Protein
... uncertain of the function of this info, which does not make the info unimportant. • Initially the RNA can be 8000 bases, actual info for protein that goes to ribosomes is about 1200 or 400 amino acids (1200 bases/ 3 bases per codon) ...
... uncertain of the function of this info, which does not make the info unimportant. • Initially the RNA can be 8000 bases, actual info for protein that goes to ribosomes is about 1200 or 400 amino acids (1200 bases/ 3 bases per codon) ...
Biotechnology Part 1
... Plasmids typically contain antibiotic resistance (Amp) 4. Select for the bacteria you want with the plasmid. Those that grow in the presence of the antibiotic have been transformed. ...
... Plasmids typically contain antibiotic resistance (Amp) 4. Select for the bacteria you want with the plasmid. Those that grow in the presence of the antibiotic have been transformed. ...
Introduction o Except for identical twins, have the same DNA. o
... The Function and Structure of DNA Human DNA consists of about ________________ bases, and more than _____________________ of those bases are the same in all people. The order, or ______________, of these bases determines the information available for building and maintaining an organism, similar to ...
... The Function and Structure of DNA Human DNA consists of about ________________ bases, and more than _____________________ of those bases are the same in all people. The order, or ______________, of these bases determines the information available for building and maintaining an organism, similar to ...
Exam 2
... P selectively labels nucleotides (via phosphate group) but not proteins because P is in nucleic acid but not protein. 35S elements selectively labels proteins but not nucleic acids because S is in protein but not nucleic acids. Thus, the location of the DNA and proteins could be independently follow ...
... P selectively labels nucleotides (via phosphate group) but not proteins because P is in nucleic acid but not protein. 35S elements selectively labels proteins but not nucleic acids because S is in protein but not nucleic acids. Thus, the location of the DNA and proteins could be independently follow ...
Changes in signal transduction pathways can alter
... 2. The sequence of nucleotides on the mRNA is read in triplets called codons. 3. Each codon encodes a specific amino acid, which can be deduced by using a genetic code chart. Many amino acids have more than one codon. 4. tRNA brings the correct amino acid to the correct place on the mRNA. 5. The ami ...
... 2. The sequence of nucleotides on the mRNA is read in triplets called codons. 3. Each codon encodes a specific amino acid, which can be deduced by using a genetic code chart. Many amino acids have more than one codon. 4. tRNA brings the correct amino acid to the correct place on the mRNA. 5. The ami ...
Lect.5 - Department of Engineering and Physics
... • DNA Helicase: unwinds the double helix • Single-Stranded DNA Binding: keep DNA from winding ...
... • DNA Helicase: unwinds the double helix • Single-Stranded DNA Binding: keep DNA from winding ...
19. IMG-ER Curation Environment
... Curation of annotation in one genome (or a set of genomes) a) Your favorite genes (experimental verification, etc.) -> use Find Genes, Gene Search or BLAST b) “Compare Annotations” on Organism Details ...
... Curation of annotation in one genome (or a set of genomes) a) Your favorite genes (experimental verification, etc.) -> use Find Genes, Gene Search or BLAST b) “Compare Annotations” on Organism Details ...
1. The I gene determines the synthesis of a repressor molecule
... Another way of labeling mutants of the operator is to denote that they lead to a constitutive phenotype; lacO– (or a–) can also be written as lacOc. There are also mutations of the repressor that fail to bind inducer (allolactose) as opposed to fail to bind DNA. These two classes have quite differen ...
... Another way of labeling mutants of the operator is to denote that they lead to a constitutive phenotype; lacO– (or a–) can also be written as lacOc. There are also mutations of the repressor that fail to bind inducer (allolactose) as opposed to fail to bind DNA. These two classes have quite differen ...
Chapter 9 answers
... Your friend Gorinda wants to know if there are ever mutations that don’t cause problems. What do you tell him? Certainly. If a mutation is in a place that is not actually read to make an amino acid chain, then it may not cause any change at all. If the mutation falls at the end of a codon, it may st ...
... Your friend Gorinda wants to know if there are ever mutations that don’t cause problems. What do you tell him? Certainly. If a mutation is in a place that is not actually read to make an amino acid chain, then it may not cause any change at all. If the mutation falls at the end of a codon, it may st ...
Ch 11- Controlling Gene Expression
... • Transcription factors- regulatory proteins that turn on eukaryotic transcription (in addition to RNA pol) – Activators are one type that bind to enhancer DNA sequences; sequences that regulate far from gene – DNA bends and TF’s bind to create an area where RNA pol can bind to – Silencers- are sequ ...
... • Transcription factors- regulatory proteins that turn on eukaryotic transcription (in addition to RNA pol) – Activators are one type that bind to enhancer DNA sequences; sequences that regulate far from gene – DNA bends and TF’s bind to create an area where RNA pol can bind to – Silencers- are sequ ...
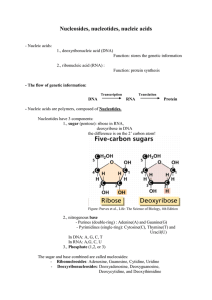
Nucleosides, nucleotides, nucleic acids
... protein synthesis. Single stranded. - ribosomal RNA = rRNA : components of the ribosome, which is the site of protein synthesis (translation). rRNA forms self-complementary double-stranded regions (in RNA there is Uracil instead of Thymine as a base, it forms double hydrogen bonds with Adenine). - t ...
... protein synthesis. Single stranded. - ribosomal RNA = rRNA : components of the ribosome, which is the site of protein synthesis (translation). rRNA forms self-complementary double-stranded regions (in RNA there is Uracil instead of Thymine as a base, it forms double hydrogen bonds with Adenine). - t ...
Transformation_Slides_000
... The FP can be seen and measured, even though the protein of interest cannot be seen. Anytime the protein of interest is made in the cell, the FP will also be made. ...
... The FP can be seen and measured, even though the protein of interest cannot be seen. Anytime the protein of interest is made in the cell, the FP will also be made. ...
The Secret Code of Life:
... • On your worksheets, which represents the RNA? Which represents the protein? ...
... • On your worksheets, which represents the RNA? Which represents the protein? ...