Assigned exercise
... understand. Pay particular attention to the sections on navigating PubMed’s home page, using fields to narrow down a search, and Boolean logic. Be prepared for a brief quiz at the beginning of the next class! When you have finished the tutorial, choose a gene, protein, disease or condition that inte ...
... understand. Pay particular attention to the sections on navigating PubMed’s home page, using fields to narrow down a search, and Boolean logic. Be prepared for a brief quiz at the beginning of the next class! When you have finished the tutorial, choose a gene, protein, disease or condition that inte ...
Daily TAKS Connection: DNA
... Any change in the sequence (order) of these nucleotides may result in a mutation 3 nucleotides code for an amino acid For example: ...
... Any change in the sequence (order) of these nucleotides may result in a mutation 3 nucleotides code for an amino acid For example: ...
Prescott`s Microbiology, 9th Edition Chapter 17 – Recombinant DNA
... Shuttle vectors can ‘shuttle’ between at least two hosts, and so can be replicated in at least two different cell types. Plasmid Yep24 can be replicated in the prokaryote E. coli or the eukaryote Saccharomyces cerevisiae. This allows easy amplification in E. coli for use in experimentation in the ye ...
... Shuttle vectors can ‘shuttle’ between at least two hosts, and so can be replicated in at least two different cell types. Plasmid Yep24 can be replicated in the prokaryote E. coli or the eukaryote Saccharomyces cerevisiae. This allows easy amplification in E. coli for use in experimentation in the ye ...
GENETIC ENGINEERING CHAPTER 20
... • Involves inserting DNA into a vector and cloning it into a cell for production of multiple copies A. Vectors – DNA molecules that will carry foreign DNA into cells: plasmids, BACs, YACs ...
... • Involves inserting DNA into a vector and cloning it into a cell for production of multiple copies A. Vectors – DNA molecules that will carry foreign DNA into cells: plasmids, BACs, YACs ...
Glossary - Bioethics Advisory Committee
... molecule made up of nucleotides or bases. There are four different types of bases in DNA and the order in which these bases are arranged determines the protein to be formed. Each individual’s body contains an identical set of DNA in nearly all of its cells. A great fraction of cellular DNA is locate ...
... molecule made up of nucleotides or bases. There are four different types of bases in DNA and the order in which these bases are arranged determines the protein to be formed. Each individual’s body contains an identical set of DNA in nearly all of its cells. A great fraction of cellular DNA is locate ...
Slide 1
... The genetic “bit” information to encode a specific amino acid is contained in a gene’s Codon. A Codon is a 3-base (3-nucleotide) sub-sequence that defines the amino acid to be incorporated into the protein. All proteins start with the Codon ATG (DNA notation) or AUG (RNA), which encodes for the amin ...
... The genetic “bit” information to encode a specific amino acid is contained in a gene’s Codon. A Codon is a 3-base (3-nucleotide) sub-sequence that defines the amino acid to be incorporated into the protein. All proteins start with the Codon ATG (DNA notation) or AUG (RNA), which encodes for the amin ...
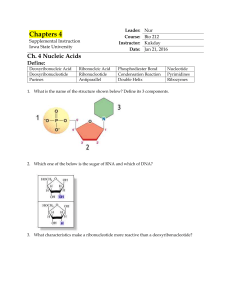
Ch. 4 Nucleic Acids Define
... 1. What is the name of the structure shown below? Define its 3 components. ...
... 1. What is the name of the structure shown below? Define its 3 components. ...
Powerpoint slides - School of Engineering and Applied Science
... Polymerase Chain Reaction (PCR) • A method that allows us to generate a large amount (relatively) of a particular DNA sequence even from an ...
... Polymerase Chain Reaction (PCR) • A method that allows us to generate a large amount (relatively) of a particular DNA sequence even from an ...
Document
... 6C explain the purpose and process of transcription and translation using models of DNA and RNA; 6D recognize that gene expression is a regulated process; 6E identify and illustrate changes in DNA and evaluate the significance of ...
... 6C explain the purpose and process of transcription and translation using models of DNA and RNA; 6D recognize that gene expression is a regulated process; 6E identify and illustrate changes in DNA and evaluate the significance of ...
DNA TECHNOLOGY - Mount Mansfield Union High School
... • 2004– South Koreans claim first cloned human – Harvard researchers grow stem cells from embryos w/ private $ • 2005- South Koreans exposed for lying about human clone • 2009- Obama overturns stem cell ban, but opposes human cloning ...
... • 2004– South Koreans claim first cloned human – Harvard researchers grow stem cells from embryos w/ private $ • 2005- South Koreans exposed for lying about human clone • 2009- Obama overturns stem cell ban, but opposes human cloning ...
Genetics and Protein Synthesis
... The F1 offspring showed only one of the two parental traits, and always the same trait. Results were always the same regardless of which parent donated the pollen. The trait not shown in the F1 reappeared in the F2 in about 25% of the offspring. Traits remained unchanged when passed to offspring: th ...
... The F1 offspring showed only one of the two parental traits, and always the same trait. Results were always the same regardless of which parent donated the pollen. The trait not shown in the F1 reappeared in the F2 in about 25% of the offspring. Traits remained unchanged when passed to offspring: th ...
Estimation Over Multiple Undirected Graphs
... Observed attributes of genes, such as gene expressions, are used to reconstruct gene networks through graphical models. In this presentation, I will focus on estimation of multiple undirected graphs, motivated from network analysis under different experimental conditions, such as gene networks for d ...
... Observed attributes of genes, such as gene expressions, are used to reconstruct gene networks through graphical models. In this presentation, I will focus on estimation of multiple undirected graphs, motivated from network analysis under different experimental conditions, such as gene networks for d ...
DNA Handout KEY - Iowa State University
... Unwinds the original strands of DNA so they can act as templates Starts initiation with a small strand of RNA that is later replaced (primer) Removes primer and starts adding DNA Continues elongation, proofreading Joins Okazaki fragments Cuts out damaged DNA ...
... Unwinds the original strands of DNA so they can act as templates Starts initiation with a small strand of RNA that is later replaced (primer) Removes primer and starts adding DNA Continues elongation, proofreading Joins Okazaki fragments Cuts out damaged DNA ...
No Slide Title
... INTERmolecular linking of two DNAs (compare to condensin) established at replication fork-preloaded in G1? degraded at onset of anaphase to allow sister separation cohesin in pericentromeric regions recruited by HP1/K9me, may be regulated differently ...
... INTERmolecular linking of two DNAs (compare to condensin) established at replication fork-preloaded in G1? degraded at onset of anaphase to allow sister separation cohesin in pericentromeric regions recruited by HP1/K9me, may be regulated differently ...
IntroductoryDay1LectureMarch17
... • Grow the yeast and treat one group with plain water (control group) and the other group with 10% DMSO • Isolate RNA from the yeast grown in two different conditions, prepare target from it and use it on microarrays to see changes in gene expression ...
... • Grow the yeast and treat one group with plain water (control group) and the other group with 10% DMSO • Isolate RNA from the yeast grown in two different conditions, prepare target from it and use it on microarrays to see changes in gene expression ...
DNA mutations power point
... Mutations can be spontaneous or natural as a result of errors in DNA replication or gamete production. ...
... Mutations can be spontaneous or natural as a result of errors in DNA replication or gamete production. ...
1 The structure and replication of DNA
... Only a fraction of the genes in a cell are expressed. (a) Gene expression is controlled by the regulation of transcription and translation. - mRNA is transcribed from DNA in the nucleus and translated into proteins by ribosomes in the cytoplasm. i) Structure and functions of RNA. - Single strand, re ...
... Only a fraction of the genes in a cell are expressed. (a) Gene expression is controlled by the regulation of transcription and translation. - mRNA is transcribed from DNA in the nucleus and translated into proteins by ribosomes in the cytoplasm. i) Structure and functions of RNA. - Single strand, re ...
Final Take-Home Exam
... By appointment or drop in Dec. 8, 11, 12. Available most times during the day. On separate pages, briefly type your answers to the following questions. Please double-space!! Feel free to consult the instructor if you need clarification on the questions. If you use any other references besides your t ...
... By appointment or drop in Dec. 8, 11, 12. Available most times during the day. On separate pages, briefly type your answers to the following questions. Please double-space!! Feel free to consult the instructor if you need clarification on the questions. If you use any other references besides your t ...
Chapter 17 - Denton ISD
... _____________________ about 10 base pairs before AUG to distinguish start from other AUG combinations.) This is followed by the attaching of the small and large ribosomal subunits. 2) ____________- progresses in 5’-3’ direction a) Anticodon in tRNA bonds with the matching codon on mRNA at A site, us ...
... _____________________ about 10 base pairs before AUG to distinguish start from other AUG combinations.) This is followed by the attaching of the small and large ribosomal subunits. 2) ____________- progresses in 5’-3’ direction a) Anticodon in tRNA bonds with the matching codon on mRNA at A site, us ...
Final Exam Review (Spring 09)
... 4. Describe the history of how DNA was discovered and studied, including the names of the scientists and what year its structure was identified. 5. Construct a chain of DNA (12 bases), and then translate the message into a chain of amino acids/protein. 6. Define all terminology and definitions assoc ...
... 4. Describe the history of how DNA was discovered and studied, including the names of the scientists and what year its structure was identified. 5. Construct a chain of DNA (12 bases), and then translate the message into a chain of amino acids/protein. 6. Define all terminology and definitions assoc ...