LEQ: How do we splice new genes into DNA?
... positive end; smaller pieces travel farther faster; DNA fragments are separated based on the size of the fragment (# of base pairs). ...
... positive end; smaller pieces travel farther faster; DNA fragments are separated based on the size of the fragment (# of base pairs). ...
Application of Algorithm Research to Molecular Biology
... • For each living organism, there are a lot of different kinds of cells. For instance, in human beings, we have muscle cells, blood cells, neural cells etc. • How can different cells perform different functions? ...
... • For each living organism, there are a lot of different kinds of cells. For instance, in human beings, we have muscle cells, blood cells, neural cells etc. • How can different cells perform different functions? ...
Gene Cloning
... expressed by the bacteria, an uninterrupted coding sequence is needed. • Also, since introns can account for up to 90% of an eukaryotic gene, and cloning long fragments is difficult, it is sometimes desirable to work only with the expressed sequences (exons) ...
... expressed by the bacteria, an uninterrupted coding sequence is needed. • Also, since introns can account for up to 90% of an eukaryotic gene, and cloning long fragments is difficult, it is sometimes desirable to work only with the expressed sequences (exons) ...
Chapter 19 review - Iowa State University
... to be the phenotype of a larva in which the bicoid gene was expressed in both the anterior region and the posterior region of the oocyte? ...
... to be the phenotype of a larva in which the bicoid gene was expressed in both the anterior region and the posterior region of the oocyte? ...
gelfand-genetic-code
... • Recombination allows for relative mapping of gene positions on the chromosome: if two genes are close, the frequency of recombination will be lower ...
... • Recombination allows for relative mapping of gene positions on the chromosome: if two genes are close, the frequency of recombination will be lower ...
Biology 303 EXAM II 3/14/00 NAME
... C. examines amino acid substitutions with radioactive probes. D. cleaves RNA with restriction endonucleases. ...
... C. examines amino acid substitutions with radioactive probes. D. cleaves RNA with restriction endonucleases. ...
Course Outline
... To enable understanding of the principles of human nutrition and knowing the types and amounts of macronutrients that are needed to maintain optimal health. 4. To give students information about the structure and function and the clinical importance of fat-soluble vitamins in health and disease. 5. ...
... To enable understanding of the principles of human nutrition and knowing the types and amounts of macronutrients that are needed to maintain optimal health. 4. To give students information about the structure and function and the clinical importance of fat-soluble vitamins in health and disease. 5. ...
TRASK Zool 3200: Cell Biology Exam 2
... all cells in the culture begin and complete DNA replication at the exact same time. You first grow the cells in a medium that contains nutrients highly enriched in ‘heavy’ isotopes of nitrogen and carbon (15N and 13C in place of naturally‐abundant 14N and 12C). Cells growing in this ‘heavy’ medium ...
... all cells in the culture begin and complete DNA replication at the exact same time. You first grow the cells in a medium that contains nutrients highly enriched in ‘heavy’ isotopes of nitrogen and carbon (15N and 13C in place of naturally‐abundant 14N and 12C). Cells growing in this ‘heavy’ medium ...
Lecture 12
... technology and taq polymerase technology (polymerase chain reaction) are mainly used for the purpose. ...
... technology and taq polymerase technology (polymerase chain reaction) are mainly used for the purpose. ...
DNA Reccombination
... Yeast is known as Saccharomyces cerevisiae, which is the single-celled fungus used to make bread. Yeast is haploids with a genome of 16 chromosomes single set . The gene for mating has a locus on one chromosome which makes the yeast exists either in dominant mating type (G) or recessive mating ...
... Yeast is known as Saccharomyces cerevisiae, which is the single-celled fungus used to make bread. Yeast is haploids with a genome of 16 chromosomes single set . The gene for mating has a locus on one chromosome which makes the yeast exists either in dominant mating type (G) or recessive mating ...
Document
... D.) No difference in transcription rate when an activator protein was present. E.) Negative control of transcription. ...
... D.) No difference in transcription rate when an activator protein was present. E.) Negative control of transcription. ...
Intrdouction to Annotation (djs)
... 1. In any segment of DNA, typically only one frame in one strand is used for a proteincoding gene. That is, each double-stranded segment of DNA is generally part of only one gene. 2. Genes do not often overlap by more than a few bp, although up to about 30 bp is legitimate. 3. The gene density in ph ...
... 1. In any segment of DNA, typically only one frame in one strand is used for a proteincoding gene. That is, each double-stranded segment of DNA is generally part of only one gene. 2. Genes do not often overlap by more than a few bp, although up to about 30 bp is legitimate. 3. The gene density in ph ...
Bill Nye Genes Video WKSHT
... 8. Why is the white blood cell dark on the computer screen? 9. What does the nucleus of the cell contain? 10. What can you do with DNA after you take it out of an organism? a. b. 11. What 2 organisms were combined to create the message to Bill in the petri dish? 12. What do genes do? 13. Mom tells R ...
... 8. Why is the white blood cell dark on the computer screen? 9. What does the nucleus of the cell contain? 10. What can you do with DNA after you take it out of an organism? a. b. 11. What 2 organisms were combined to create the message to Bill in the petri dish? 12. What do genes do? 13. Mom tells R ...
Bill Nye Genes Video WKSHT
... 8. Why is the white blood cell dark on the computer screen? Because it has chromosomes in it. 9. What can you do with DNA after you take it out of an organism? a. Cut it into smaller pieces b. Place into another organism 10. What 2 organisms were combined to create the message to Bill in the petri d ...
... 8. Why is the white blood cell dark on the computer screen? Because it has chromosomes in it. 9. What can you do with DNA after you take it out of an organism? a. Cut it into smaller pieces b. Place into another organism 10. What 2 organisms were combined to create the message to Bill in the petri d ...
Name Date “Bill Nye: Genes” Video Worksheet 1. Where do your
... 8. Why is the white blood cell dark on the computer screen? Because it has chromosomes in it. 9. What can you do with DNA after you take it out of an organism? a. Cut it into smaller pieces b. Place into another organism 10. What 2 organisms were combined to create the message to Bill in the petri d ...
... 8. Why is the white blood cell dark on the computer screen? Because it has chromosomes in it. 9. What can you do with DNA after you take it out of an organism? a. Cut it into smaller pieces b. Place into another organism 10. What 2 organisms were combined to create the message to Bill in the petri d ...
Document
... “The Helios Gene Gun is a new way for in vivo transformation of cells or organisms apy and genetic immunization (DNA vaccination)). This gun uses Biolistic ® particle bombardment where DNA- or RNAcoated gold particles are loaded into the gun and you pull the trigger. A low pressure helium pulse deli ...
... “The Helios Gene Gun is a new way for in vivo transformation of cells or organisms apy and genetic immunization (DNA vaccination)). This gun uses Biolistic ® particle bombardment where DNA- or RNAcoated gold particles are loaded into the gun and you pull the trigger. A low pressure helium pulse deli ...
Unit 2 Terms
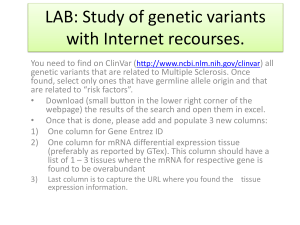
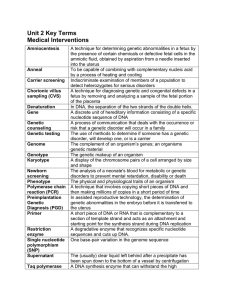
... A technique for determining genetic abnormalities in a fetus by the presence of certain chemicals or defective fetal cells in the amniotic fluid, obtained by aspiration from a needle inserted into the uterus To be capable of combining with complementary nucleic acid by a process of heating and cooli ...
... A technique for determining genetic abnormalities in a fetus by the presence of certain chemicals or defective fetal cells in the amniotic fluid, obtained by aspiration from a needle inserted into the uterus To be capable of combining with complementary nucleic acid by a process of heating and cooli ...
Constructing gene networks underlying fat - BDPorc
... acid composition (SFA, MUFA and PUFA). Subsequently, phenotype networks on the basis of their associations with transcriptomic and genomic data were constructed by using the PCIT algorithm to filter out indirect pair-wise correlations. Transcriptomic phenotype network was notably denser and showed m ...
... acid composition (SFA, MUFA and PUFA). Subsequently, phenotype networks on the basis of their associations with transcriptomic and genomic data were constructed by using the PCIT algorithm to filter out indirect pair-wise correlations. Transcriptomic phenotype network was notably denser and showed m ...
3rd Quarter Assessment Review - Belle Vernon Area School District
... Organism with 32 chromosomes • BI----32 • EI---64 • P---64 • M—64 • A---64 • T—32/32 ...
... Organism with 32 chromosomes • BI----32 • EI---64 • P---64 • M—64 • A---64 • T—32/32 ...
Close Assignment: Genetics Week 7 Test Review 1. ______ The
... 1. The molecule will be converted into an inorganic compound. 2. The amino acid sequence may be altered during protein synthesis. 3. The chromosome number will decrease in future generations. 4. The chromosome number may increase within the organisms. 46. _________Bacteria that produce colonies cont ...
... 1. The molecule will be converted into an inorganic compound. 2. The amino acid sequence may be altered during protein synthesis. 3. The chromosome number will decrease in future generations. 4. The chromosome number may increase within the organisms. 46. _________Bacteria that produce colonies cont ...